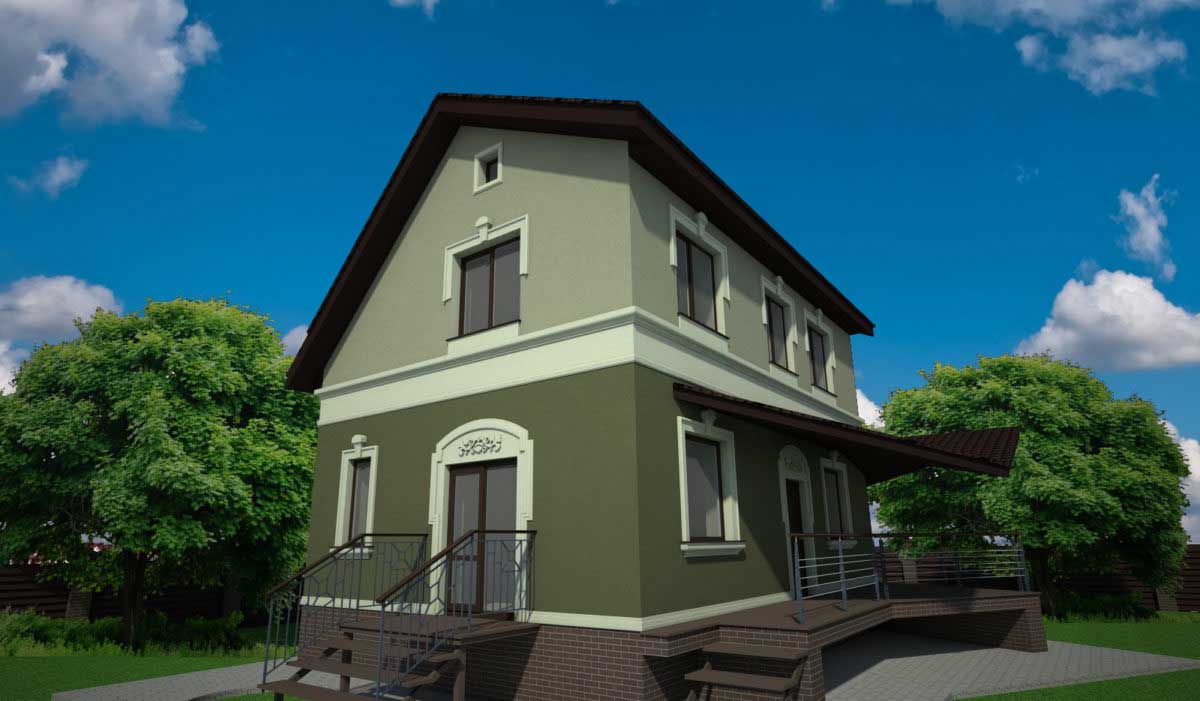
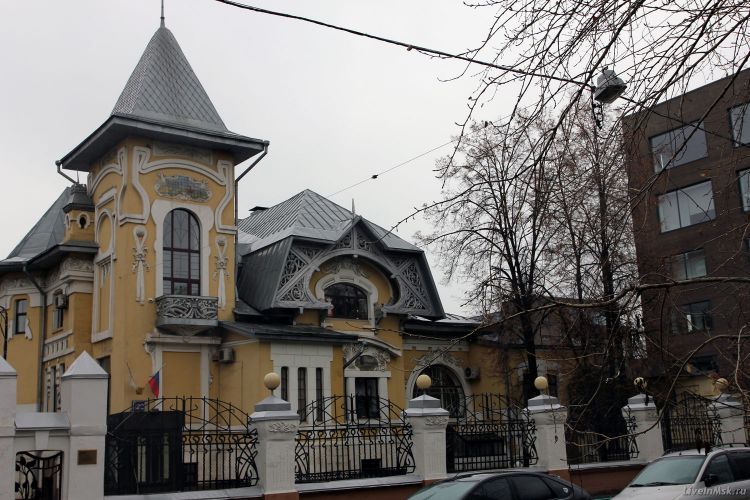
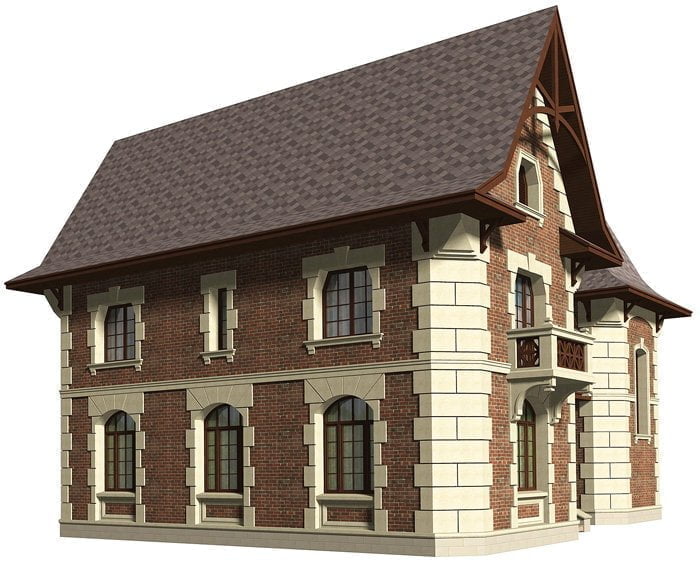
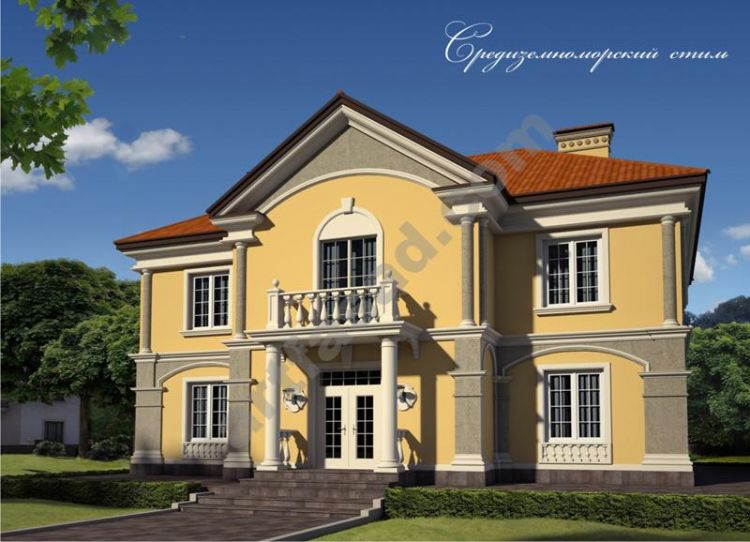
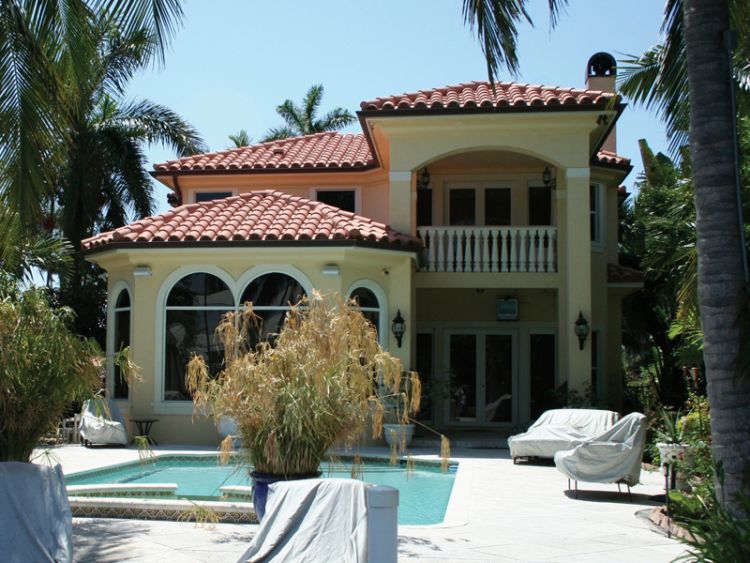
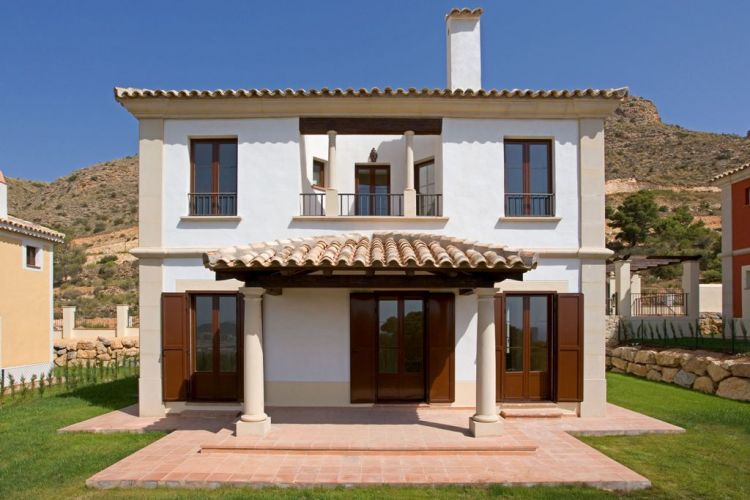
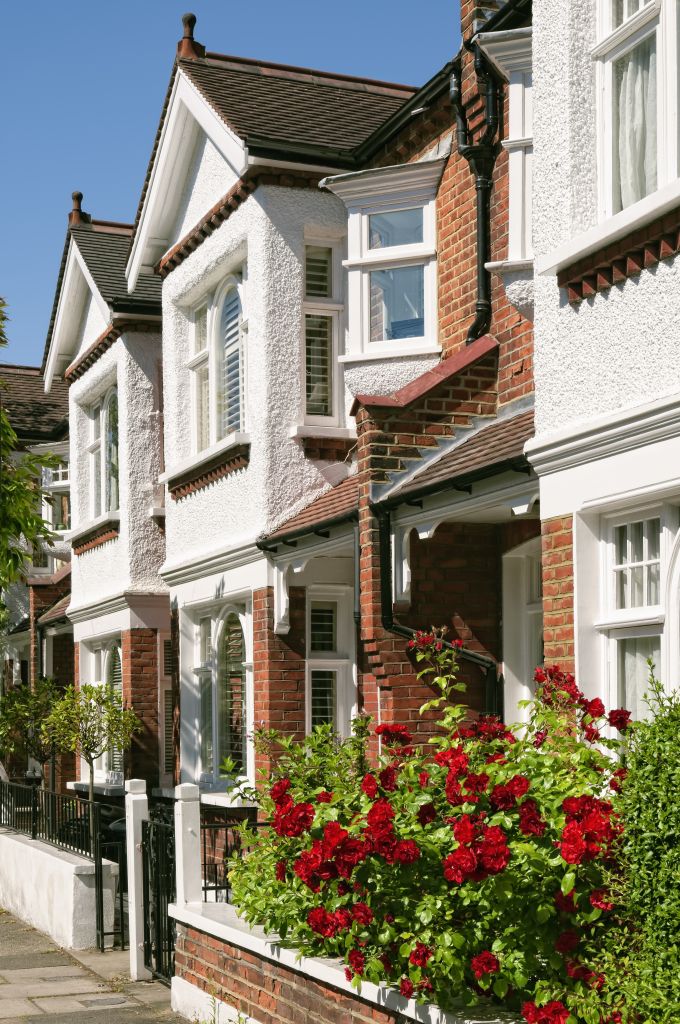
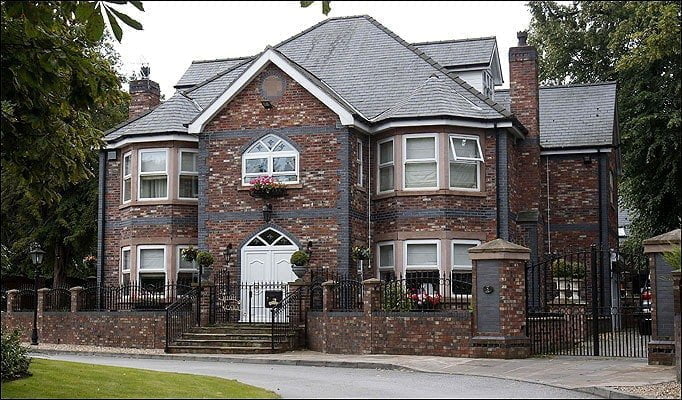
If you need help picking out architectural elements for your home’s facade, we’ve got you covered. Our company has over 10 years of experience in designing, manufacturing, and installing house facade decor. Check out our past projects on the page below to see examples of our work in various architectural styles, all featuring unique elements of decor. You might find inspiration for your own home!

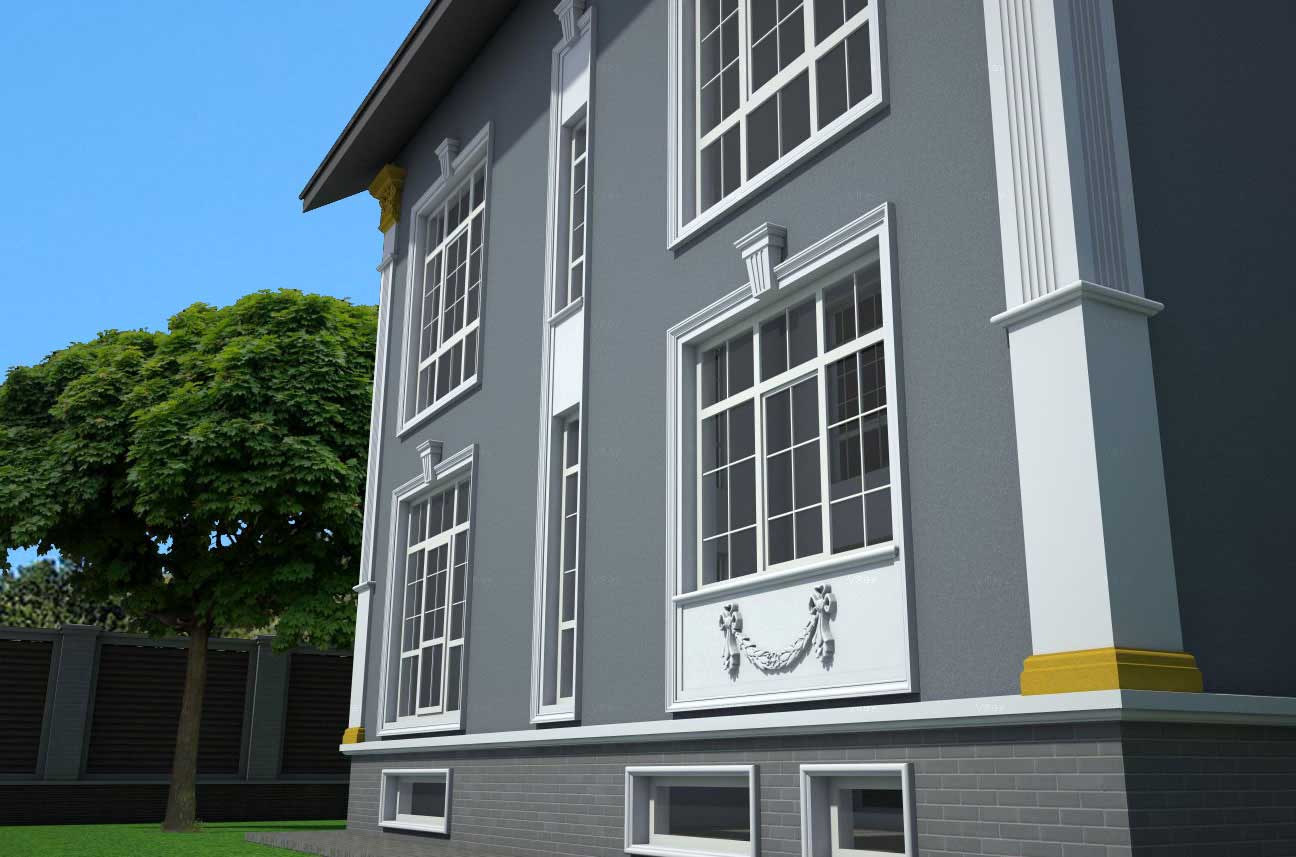
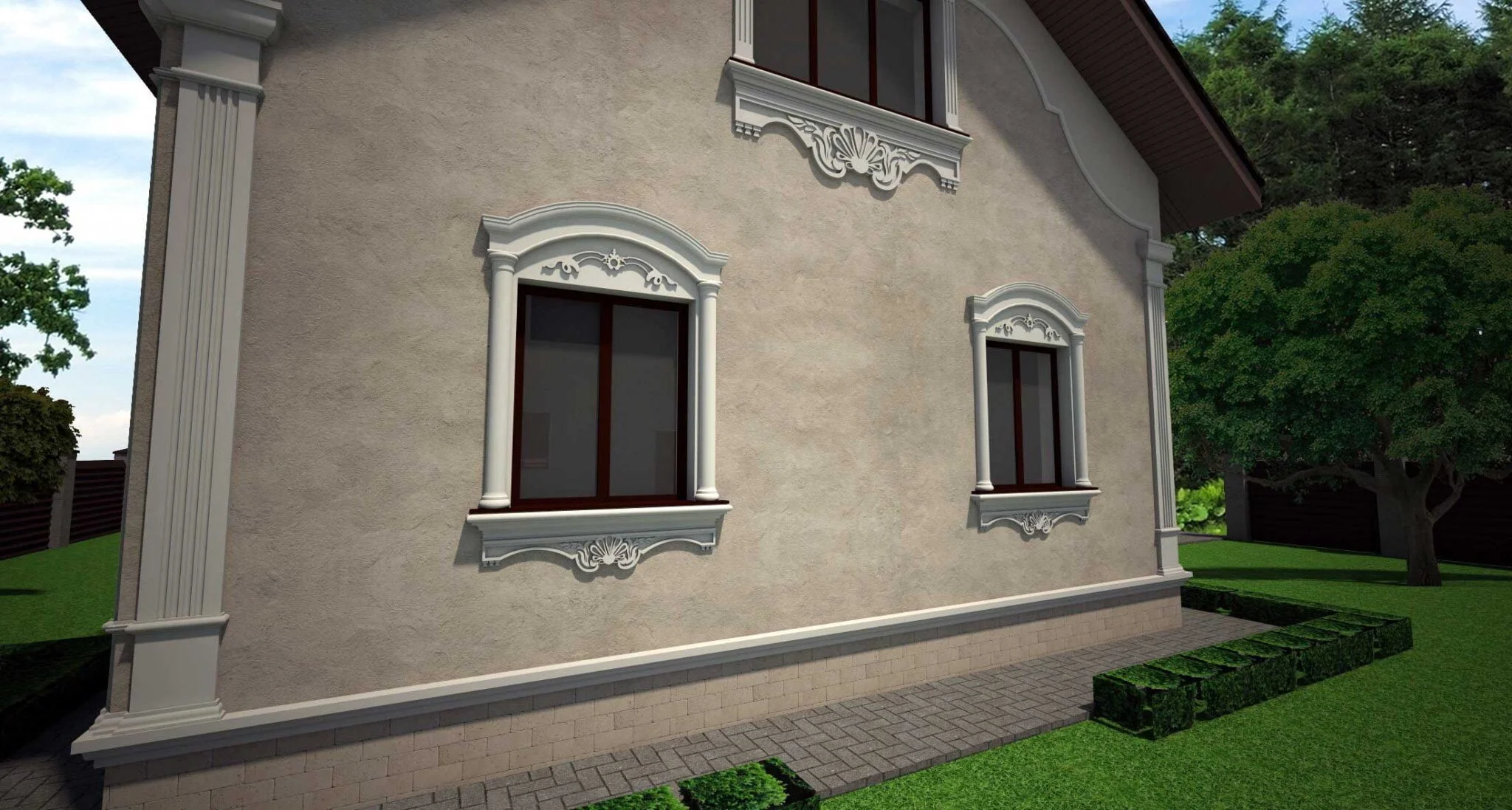
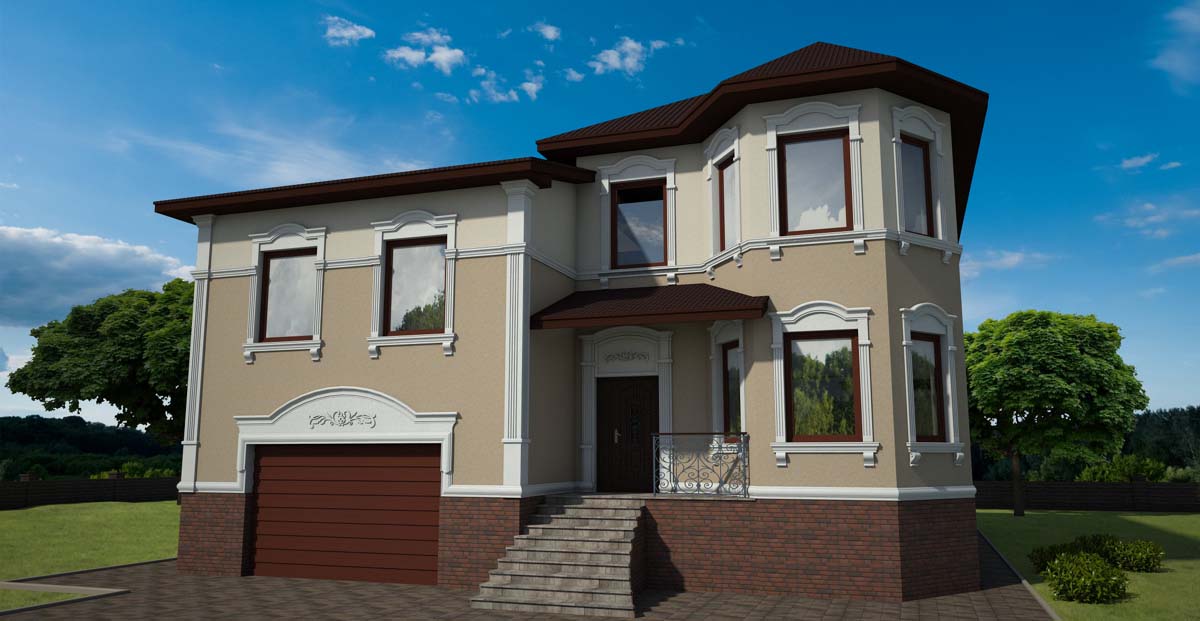
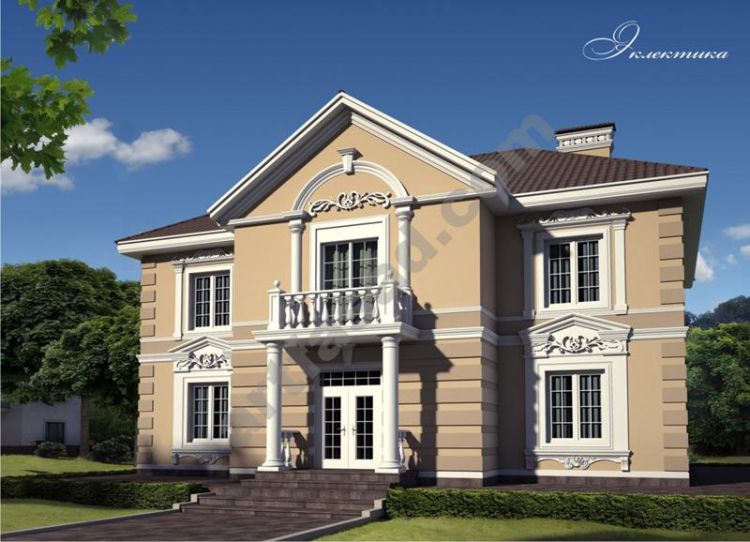
We provide a service that allows you to see a 3D visualization of your home’s facades with customized decor and colors. Our prices start at $200, which may vary depending on the complexity of your house and your desired decor. The design fee is already included in the facade decor cost. You can view, rotate, and enlarge the 3D model of your home with finishing. Below, you can find some examples. Typically, we provide the initial design for the facade decoration within 2-3 days.

