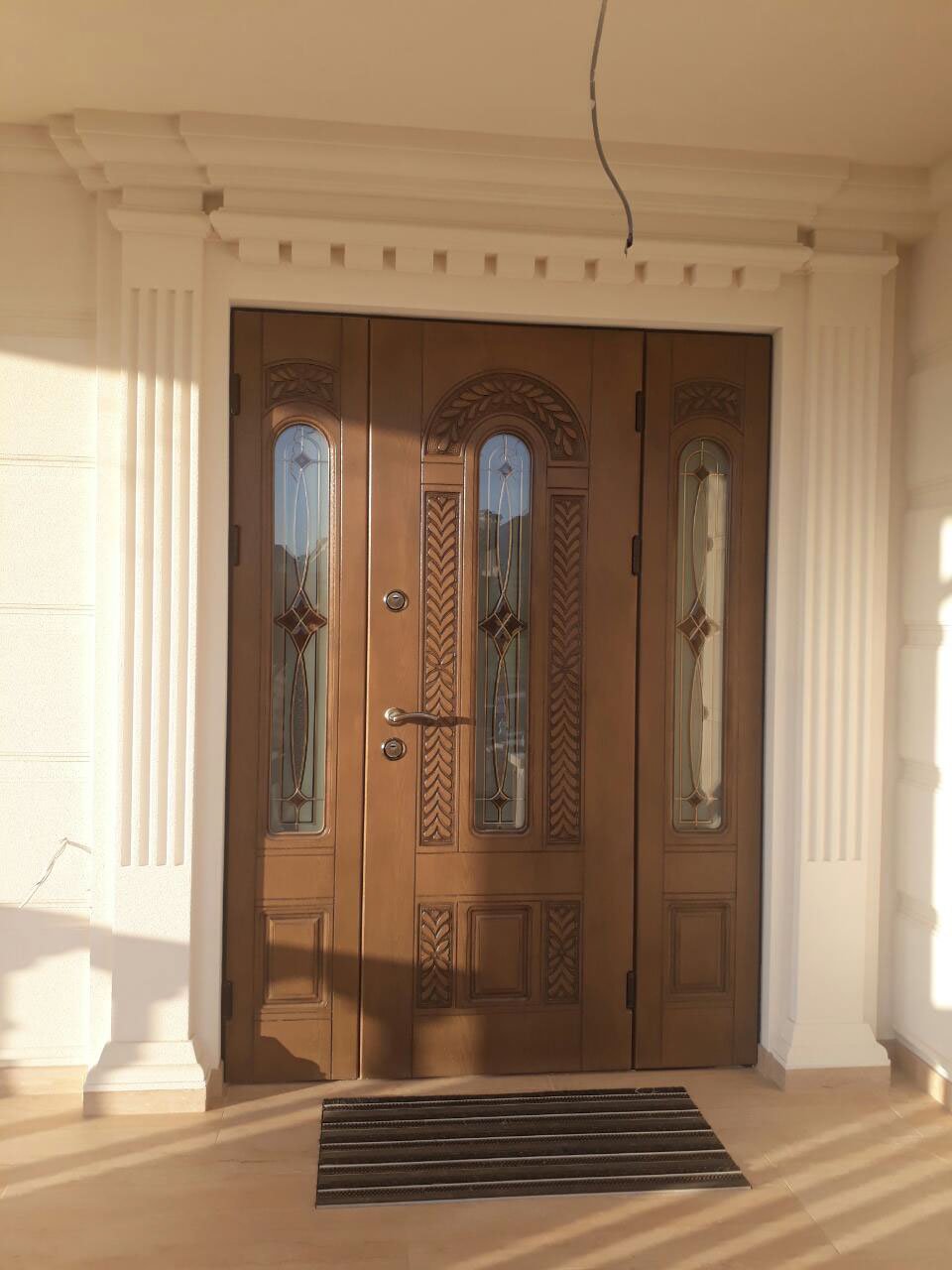
Foam architecture is a relatively new concept that is gaining popularity in the field of sustainable design. Foam, a lightweight and versatile material, has a wide range of properties that make it a suitable alternative to traditional building materials. Its insulation properties, low carbon footprint, and ease of use make it a cost-effective and sustainable option for architects and builders. Additionally, foam can be easily shaped, cut, and molded to create unique and dynamic designs, allowing architects to push the boundaries of traditional architecture. Its potential as a sustainable building material makes it an exciting and promising field for architects and builders to explore.