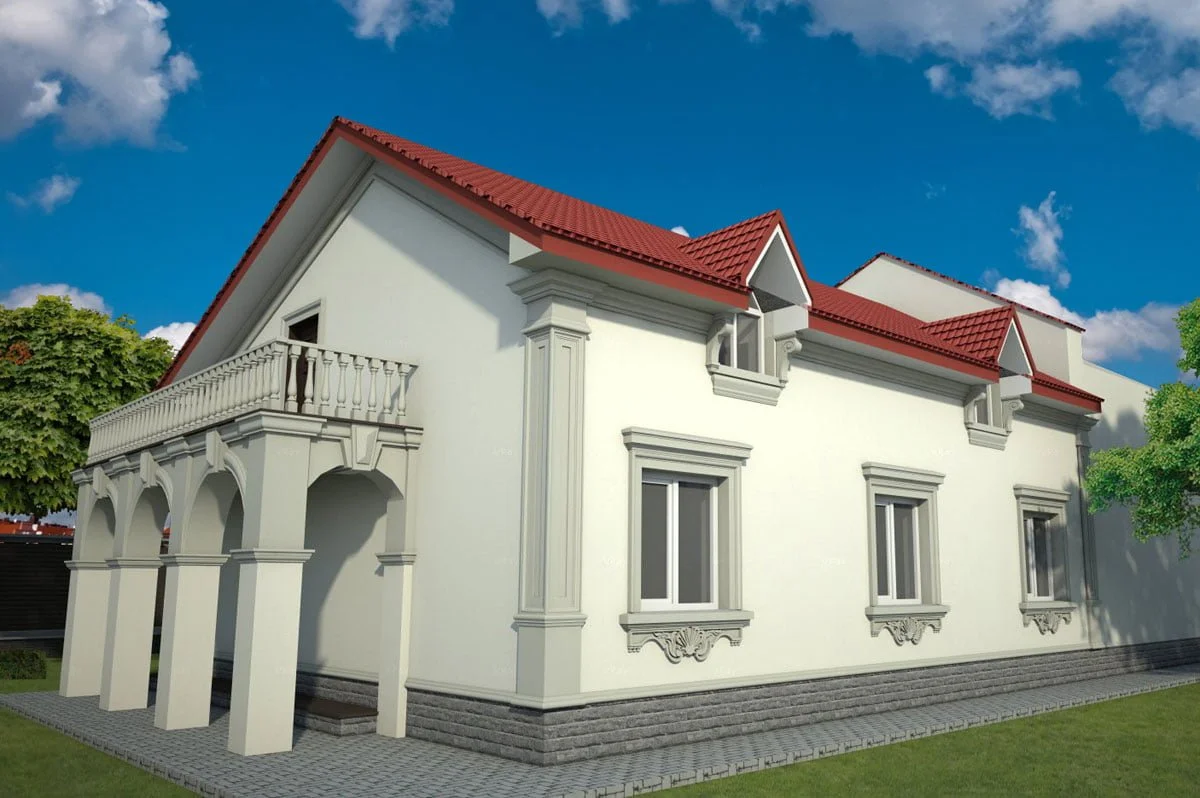
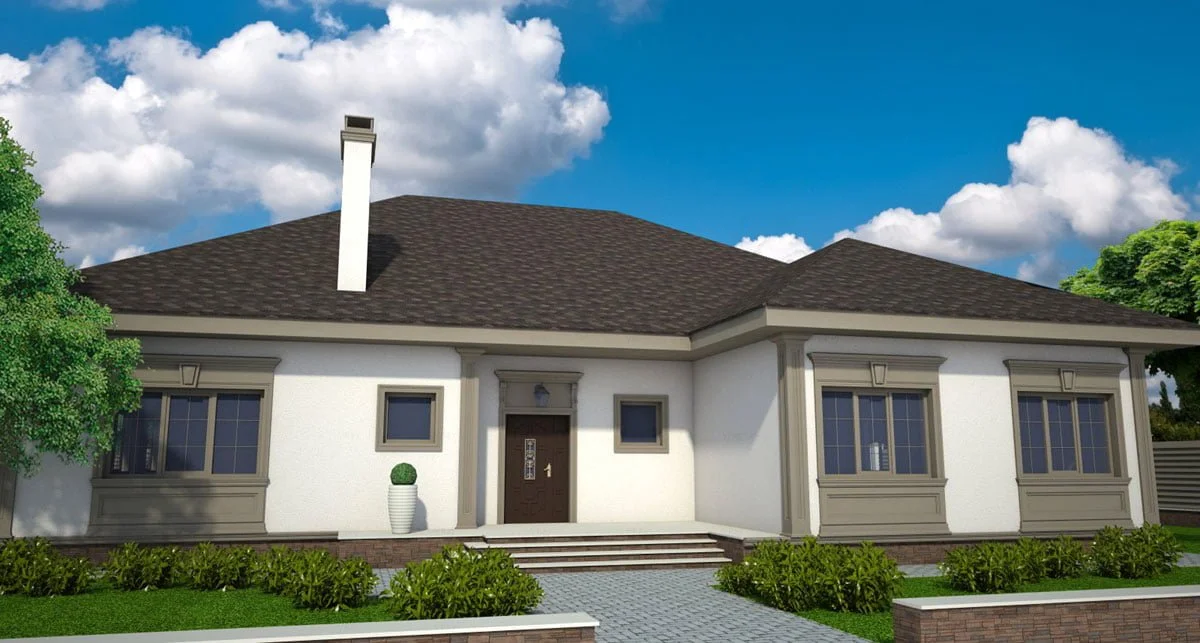
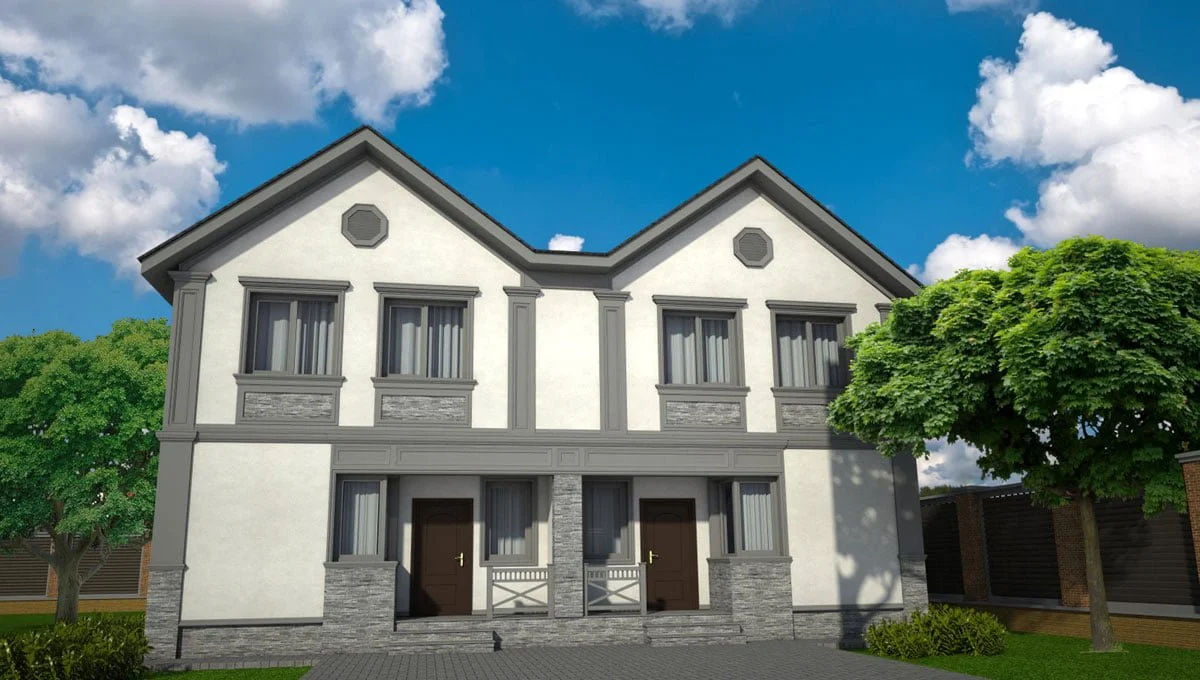
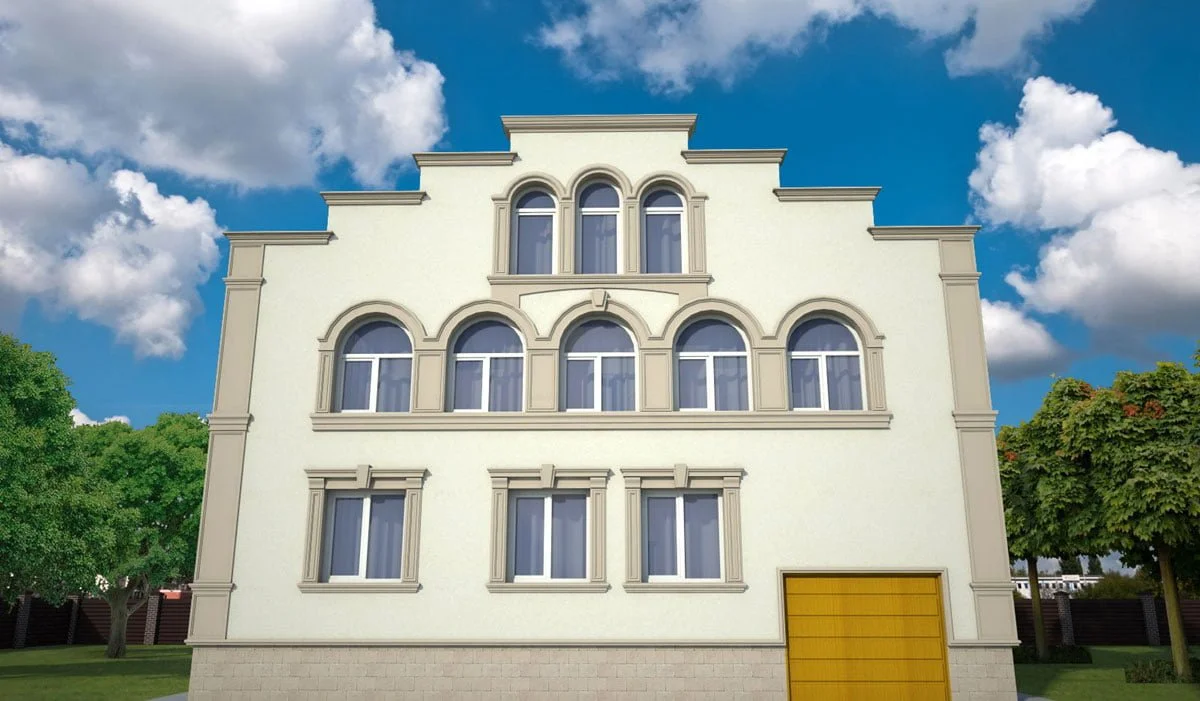
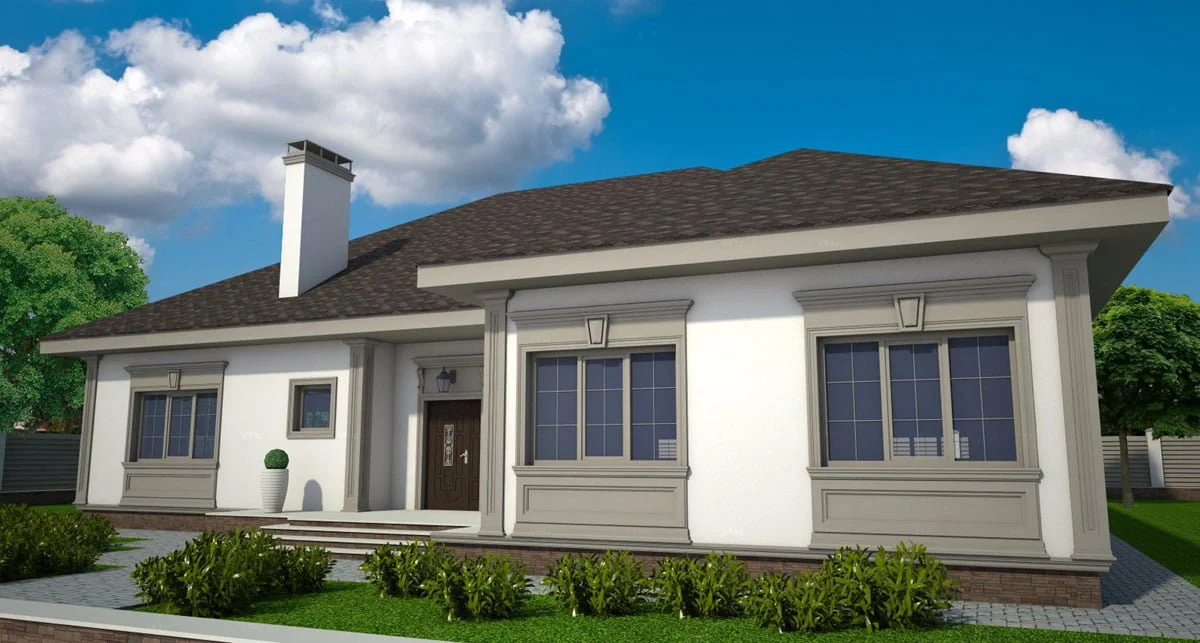
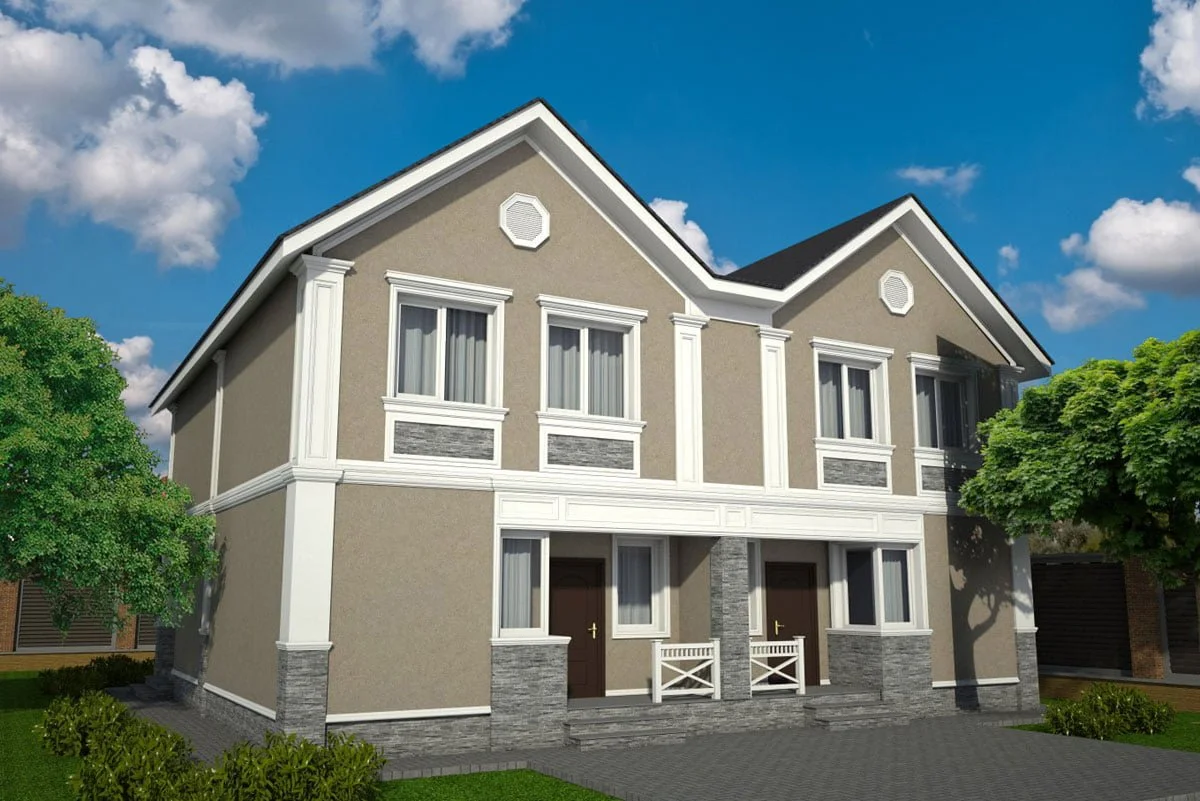