Physical and chemical properties of foam
Foam is a lightweight and porous material that is composed of small, closed cells filled with gas. The most common types of foam used in construction are polystyrene, polyurethane, and polyethylene. These foams have different physical and chemical properties that make them suitable for different applications. For example, polystyrene is a rigid foam that is commonly used in insulation and as a core material in sandwich panels. Polyurethane foam is a flexible foam that is used in insulation, cushions and upholstery. On the other hand, Polyethylene foam is a durable and closed-cell foam that is used in flotation devices, packaging and insulation. Each type of foam has its own unique properties, such as its density, thermal conductivity, and fire resistance, which should be considered when choosing the appropriate foam for a specific application.

Advantages of using foam in architecture
Foam has several advantages when it comes to architecture and construction. One of the main advantages is its insulation properties, which make it an energy-efficient building material. Foam has a low thermal conductivity, which means it can effectively reduce heat loss or gain through building envelopes. It also has a low water vapor permeability, which helps to prevent moisture buildup in buildings.
Another advantage of foam is its low weight and high strength-to-weight ratio. This makes it easy to transport, handle and install, which can save time and labor costs during construction. Foam can also be easily shaped and cut to create unique and complex designs, allowing architects to push the boundaries of traditional architecture. It is a cost-effective material compared to traditional insulation materials and its long-lasting durability makes it a sustainable investment for any building. Additionally, foam can be easily recycled or repurposed at the end of its useful life, making it an environmentally friendly option for construction.

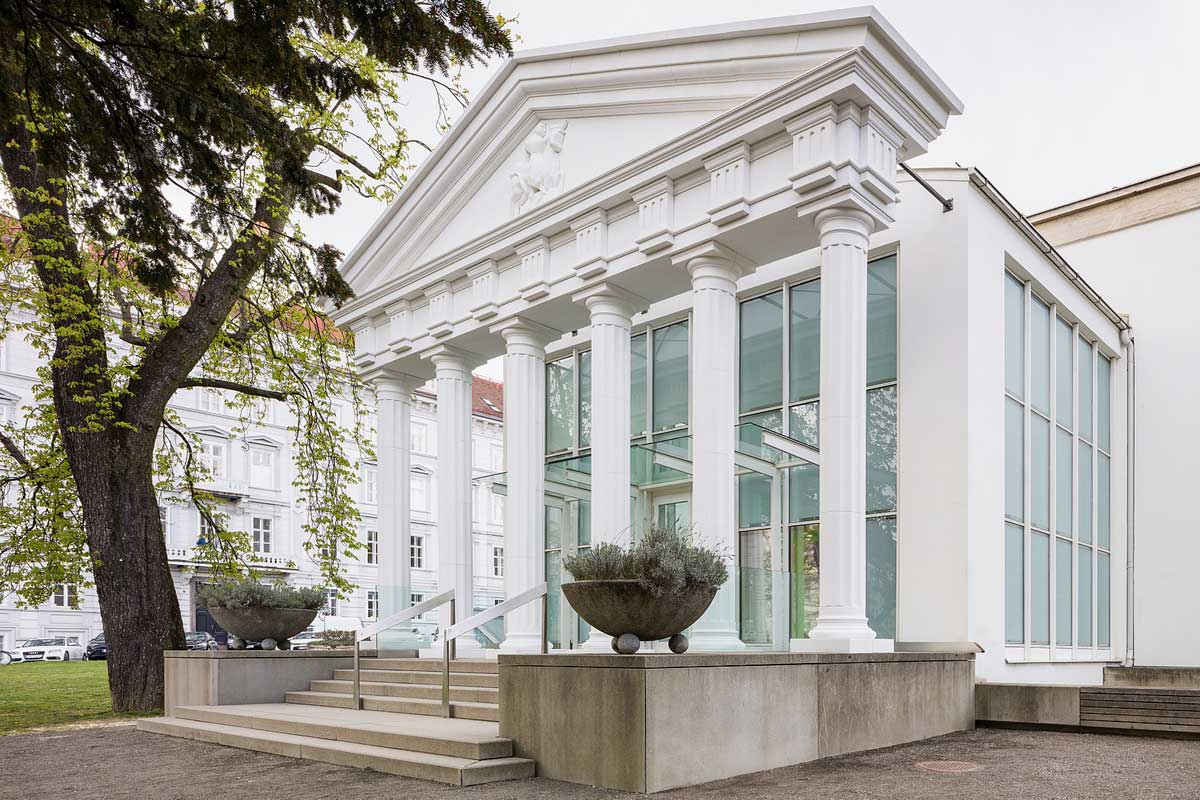
Examples of foam architecture around the world
Foam architecture is being used in a variety of ways around the world, from small scale projects to large scale structures. One example is the “Foam Dome” in Japan, which is a temporary pavilion made entirely out of foam blocks that serves as a venue for events and exhibitions. Another example is the “Foam House” in Germany, which is a residential building that uses foam insulation to reduce energy consumption.
In the United States, the “Foam Dome House” in Texas is an example of how foam can be used to create unique and sustainable architecture. The house is constructed using insulated foam blocks and is designed to be highly energy-efficient. Other examples of foam architecture include the “Foam Cube” in the Netherlands, a small exhibition space made of foam blocks, and the “Foam Tower” in China, a skyscraper built using foam concrete. These examples demonstrate the versatility and potential of foam as a building material and how it can be used in a variety of ways to create innovative and sustainable architecture.
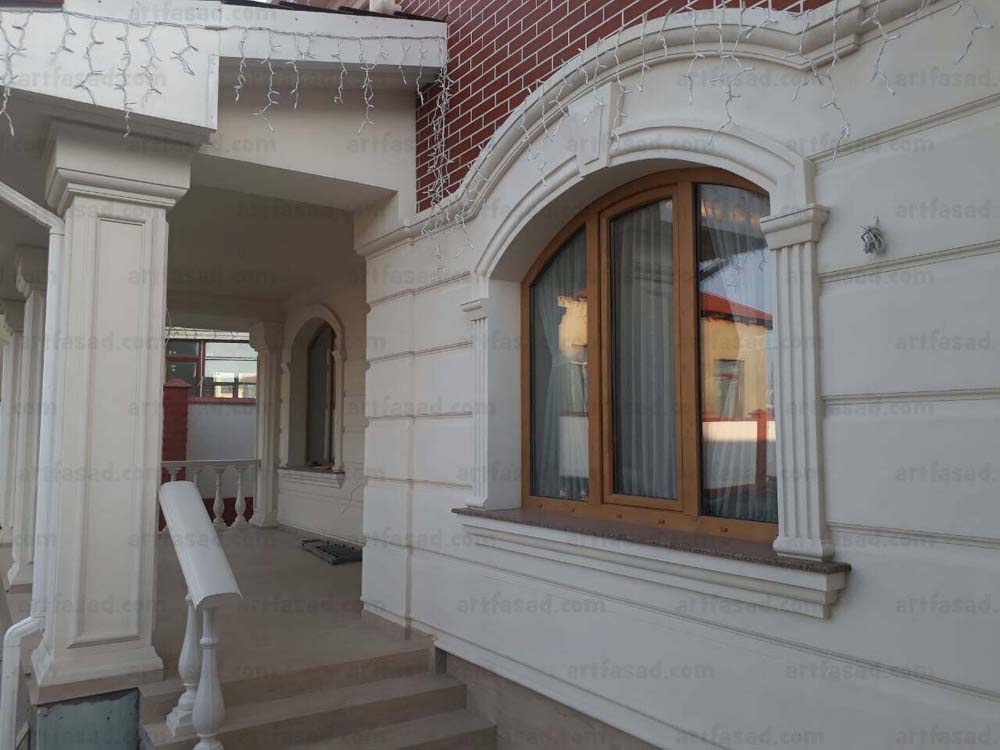

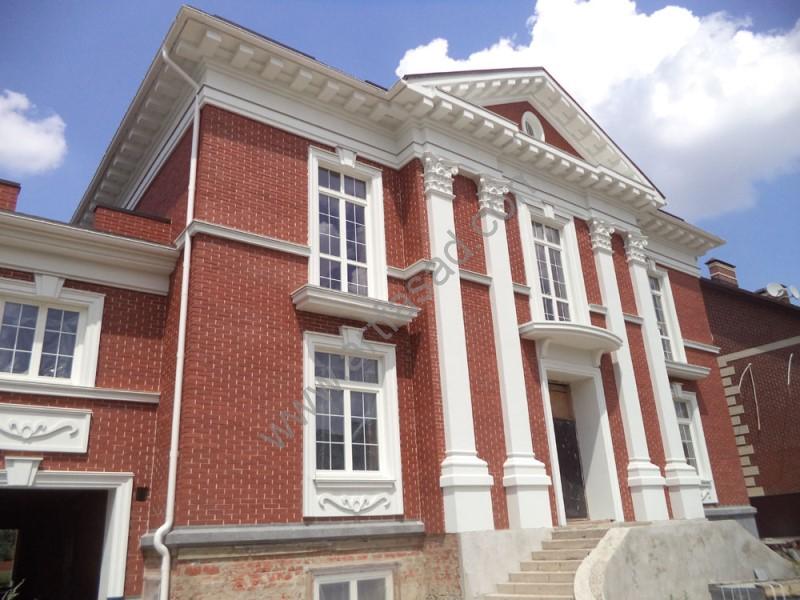
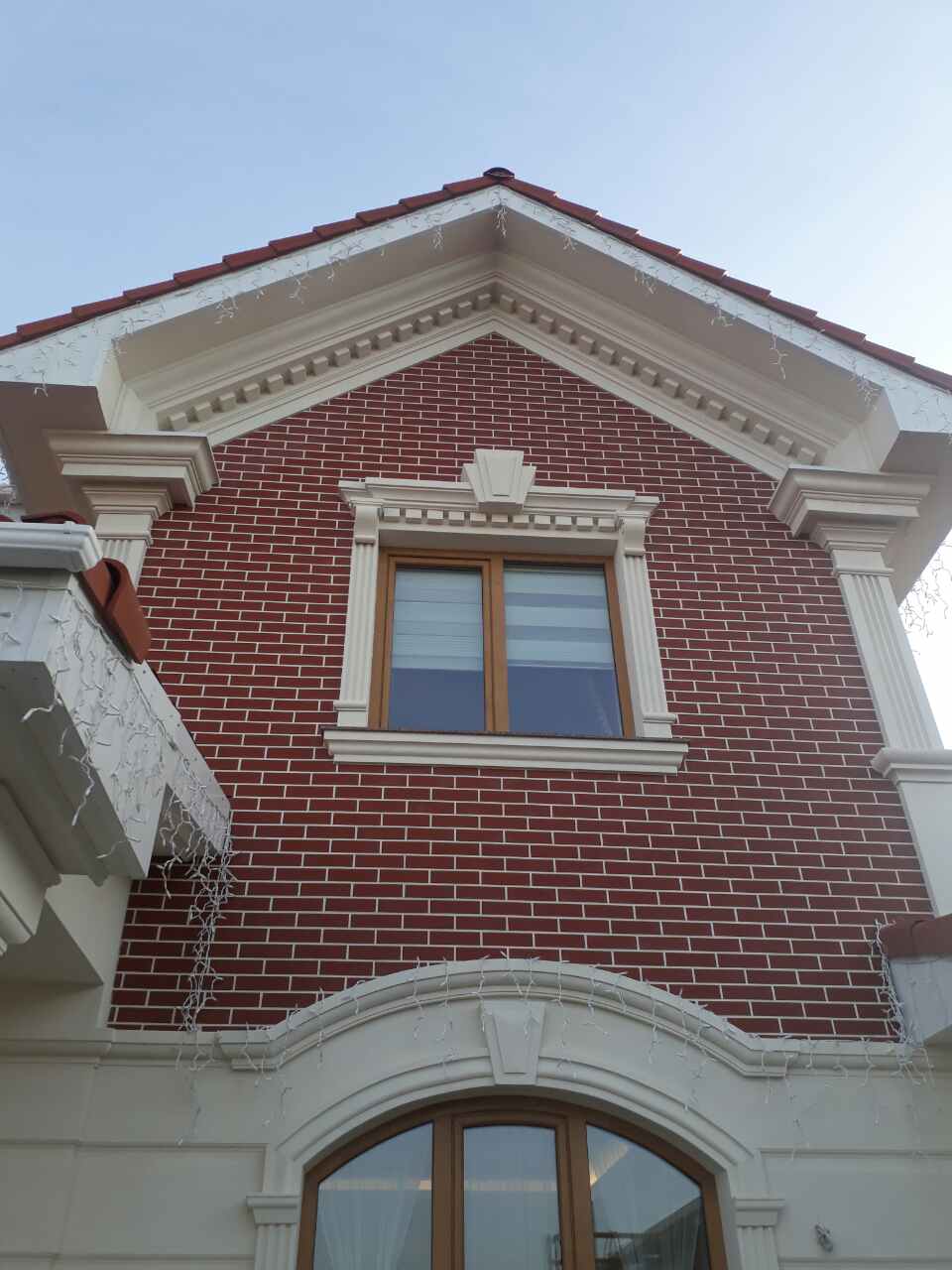
How architects are using foam to create innovative and sustainable designs
Architects are using foam in a variety of ways to create innovative and sustainable designs. One popular use of foam is in insulation, where it is used to improve energy efficiency and reduce the carbon footprint of buildings. Foam can also be used as a core material in sandwich panels, which are used to create lightweight and strong structures.