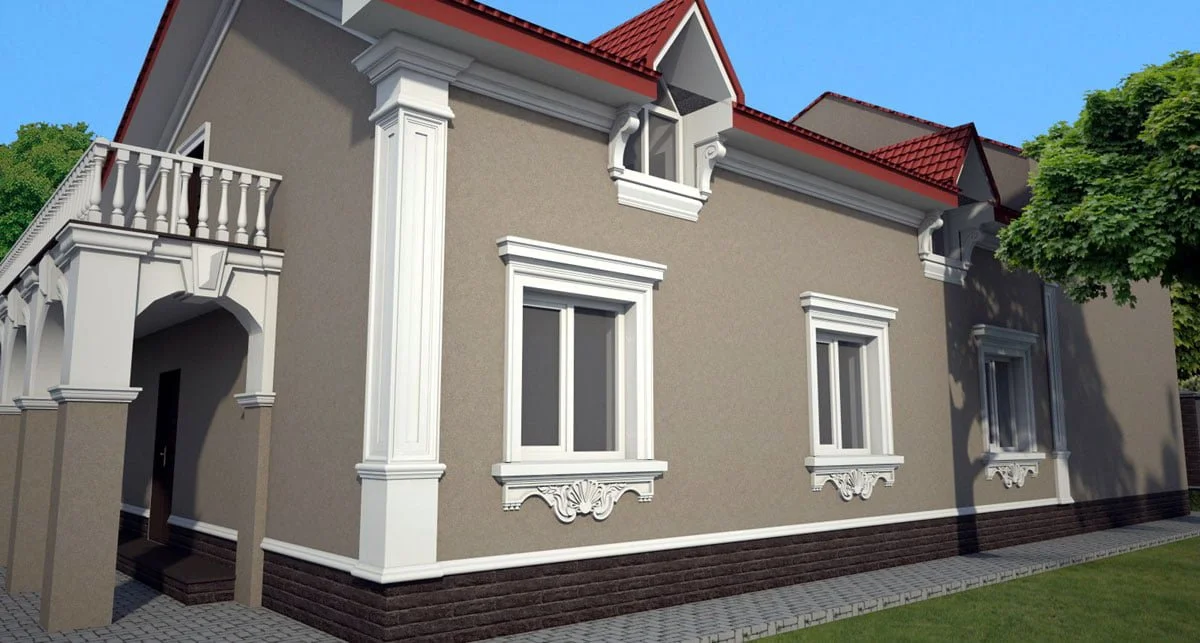
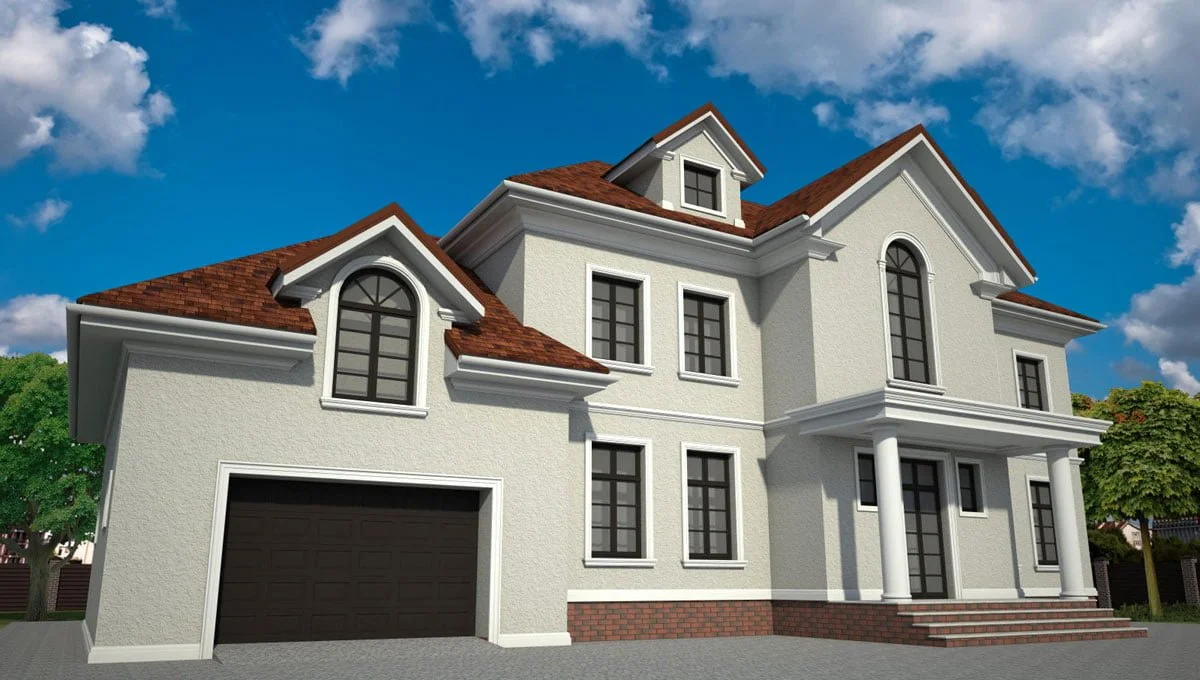
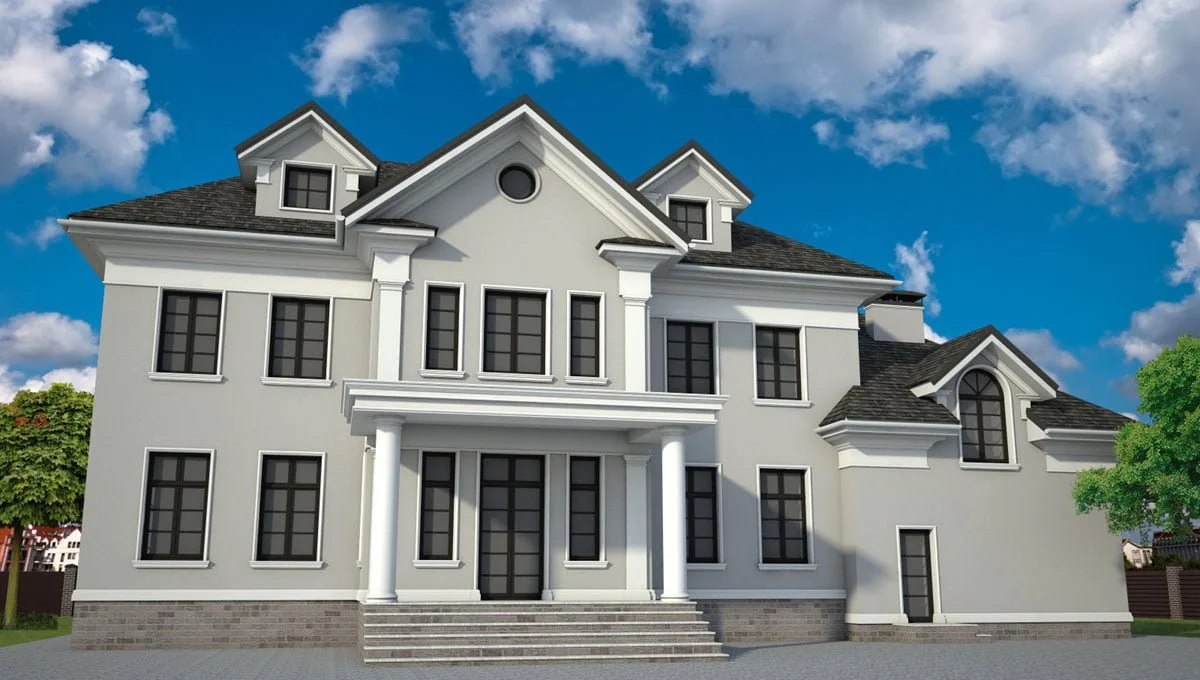
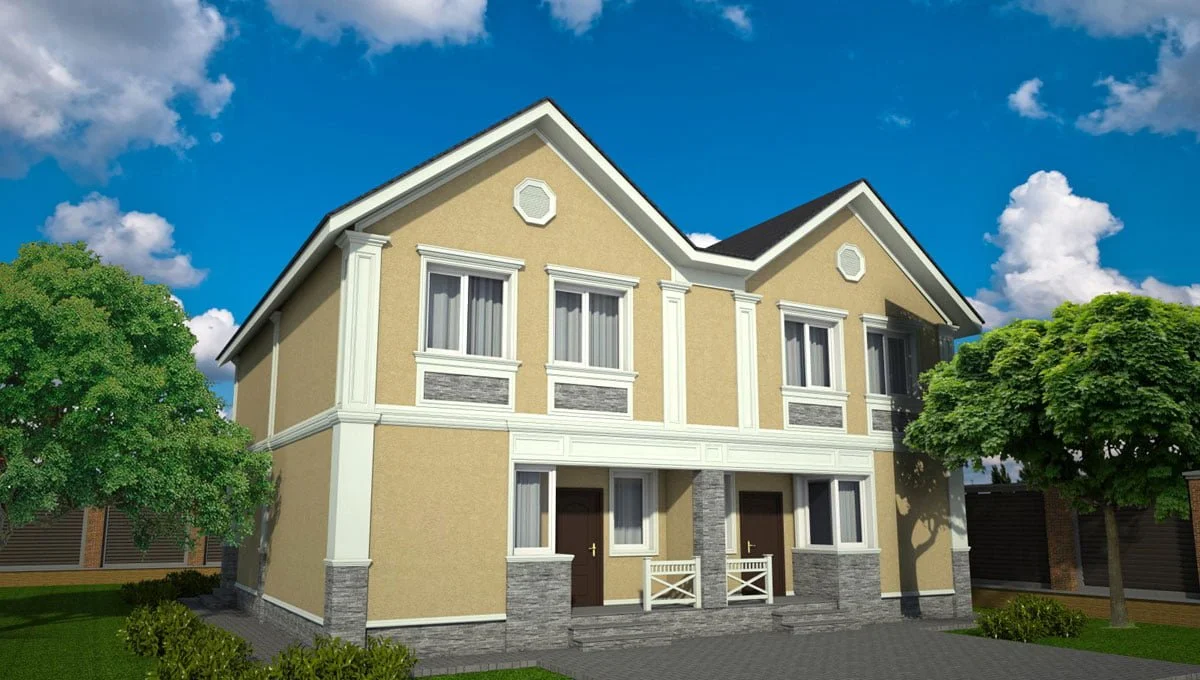
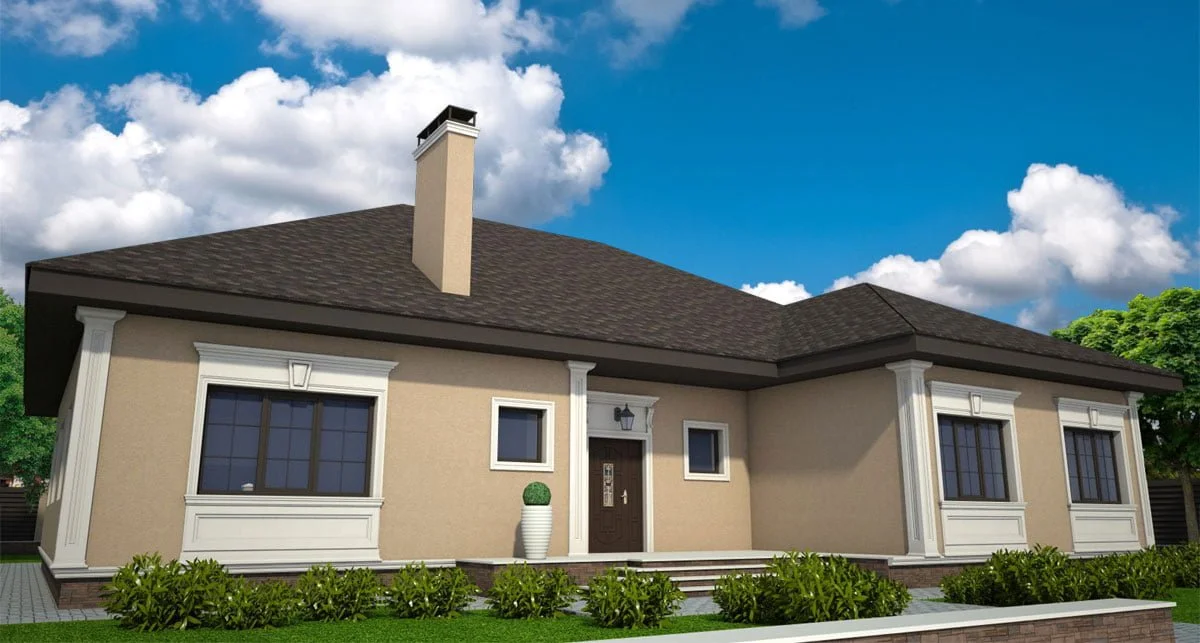
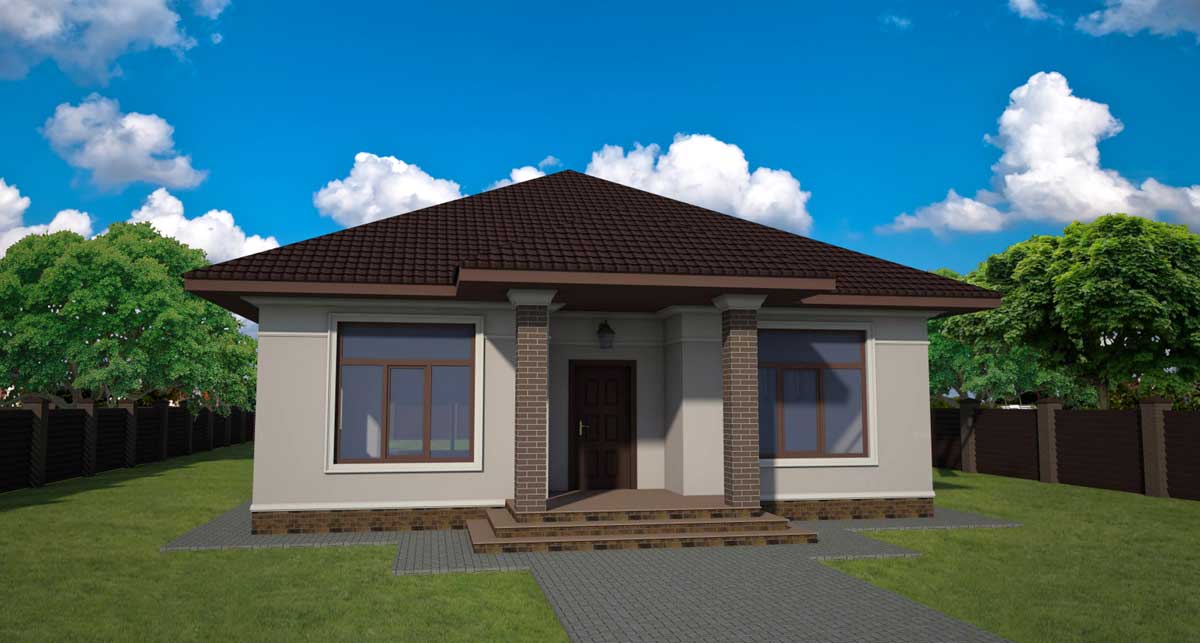
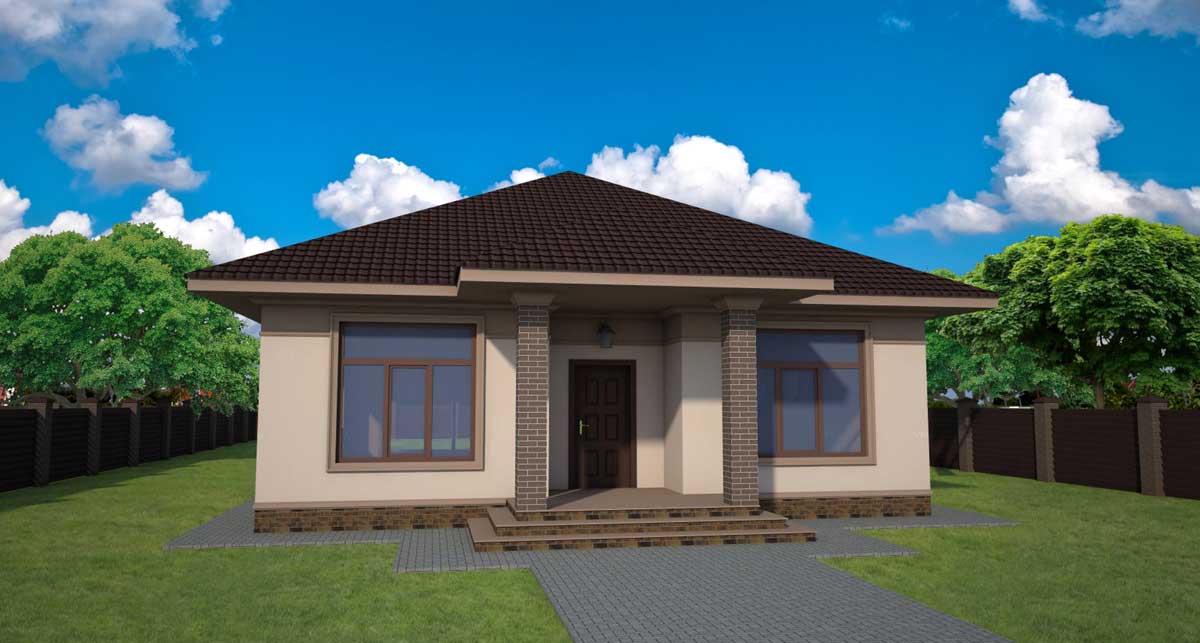