Another way architects are using foam is by shaping and cutting it to create unique and complex designs. For example, architects can use foam to create intricate sculptures and decorative elements, such as moldings and cornices, that add visual interest to a building. Foam can also be used to create customized building components, such as columns and beams, that are both functional and aesthetically pleasing.

Foam can also be used in green building, architects are using it to create green roofs and walls, which can help to reduce the heat island effect and improve air quality. Architects are also using foam in sustainable landscaping, creating sculptures, planters, and other decorative elements that can improve the environment and create a sense of place.
In conclusion, architects are using foam to create innovative and sustainable designs that not only improve the functionality of a building but also enhance its aesthetic appeal.

How foam is used in construction
Foam is used in a variety of ways in construction, from insulation to structural elements. One of the most common uses of foam in construction is as insulation. Foam insulation can be used in walls, roofs, and floors to improve energy efficiency and reduce heating and cooling costs. It can also be used in underground construction, such as foundation insulation, to prevent heat loss and moisture buildup.
Foam can also be used as a core material in sandwich panels, which are used to create lightweight and strong structures. Sandwich panels consist of two layers of a structural material, such as concrete or steel, with a foam core. These panels can be used to create walls, floors, and roofs, and are commonly used in prefabrication and modular construction.

Foam can also be used to create customized building components, such as columns and beams, that are both functional and aesthetically pleasing. This is done by shaping and cutting foam to create the desired shape, and then covering it with a layer of concrete or other finish material.
Foam can also be used in landscaping and exterior design, such as creating sculptures, planters, and other decorative elements.
In conclusion, foam is used in a variety of ways in construction, from insulation to structural elements, and exterior design, providing architects and builders with a versatile and sustainable building material.
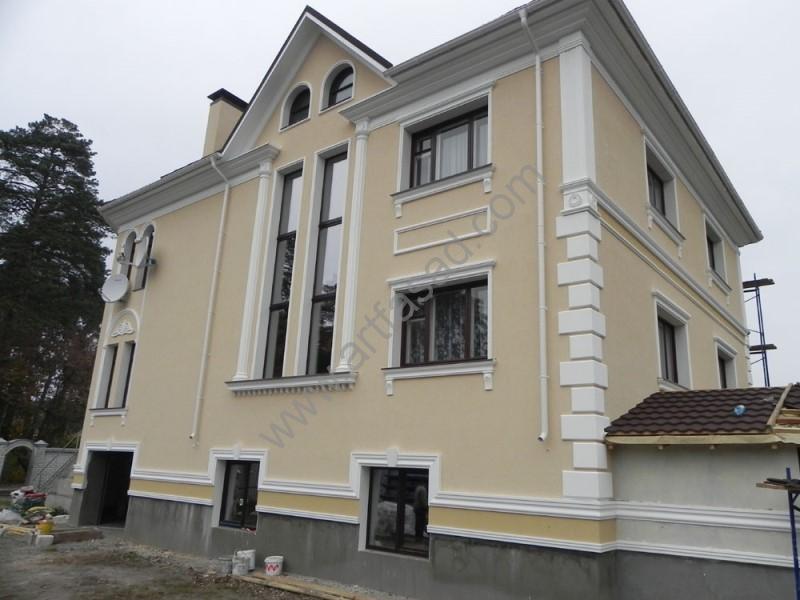

Techniques for working with foam
There are several techniques for working with foam that architects and builders can use to create innovative and sustainable designs.
One technique is shaping and cutting foam. This can be done using hand tools, such as knives and saws, or with specialized power tools, such as hot wire cutters or CNC routers. This technique allows architects to create customized building components, such as columns and beams, that are both functional and aesthetically pleasing.
Another technique is using foam in combination with other materials, such as concrete or steel. This can be done by using foam as a core material in sandwich panels, or by covering shaped foam with a layer of concrete or other finish material. This technique allows architects to create lightweight and strong structures that are also energy-efficient.

A third technique is using foam for insulation, this can be done by injecting foam into walls, roofs, and floors, or by installing foam boards on the exterior of a building. This technique improves energy efficiency and reduces heating and cooling costs.
A fourth technique is using foam in landscaping, architects can use foam to create sculptures, planters, and other decorative elements that can improve the environment and create a sense of place.
In conclusion, there are several techniques for working with foam that architects and builders can use to create innovative and sustainable designs, such as shaping, cutting, using in combination with other materials, insulation and landscaping.