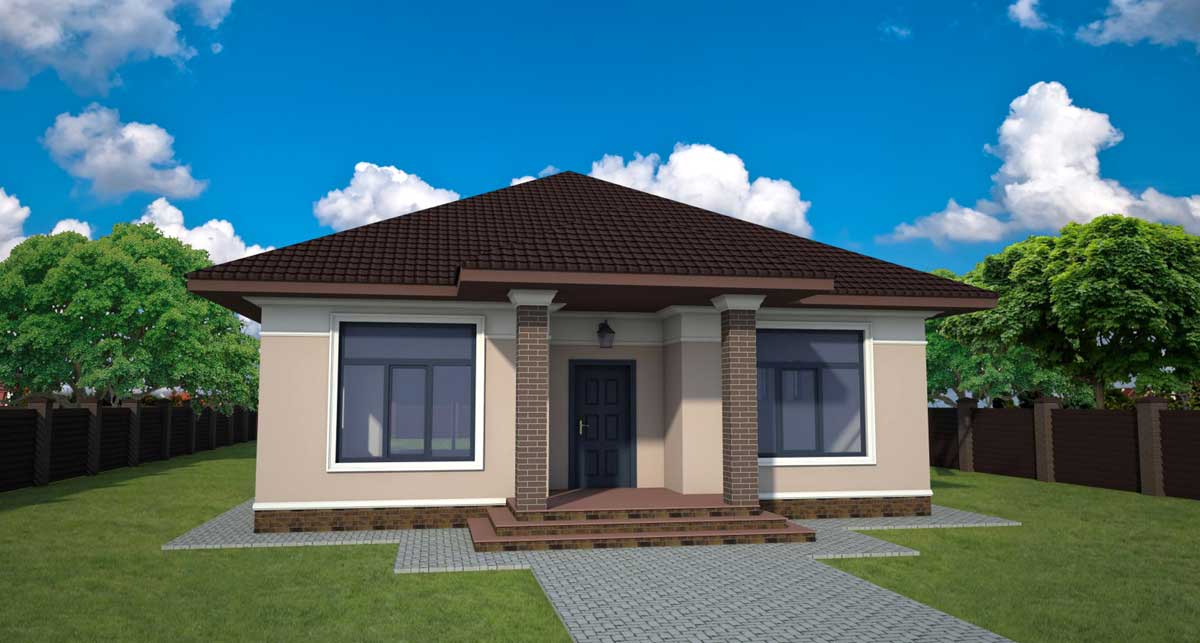
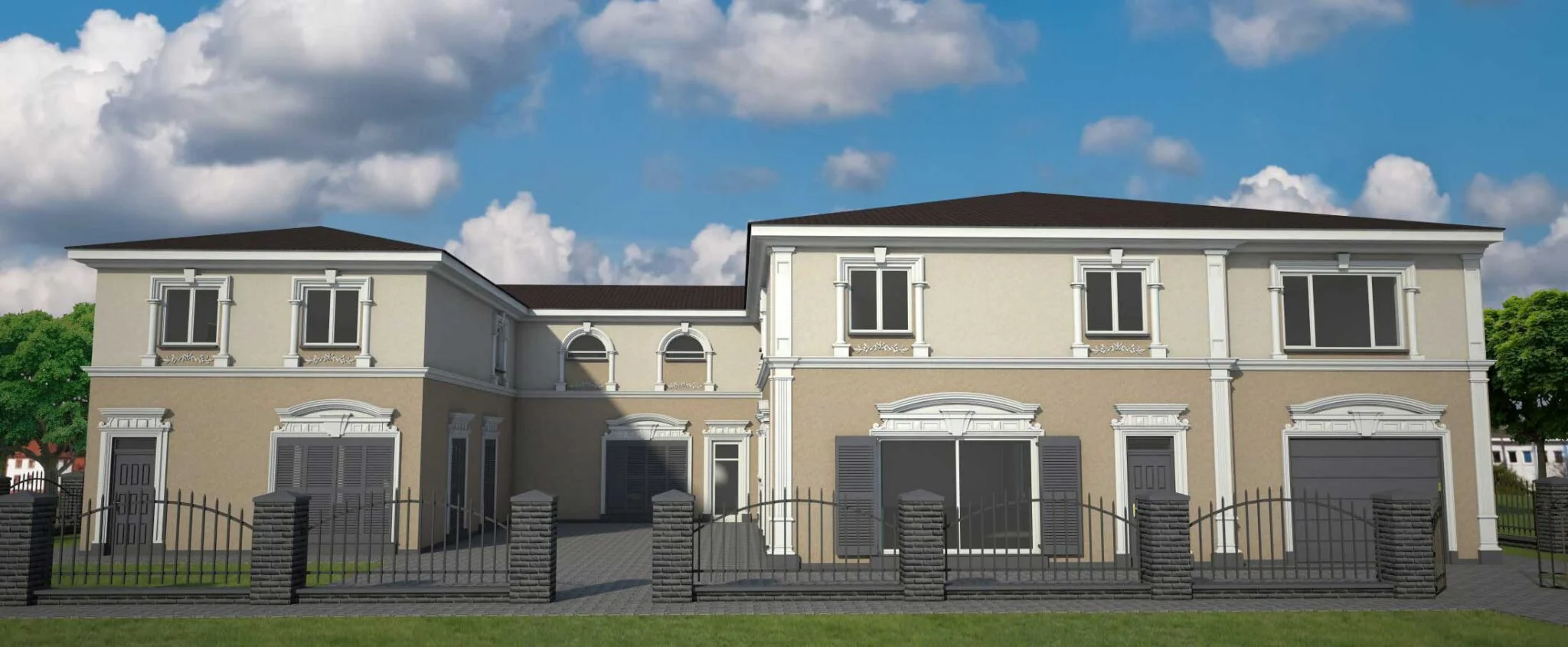
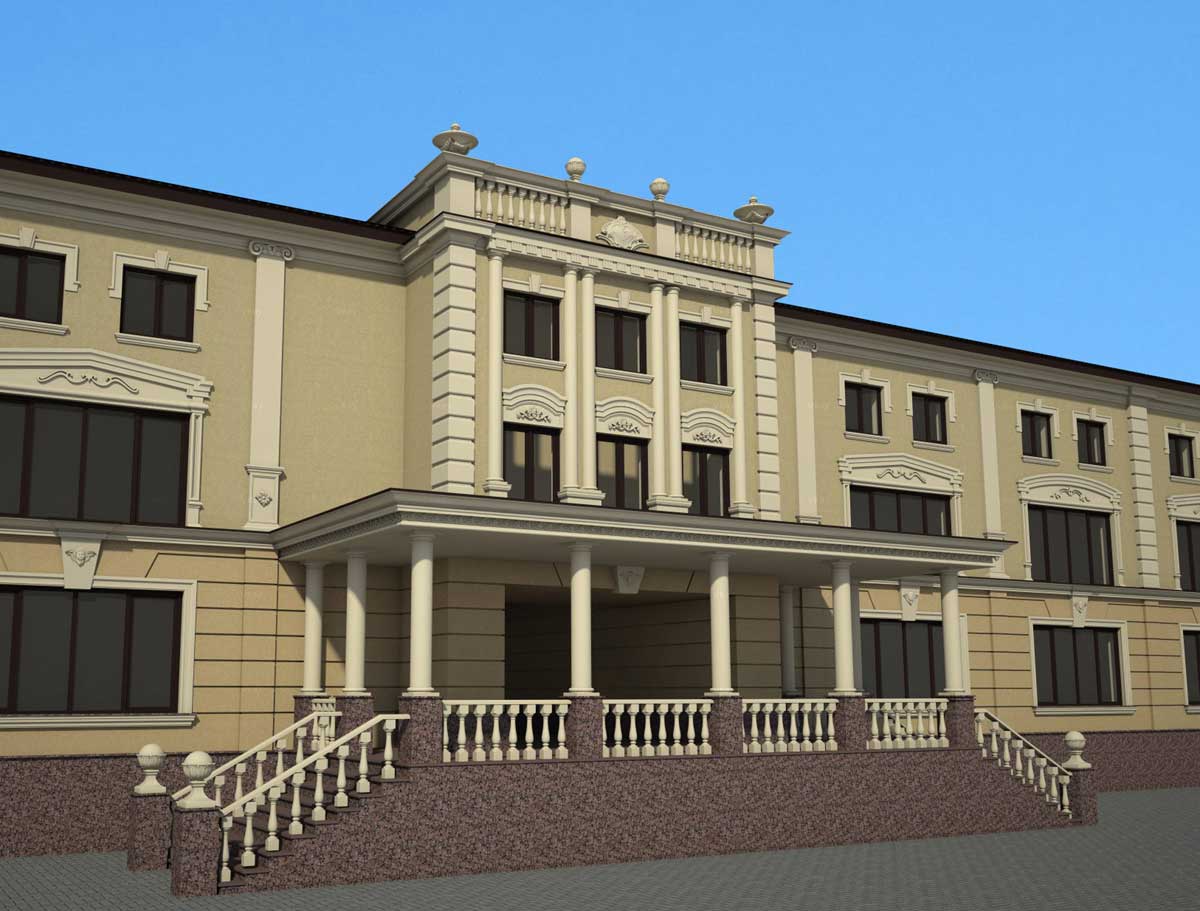
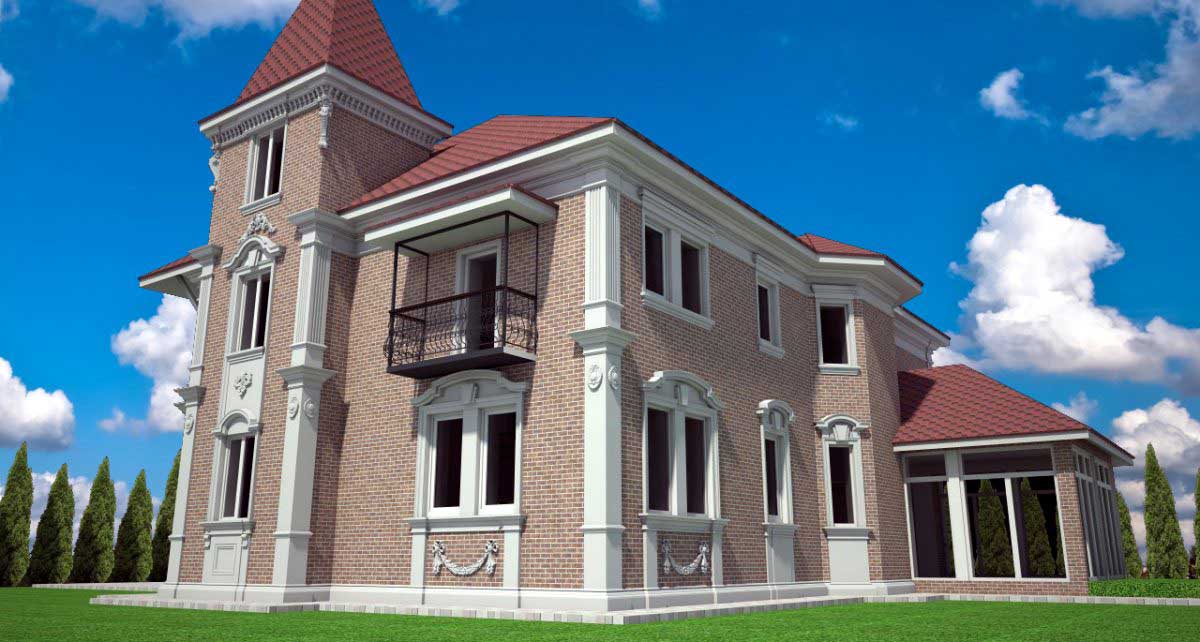
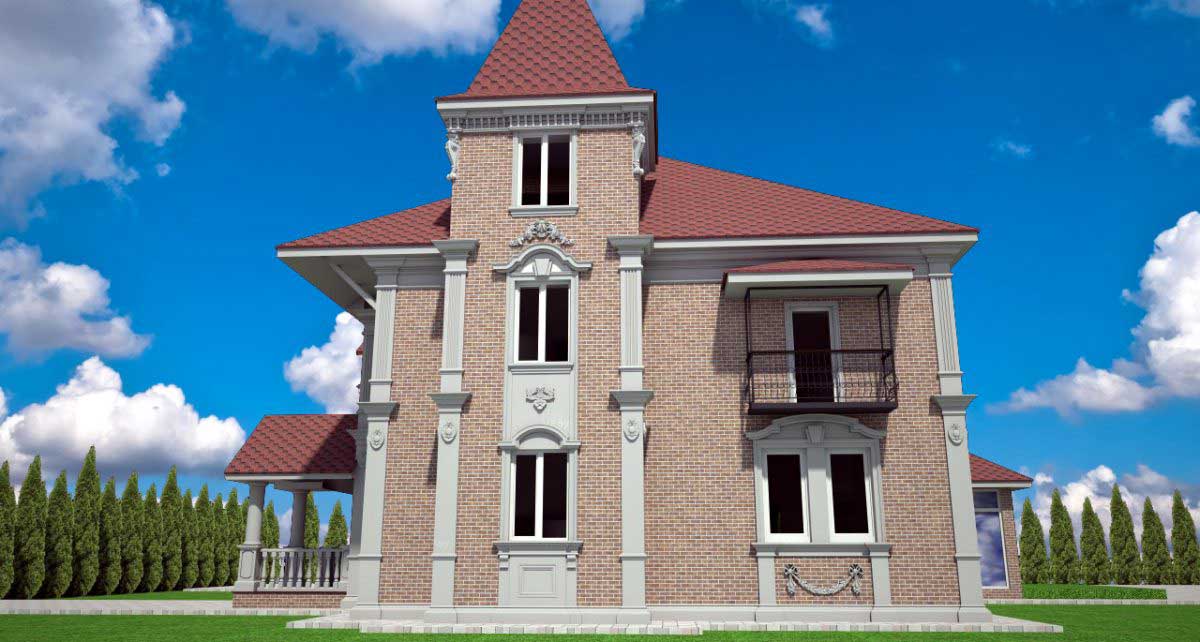
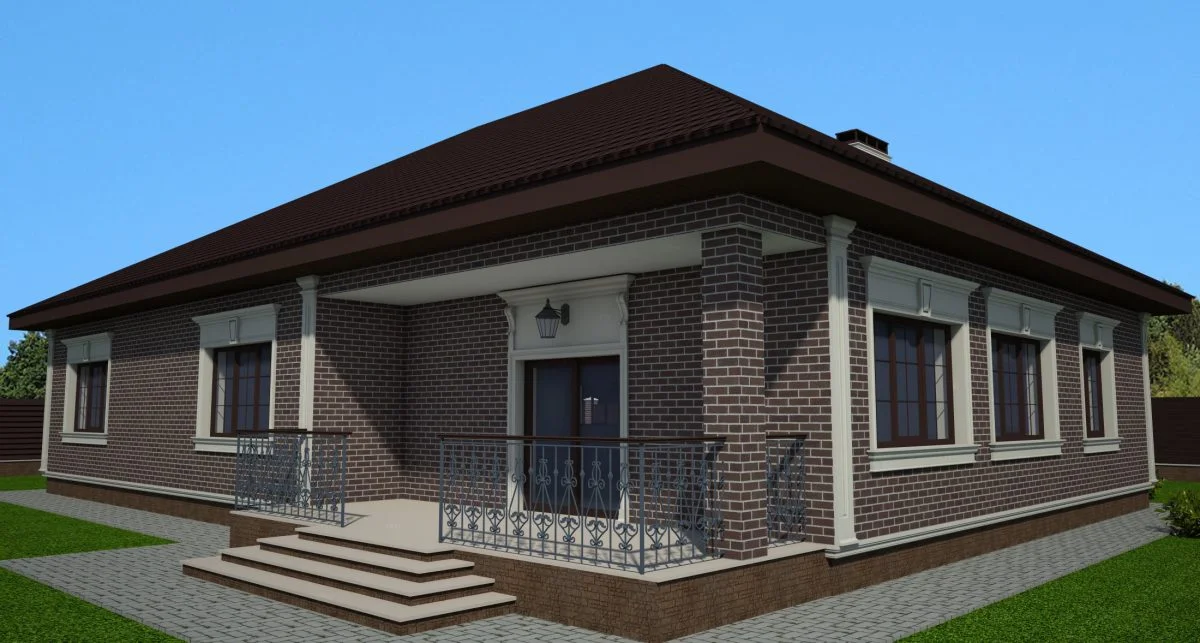
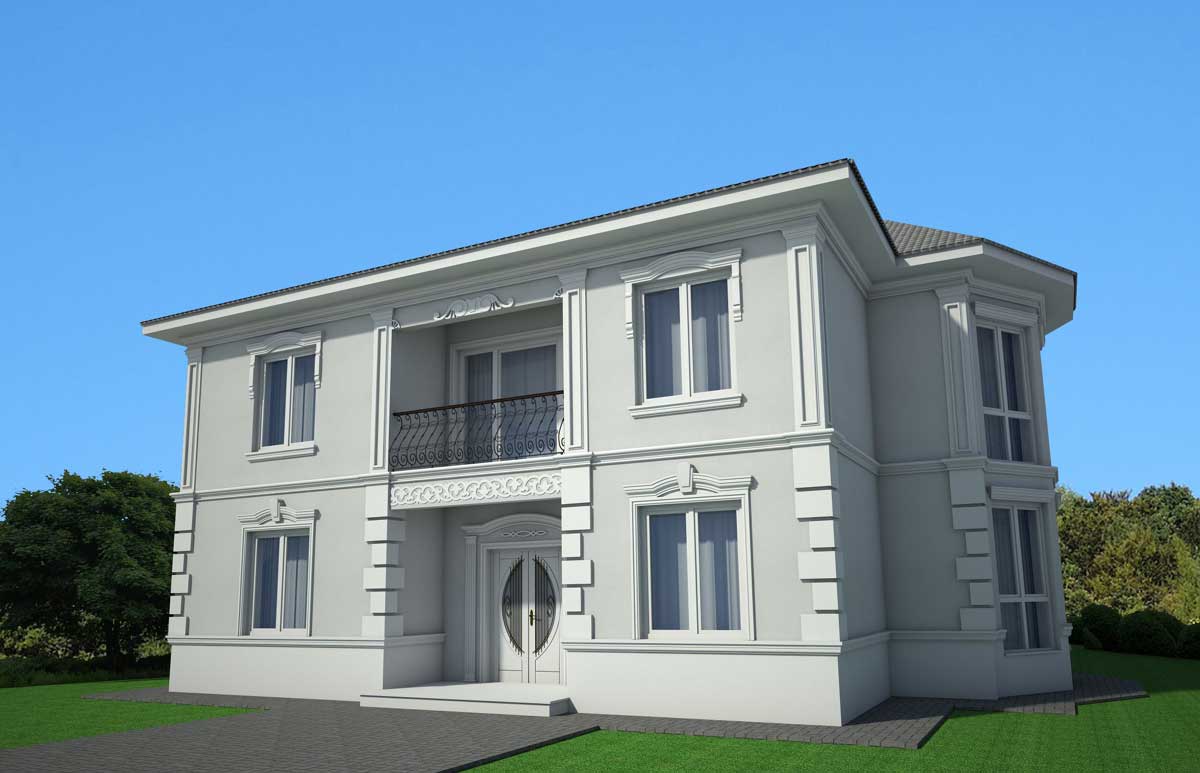
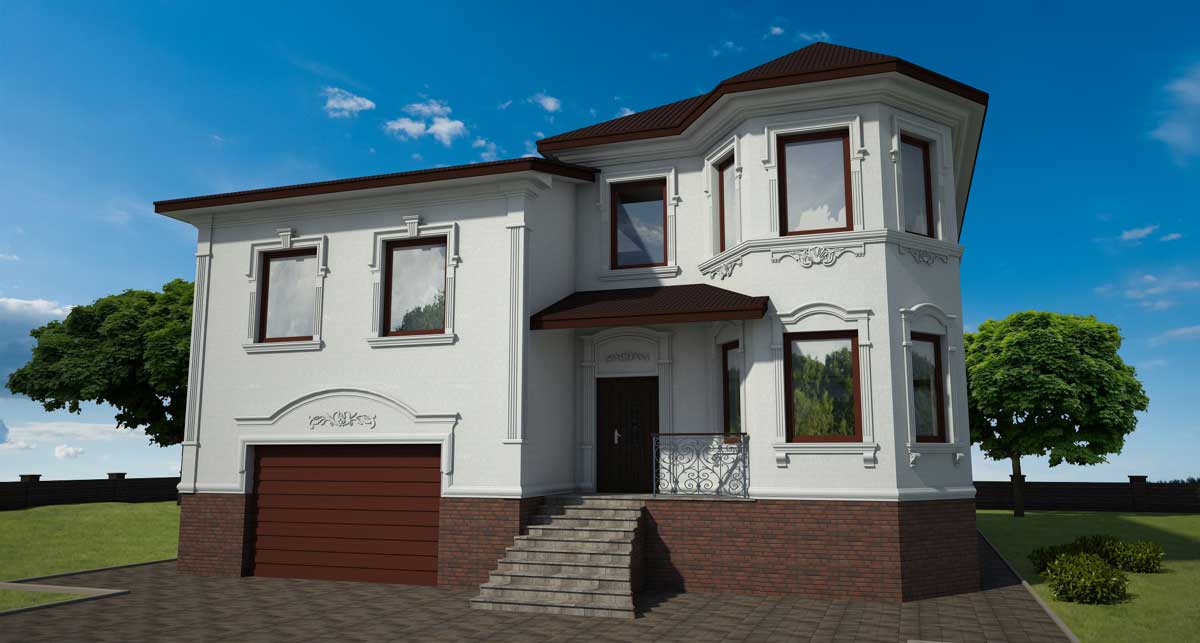
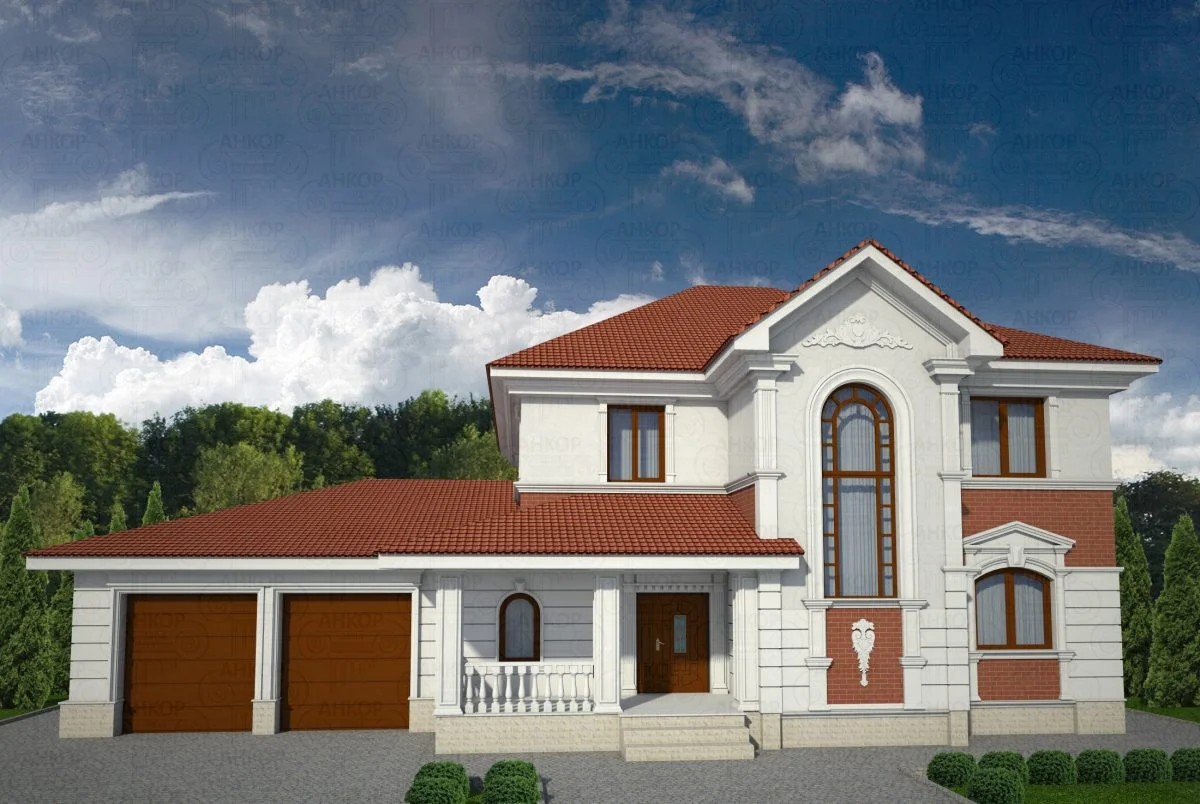
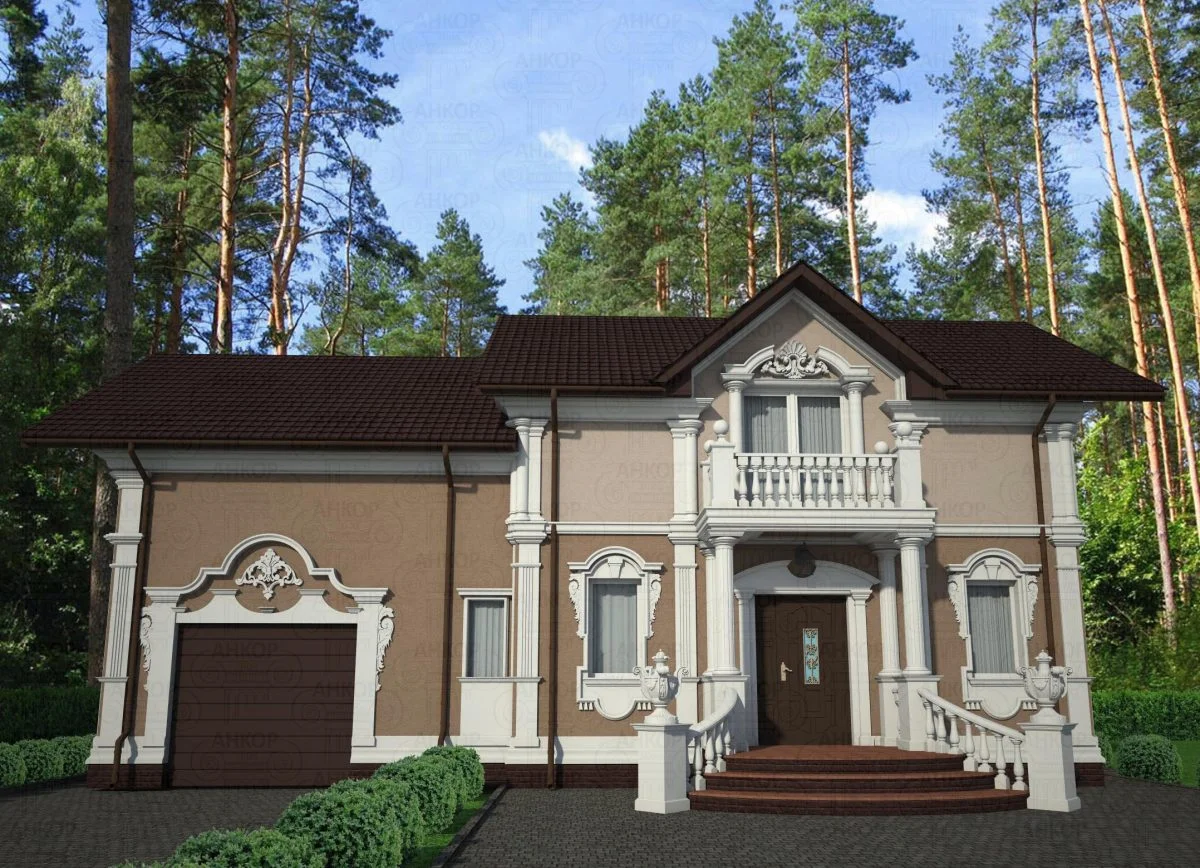
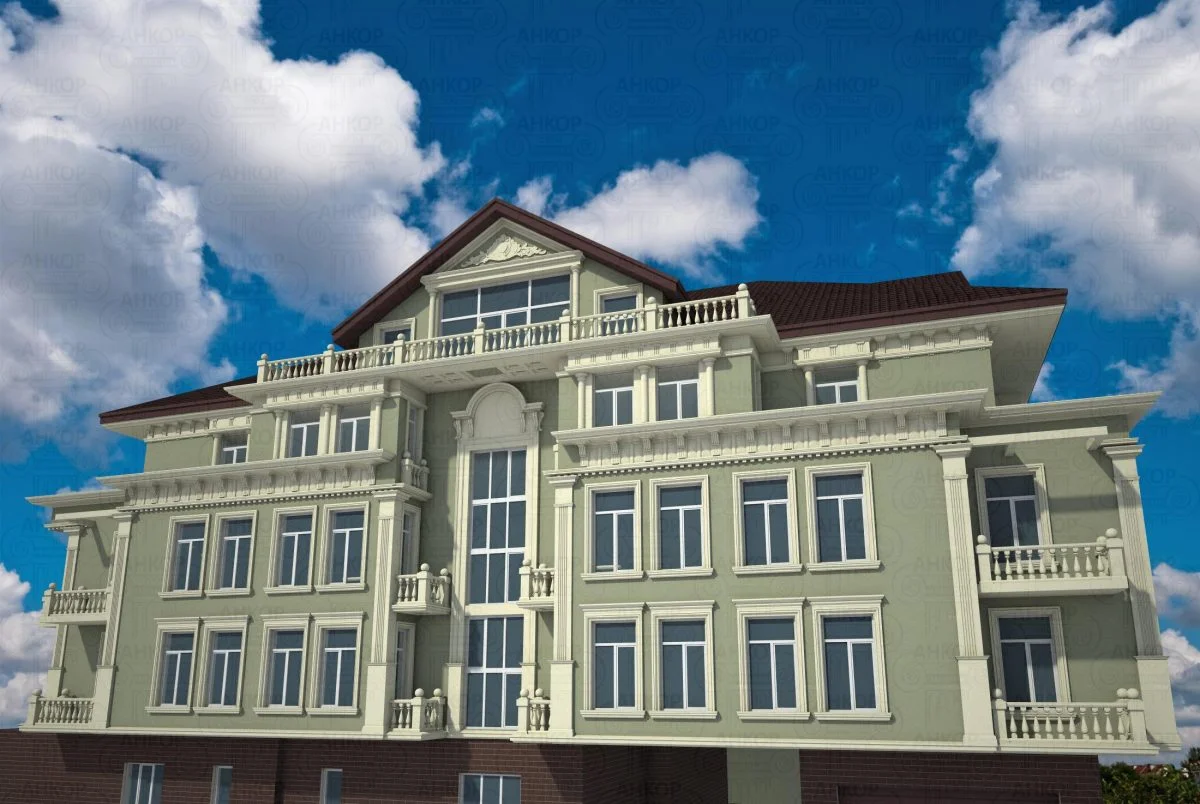
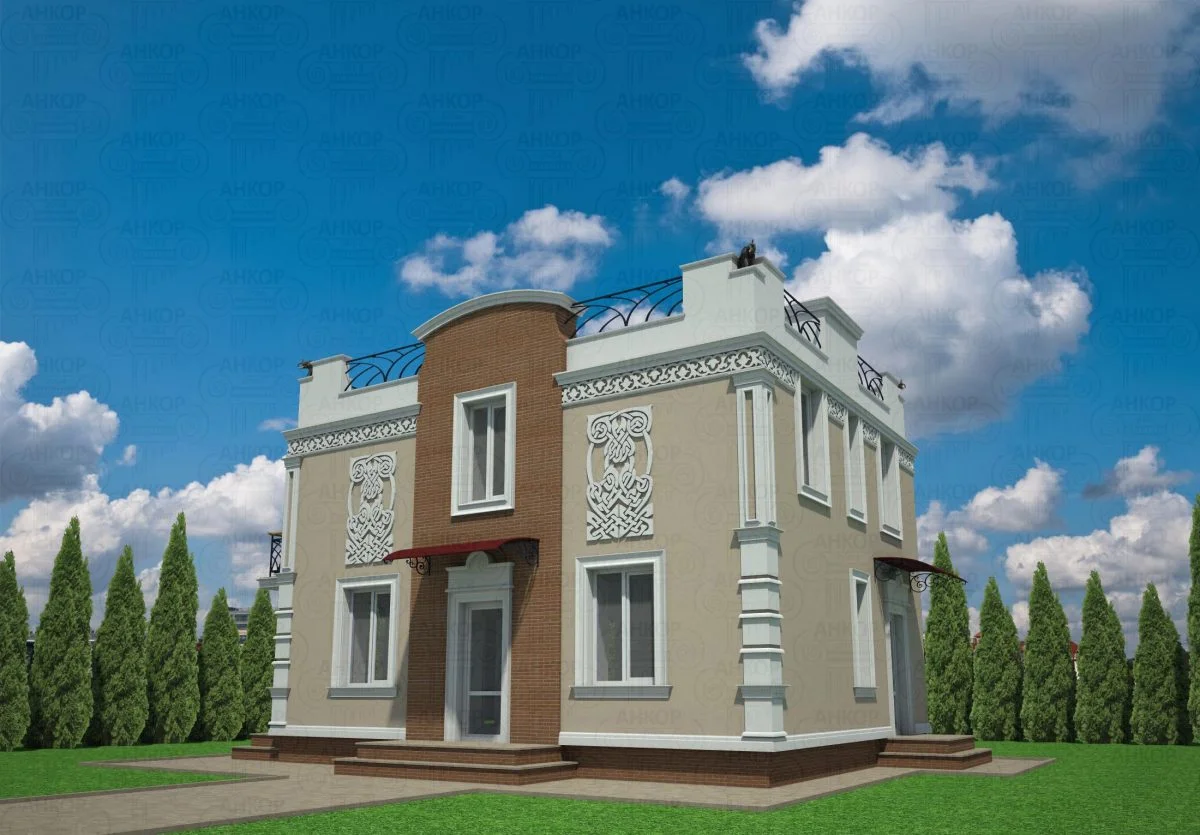
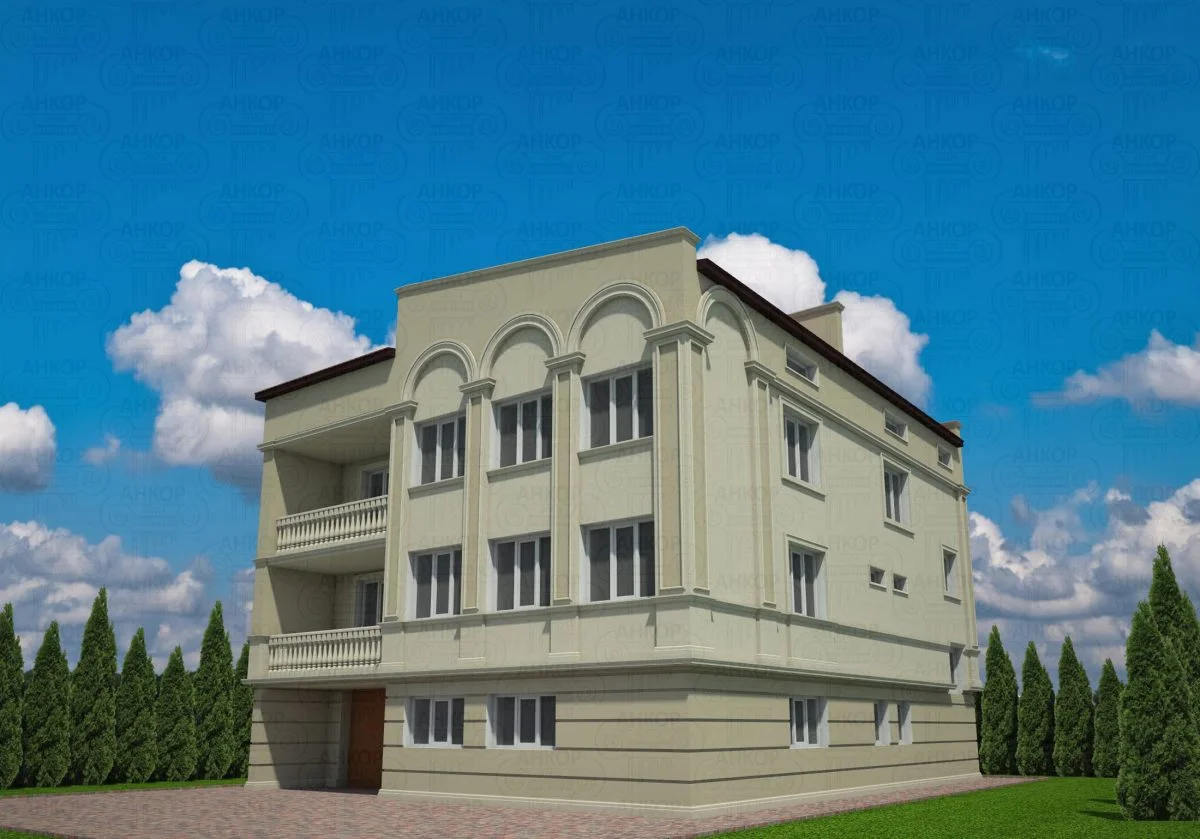