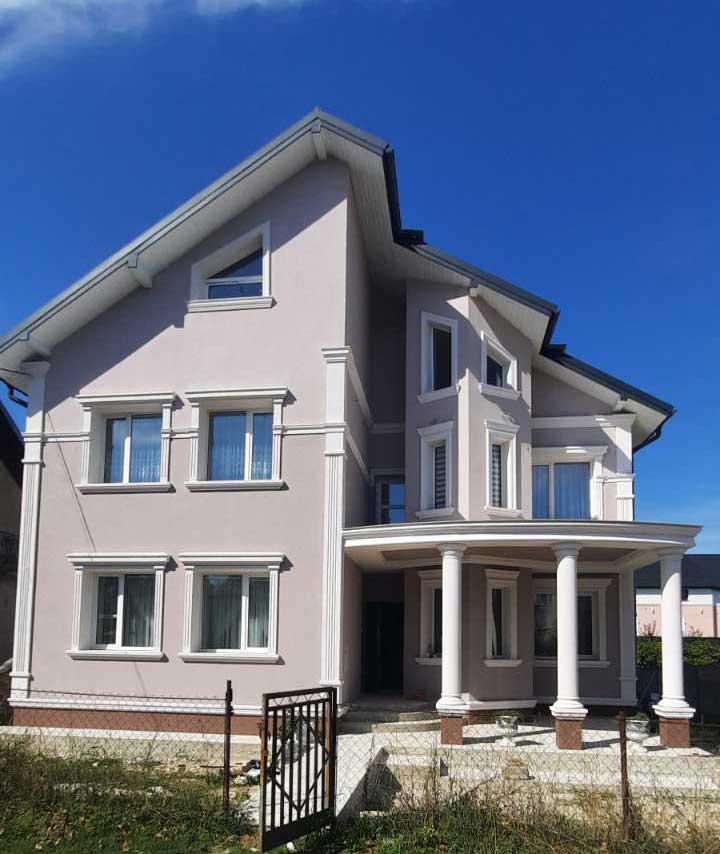

How foam can be used in green building
Foam can be used in a variety of ways in green building to create energy-efficient and sustainable structures.
One way foam can be used in green building is as insulation, which can improve energy efficiency and reduce heating and cooling costs. Foam insulation can be used in walls, roofs, and floors, and can also be used in underground construction, such as foundation insulation, to prevent heat loss and moisture buildup.
Another way foam can be used in green building is by creating green roofs and walls. Green roofs and walls are vegetated surfaces that can help to reduce the heat island effect, improve air quality, and manage stormwater runoff. Foam can be used as a lightweight growing medium for green roofs and walls, or as a structural component in the system.

Foam can also be used in sustainable landscaping, creating sculptures, planters, and other decorative elements that can improve the environment and create a sense of place.
Foam can also be used in sustainable construction, as it can be easily recycled or repurposed at the end of its useful life, making it an environmentally friendly option for construction.
In conclusion, foam can be used in a variety of ways in green building, such as insulation, green roofs and walls, sustainable landscaping and construction, providing architects and builders with a sustainable building material that helps in creating energy-efficient and environmentally friendly structures.
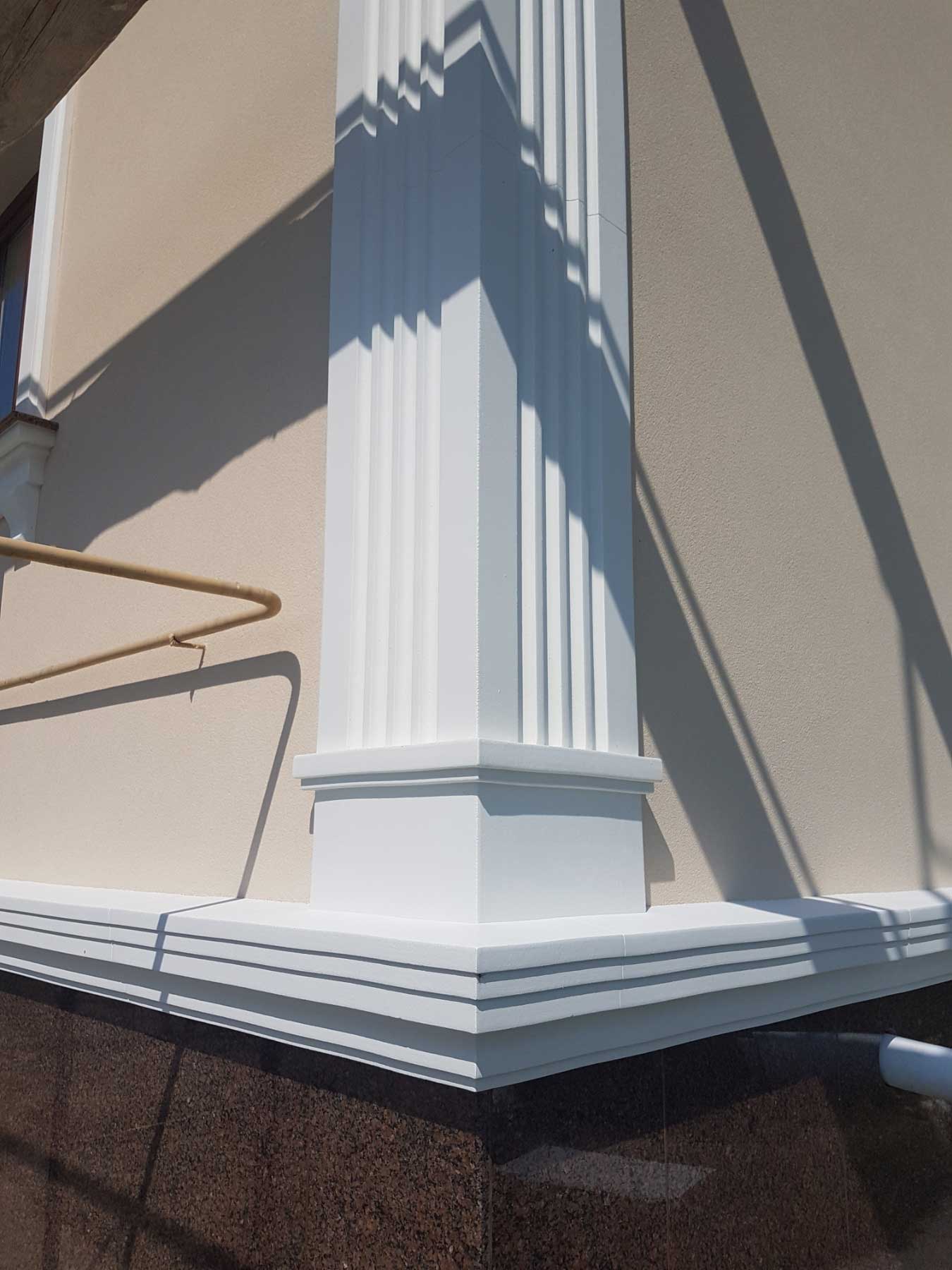

Foam recycling and repurposing
Foam recycling and repurposing is an important aspect of sustainable architecture and construction. Recycling and repurposing foam can help to reduce waste and conserve resources.
One way foam can be recycled is by shredding it and using it as a filling material for pillows, cushions, and stuffed toys. It can also be used as an aggregate in lightweight concrete, or as a growing medium for green roofs and walls.