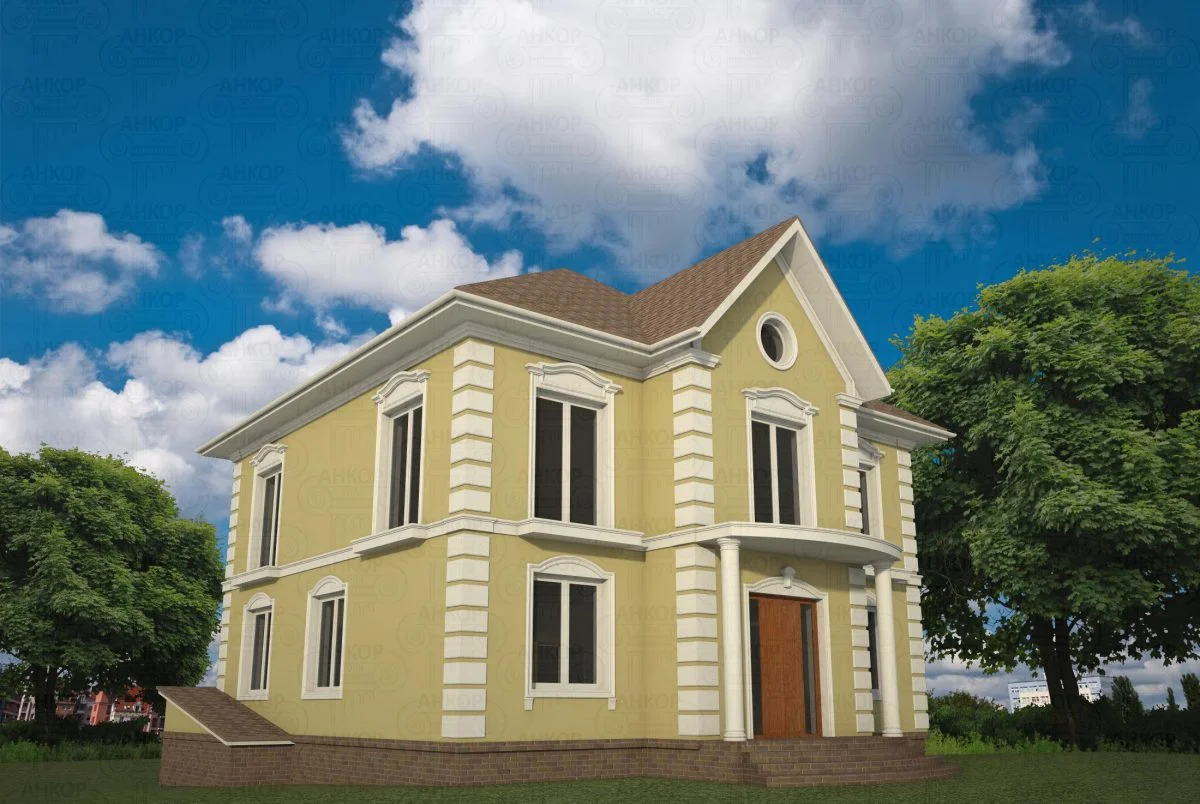
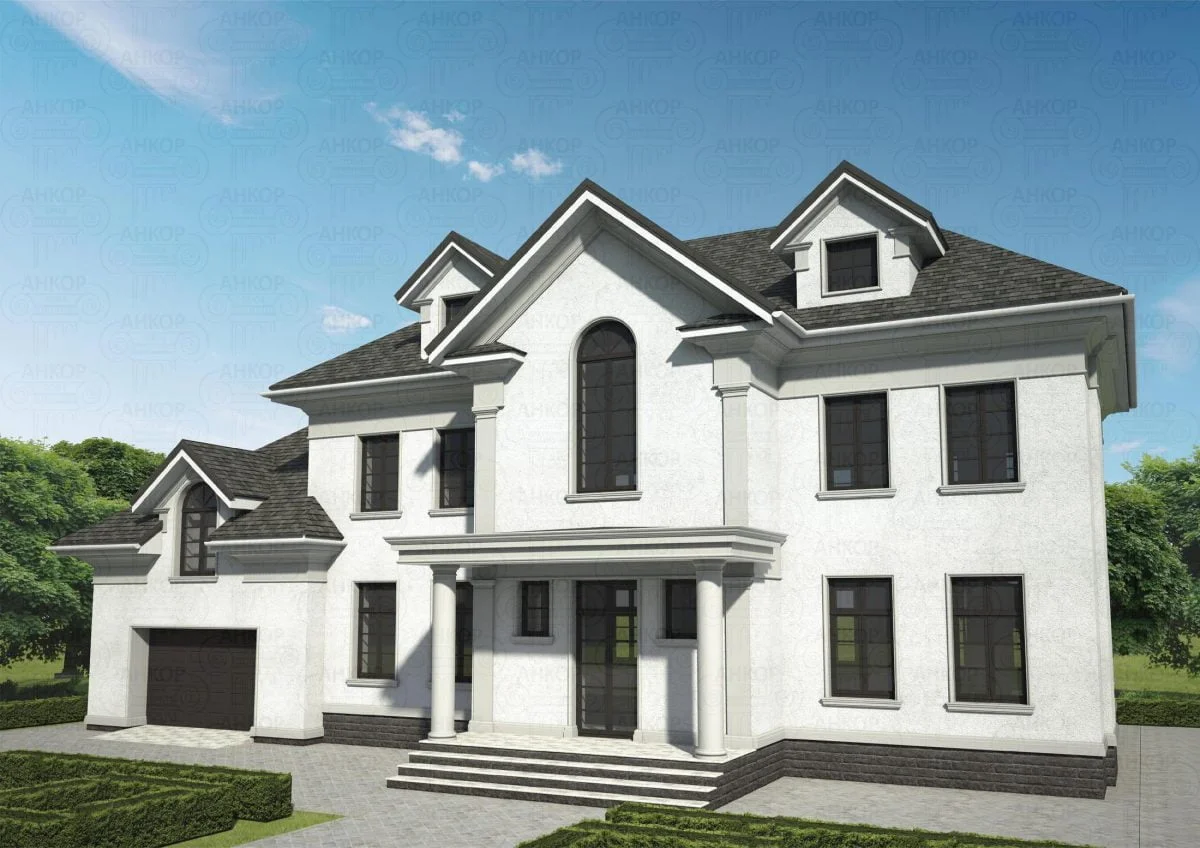
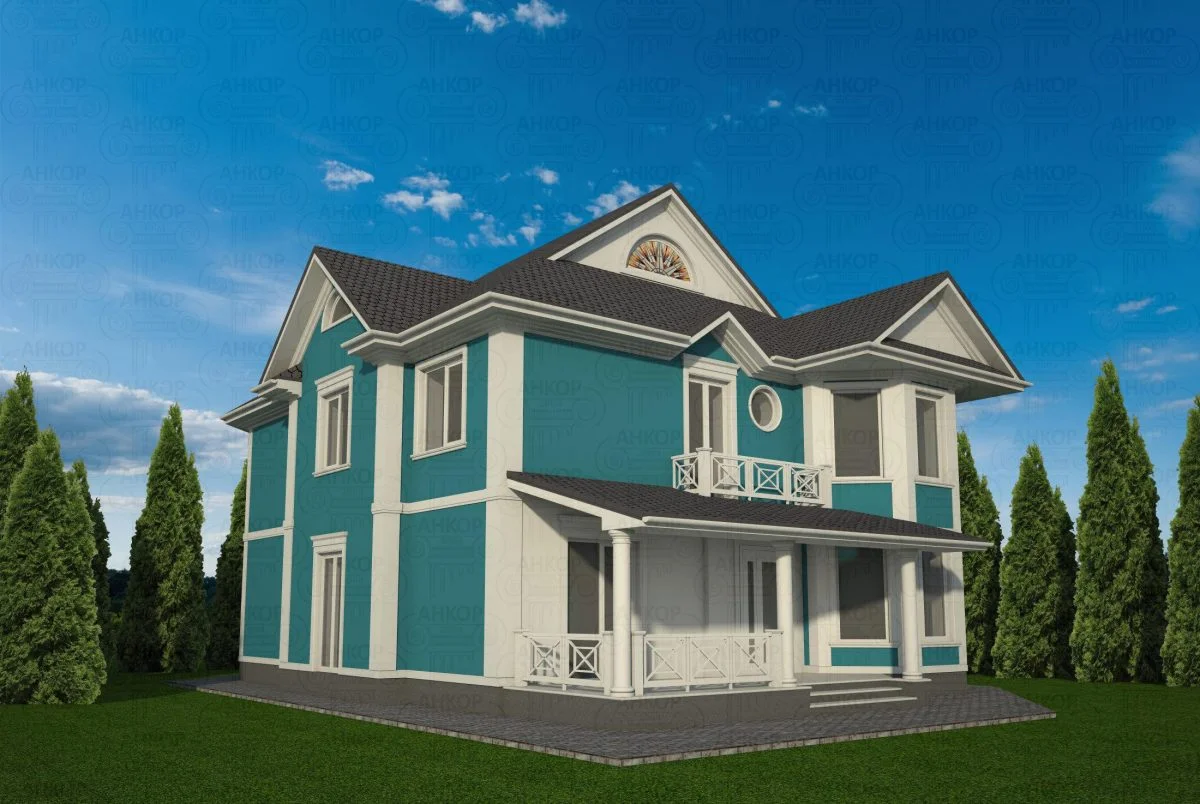
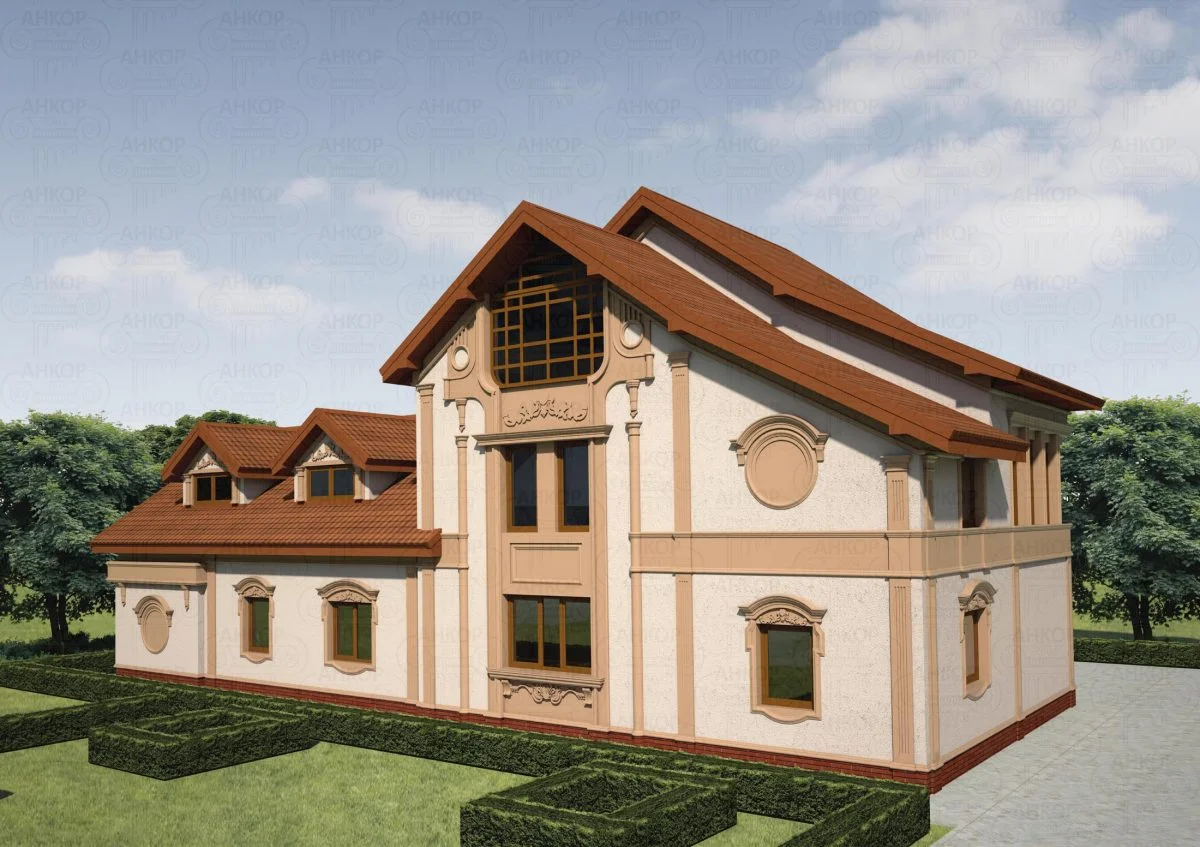
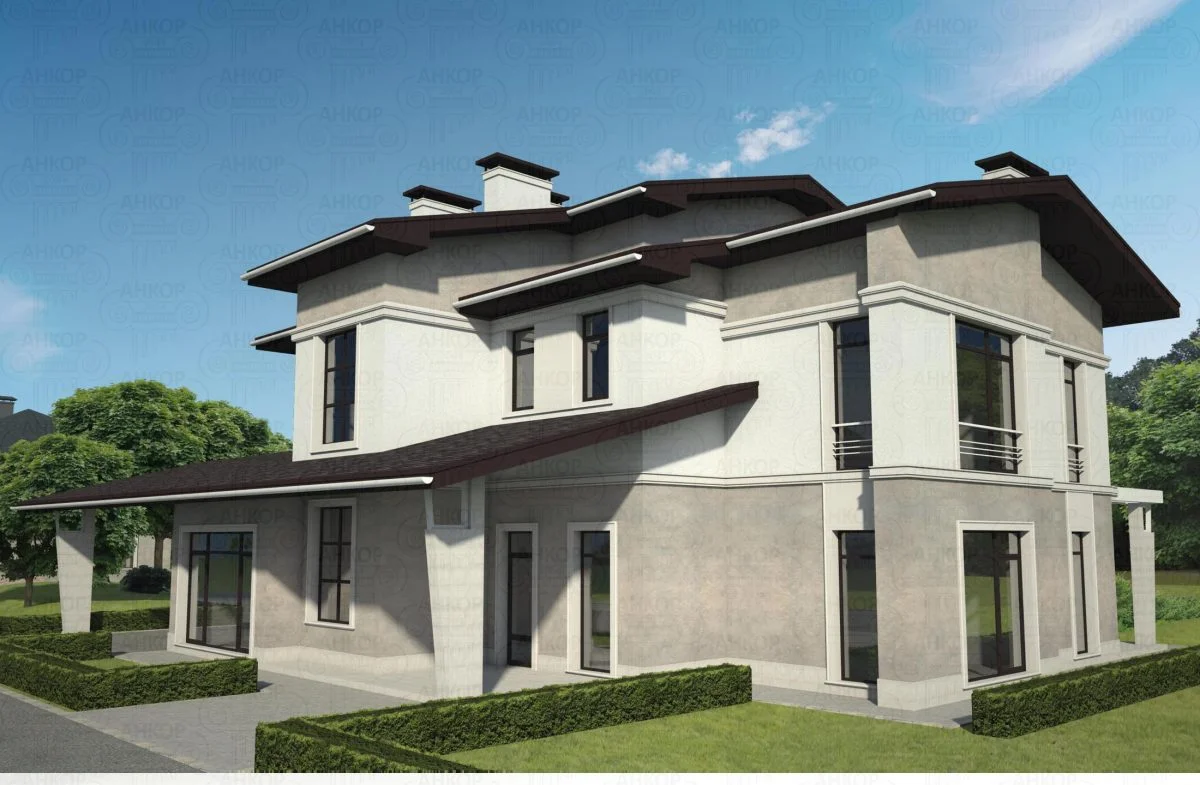
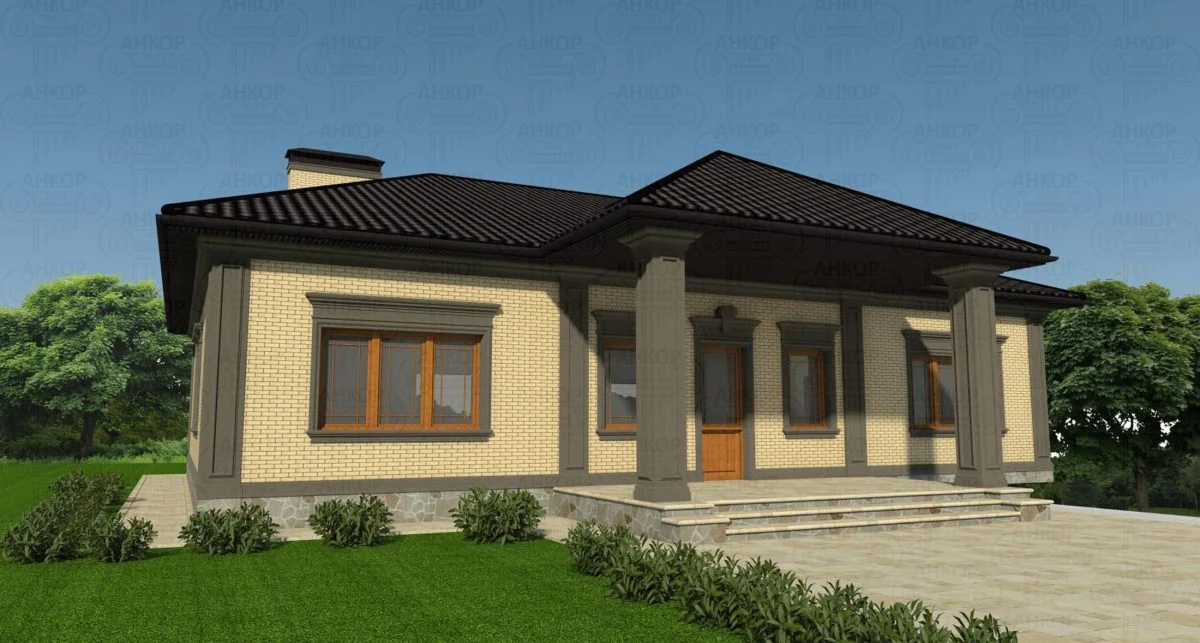
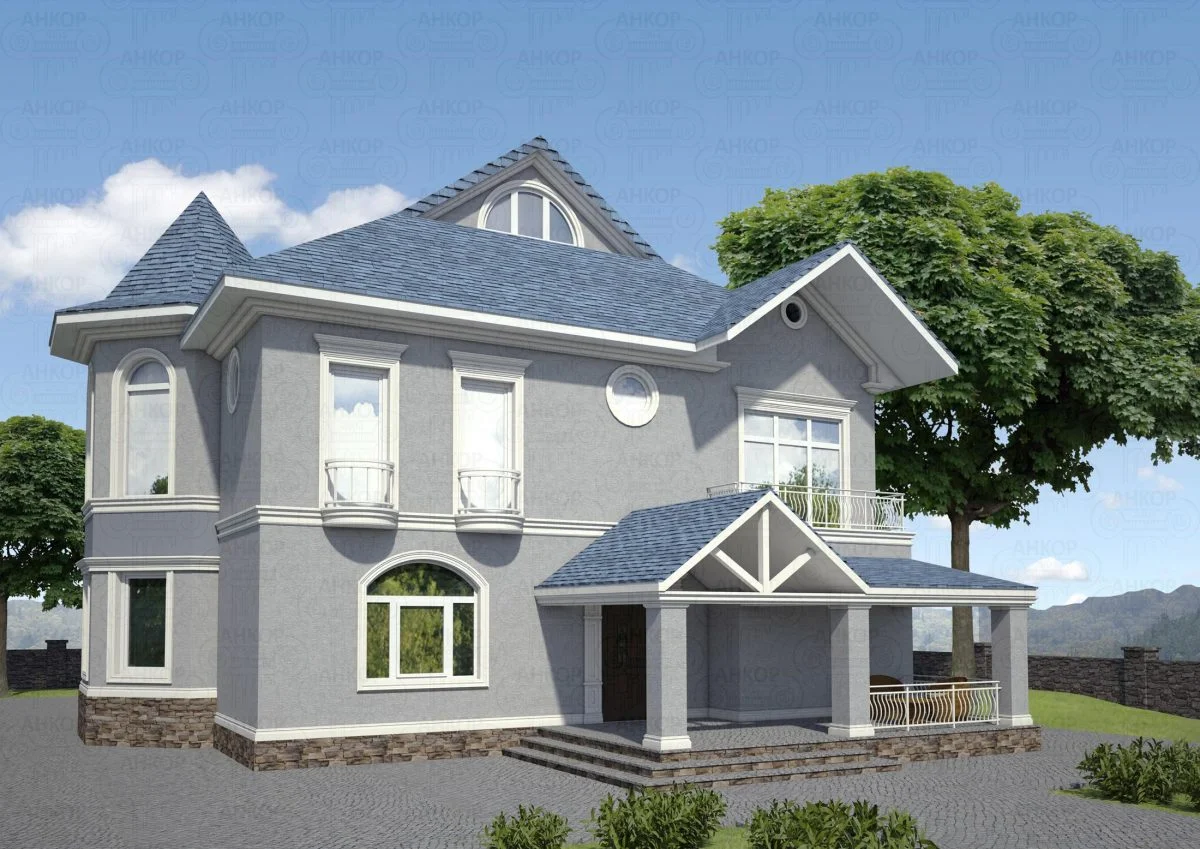
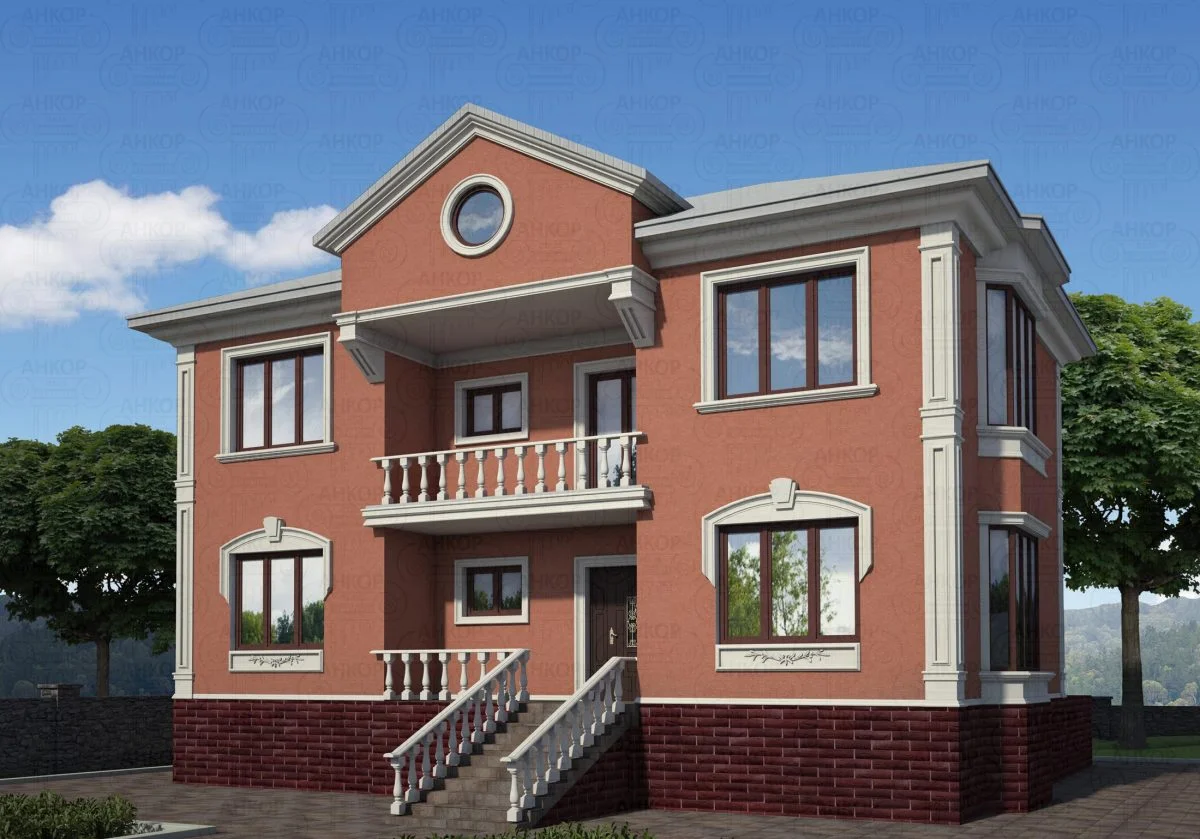
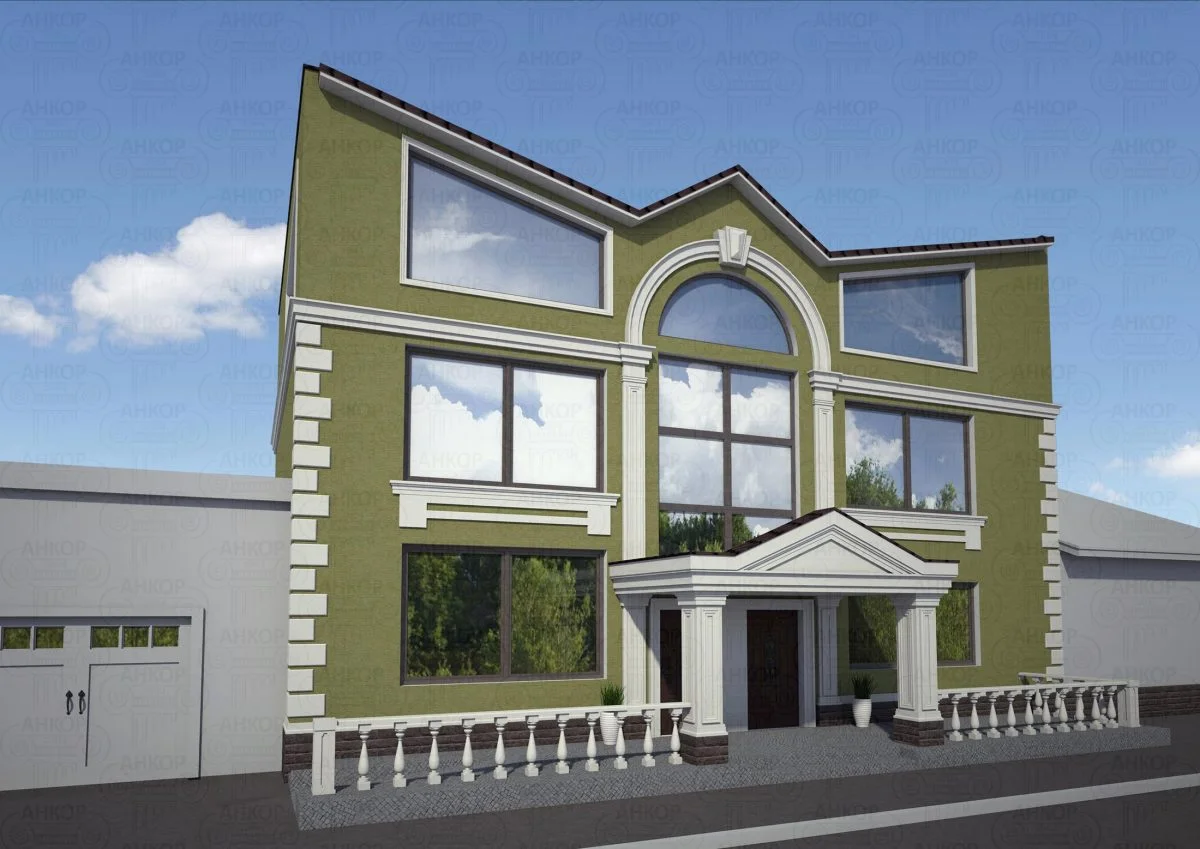
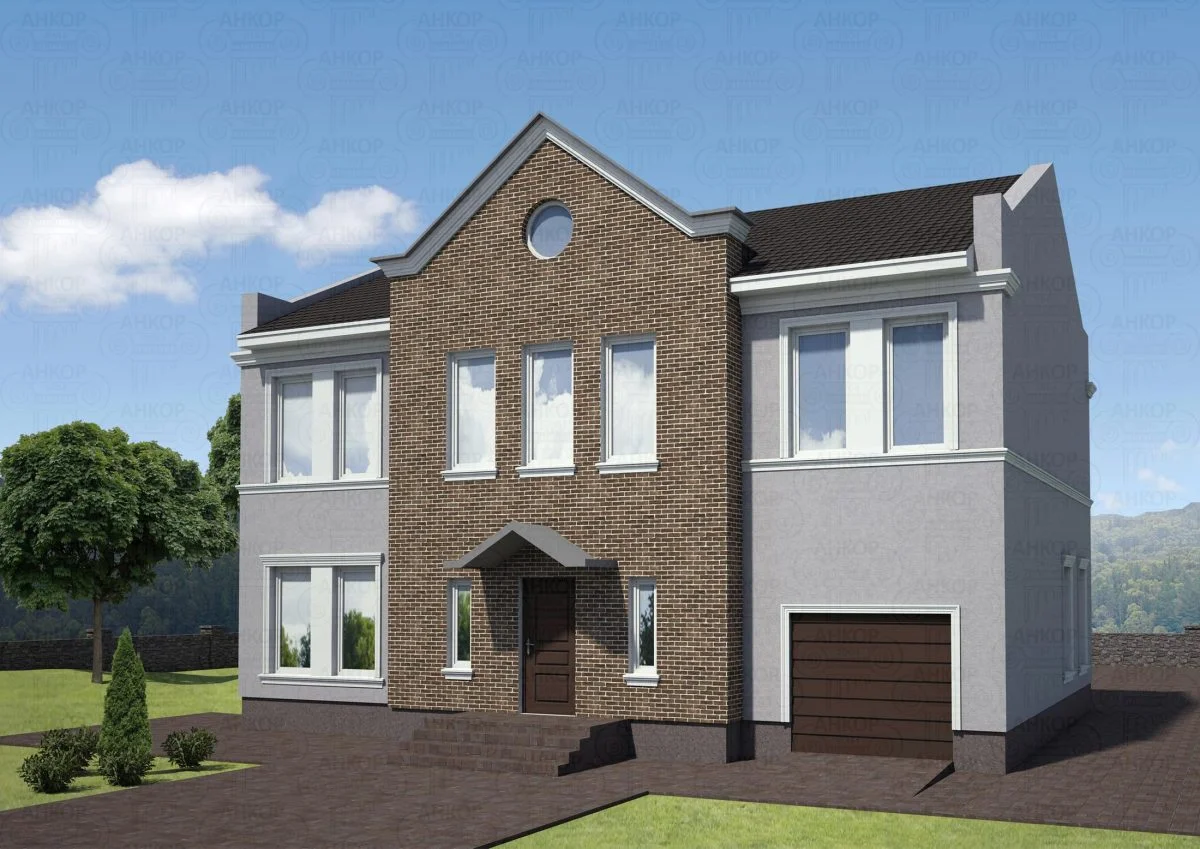
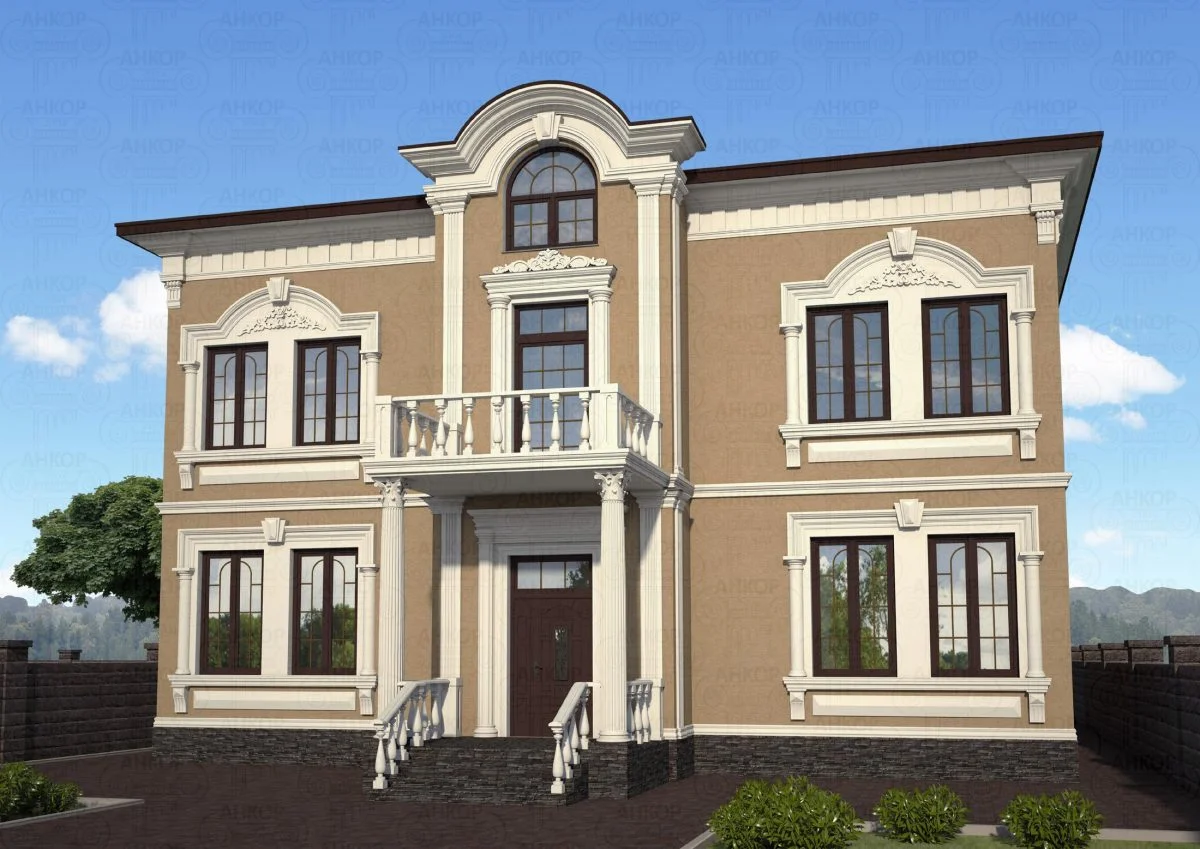
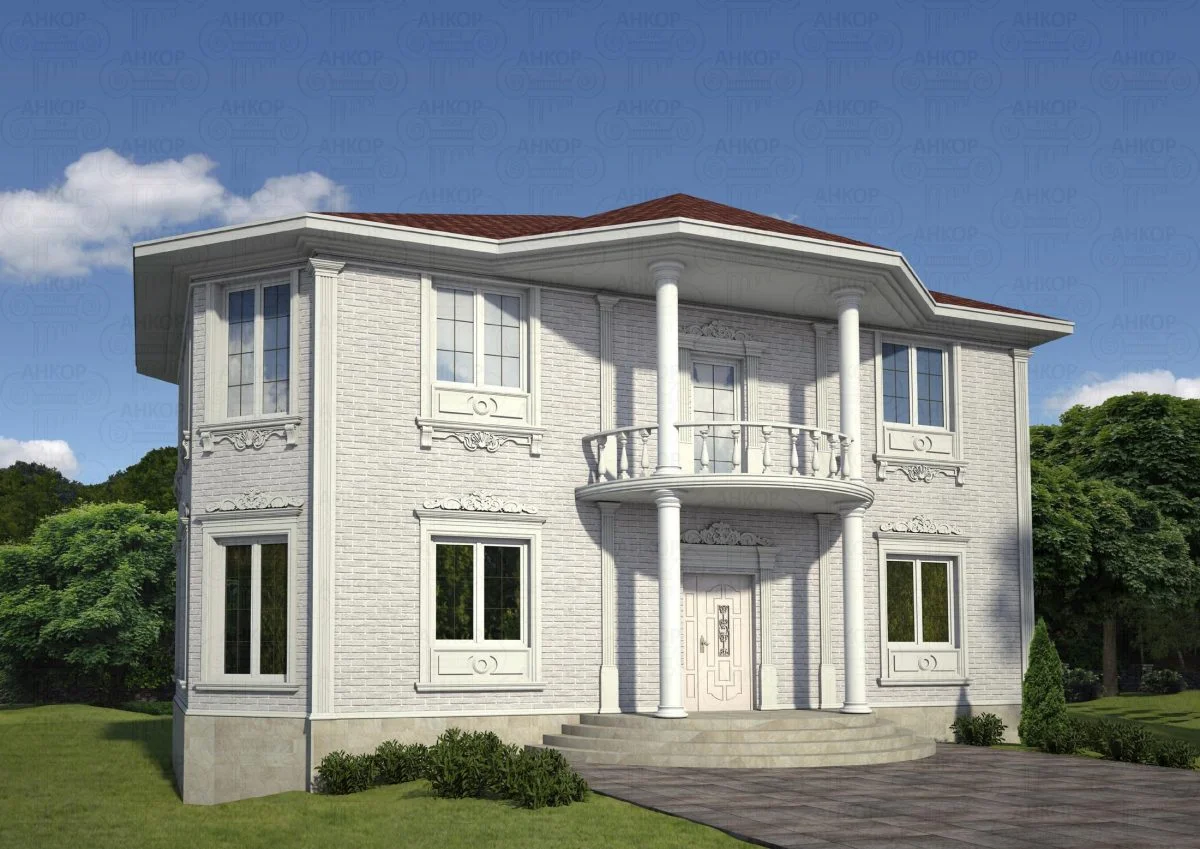
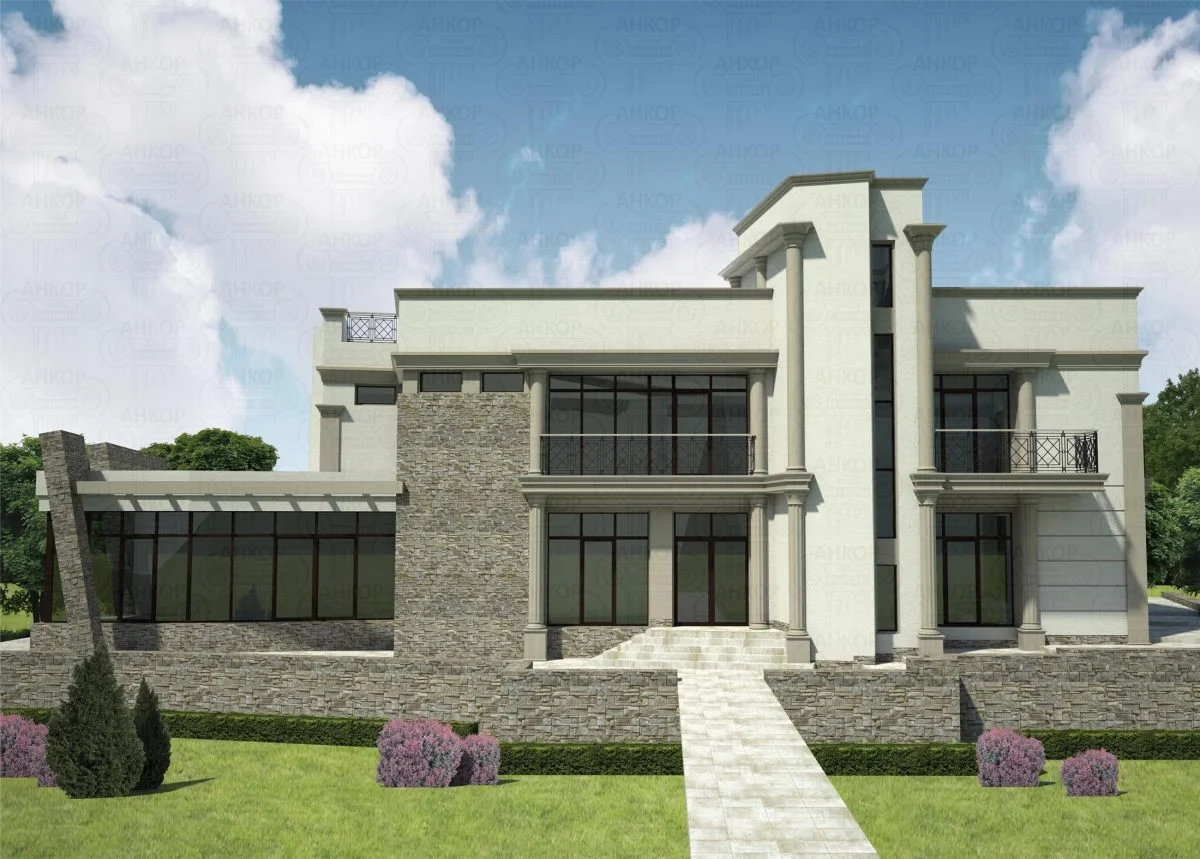