Another way foam can be repurposed is by using it in art and design projects. Shaped and sculpted foam can be used to create unique and eye-catching sculptures, decorative elements, and other artistic creations.
Foam can also be used in many other ways, such as flotation devices, packaging, and insulation.
In conclusion, foam recycling and repurposing is an important aspect of sustainable architecture and construction, as it helps to reduce waste and conserve resources, and also can be used in various ways that can add value to our lives.
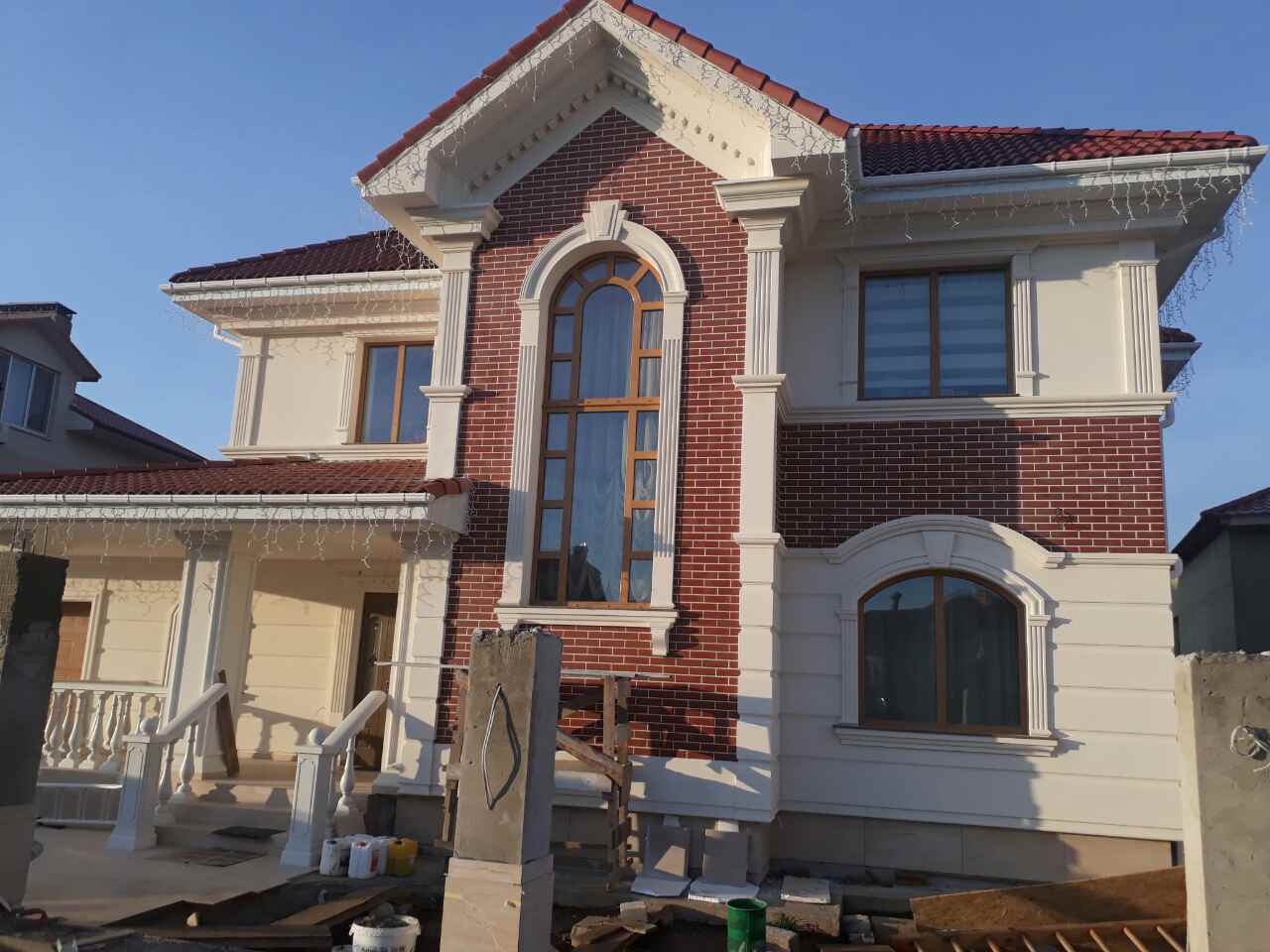

Life Cycle Analysis of foam
Life Cycle Analysis (LCA) is a method used to evaluate the environmental impact of a product or material over its entire life cycle, from extraction of raw materials to disposal or recycling.
When conducting an LCA of foam, several factors should be considered, such as the energy and resources used to produce the foam, the energy and resources used during the manufacturing process, and the energy and resources used during the use phase of the foam. Additionally, the end-of-life scenario for the foam should be considered, including the potential for recycling or repurposing.
One of the main advantages of foam is that it has a low environmental impact during the production phase, as it is made from a simple chemical reaction between liquid components, and it doesn’t require a lot of energy. Additionally, foam can be easily recycled or repurposed at the end of its useful life, which helps to conserve resources and reduce waste.
On the other hand, foam can have a significant environmental impact during the use phase if not properly disposed of. It can take a long time to decompose in landfills and release harmful chemicals in the process. Therefore, it is important that foam waste is properly handled and recycled or repurposed to minimize its environmental impact.
In conclusion, LCA of foam shows that foam has a low environmental impact during the production phase and can be easily recycled or repurposed, but it is important to consider the proper disposal of foam waste to minimize its environmental impact.

Future possibilities for foam architecture
The future possibilities for foam architecture are vast and exciting. As architects and builders continue to explore the potential of foam as a building material, new and innovative uses will be discovered.
One possibility for the future of foam architecture is the increased use of foam in prefabrication and modular construction. The lightweight and strong properties of foam make it a suitable material for prefabricated building components, such as walls, floors, and roofs. This can lead to faster and more efficient construction, as well as improved energy efficiency and sustainability.
Another possibility is the use of foam in 3D printing of building components. 3D printing can produce complex and customized designs, making it possible to create unique and energy-efficient buildings using foam.
Foam can also play a role in the development of sustainable and green building, as it can be used to create green roofs, walls, and other landscaping elements that improve the environment and create a sense of place.
Foam can also be used in a variety of ways in construction, such as insulation, structural elements, and exterior design. This versatility makes it an exciting and promising field for architects and builders to explore.
In conclusion, the future possibilities for foam architecture are vast, as it can be used in prefabrication, modular construction, 3D printing, sustainable and green building, and in a variety of ways in construction, making it an exciting and promising field for architects and builders to explore.