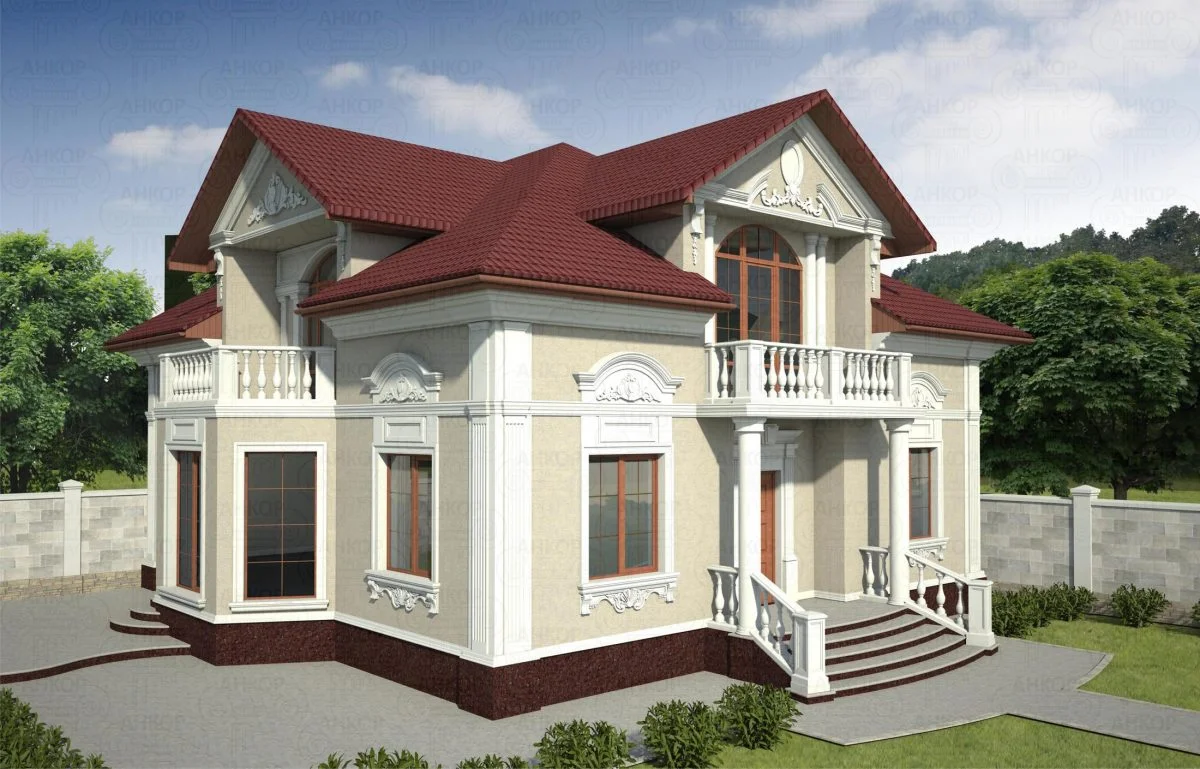
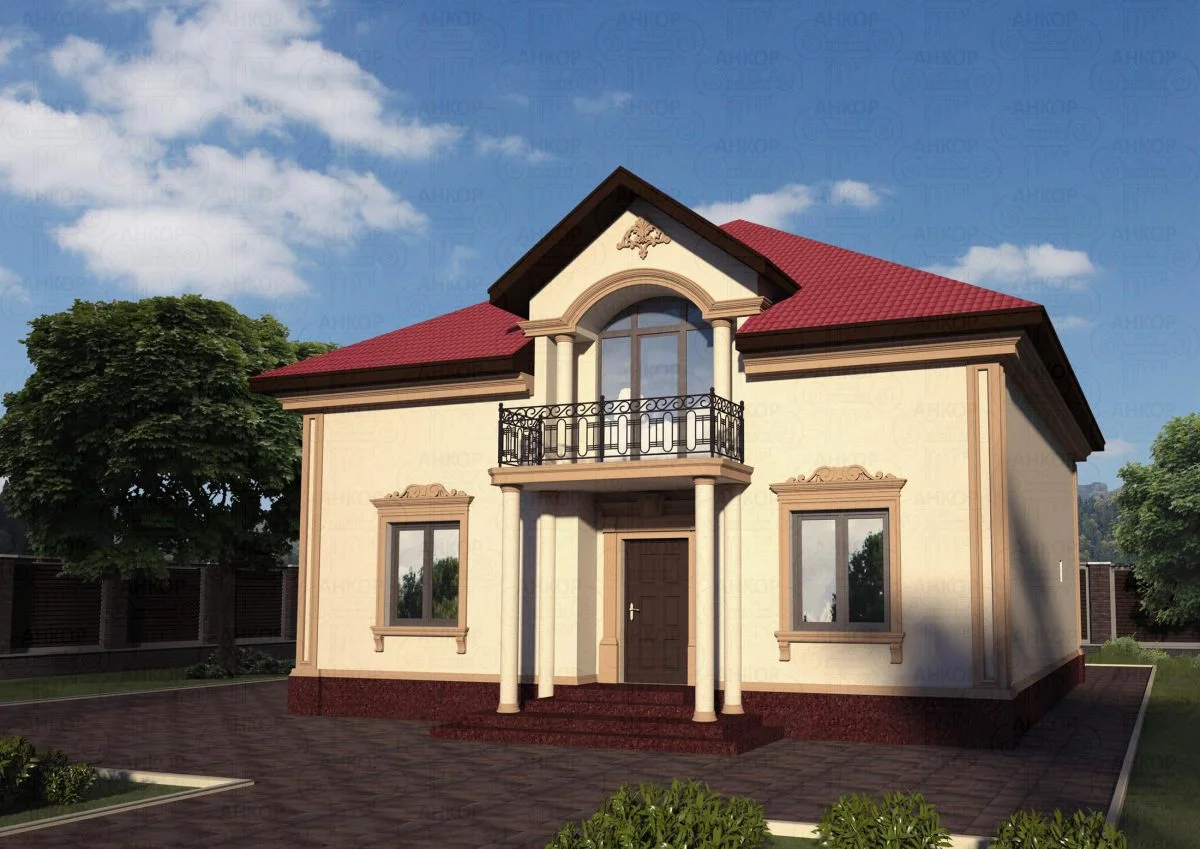
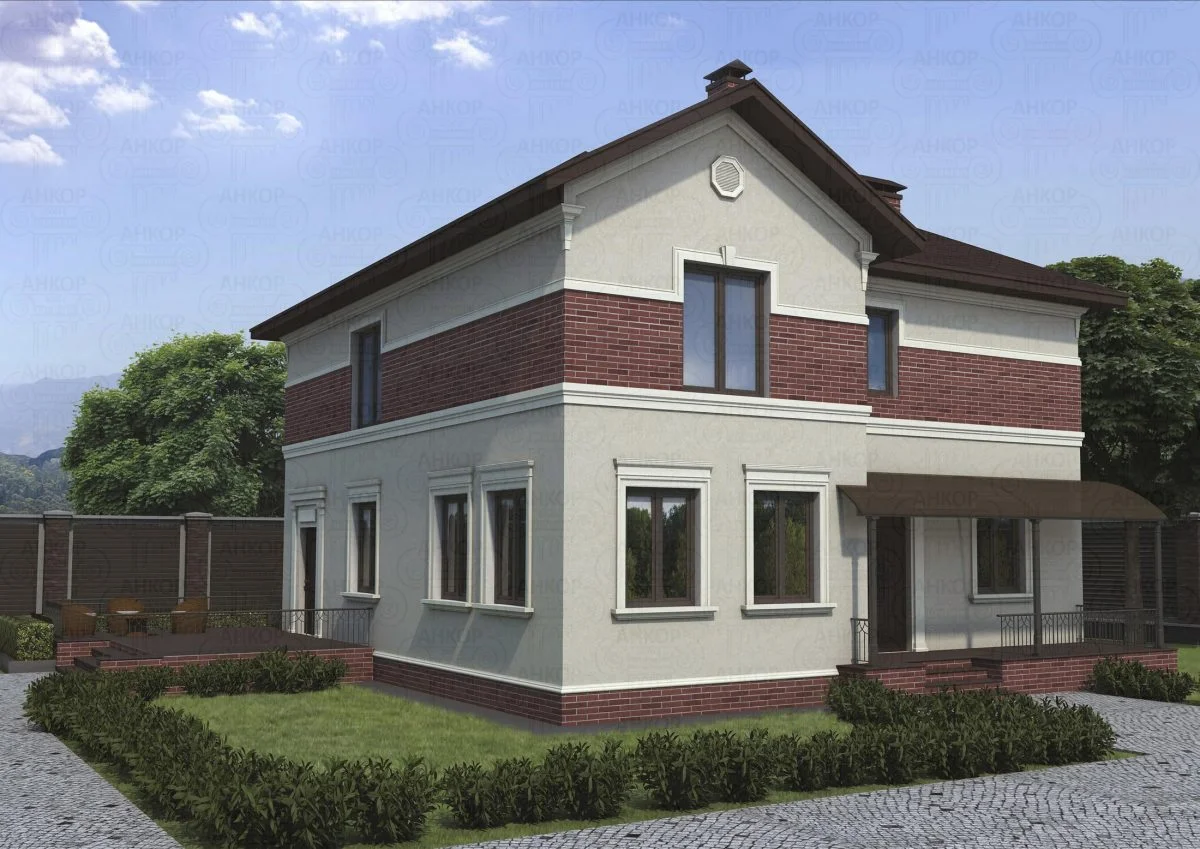
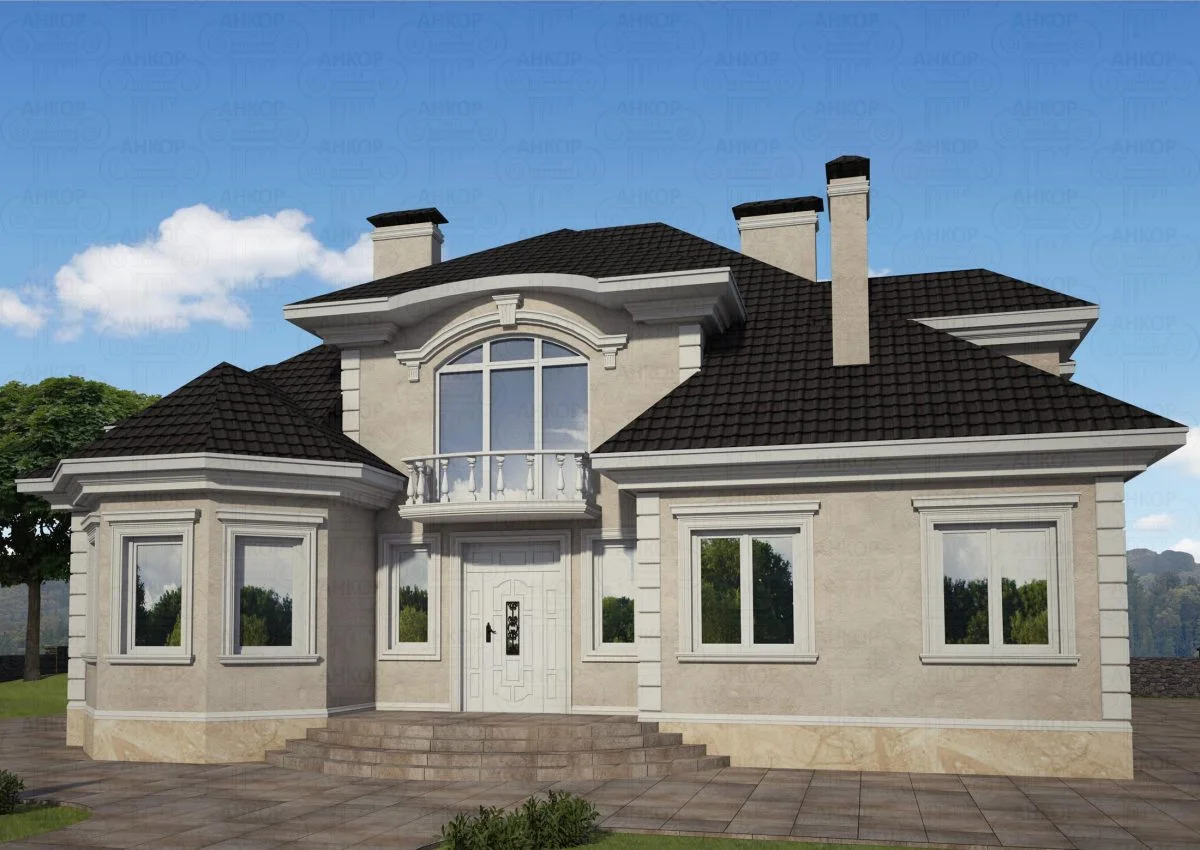
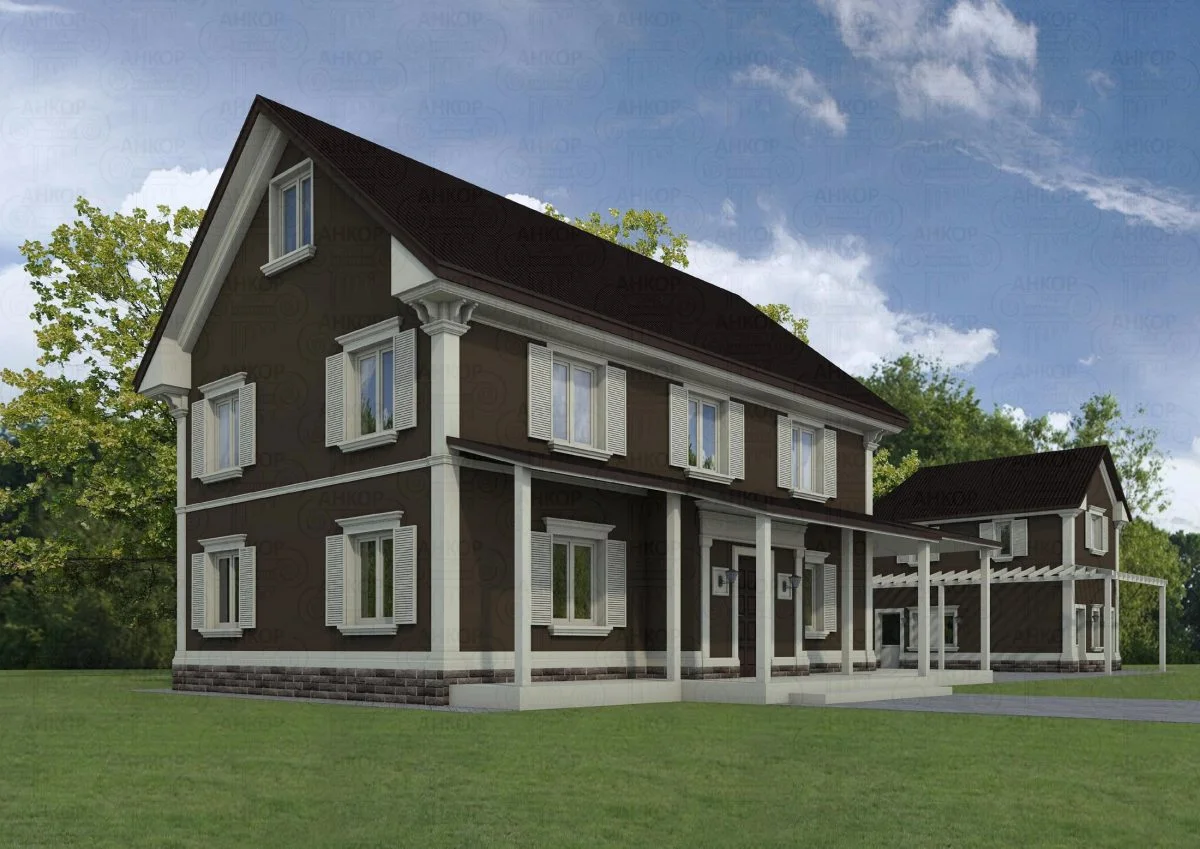
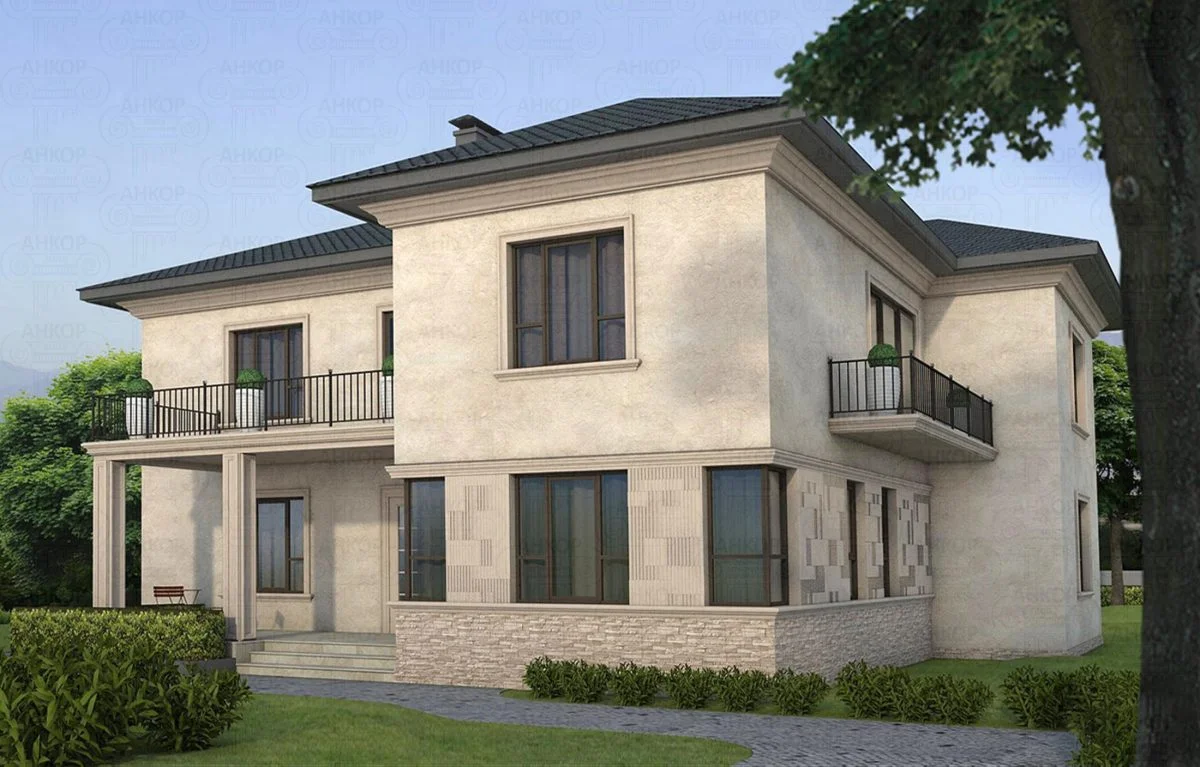
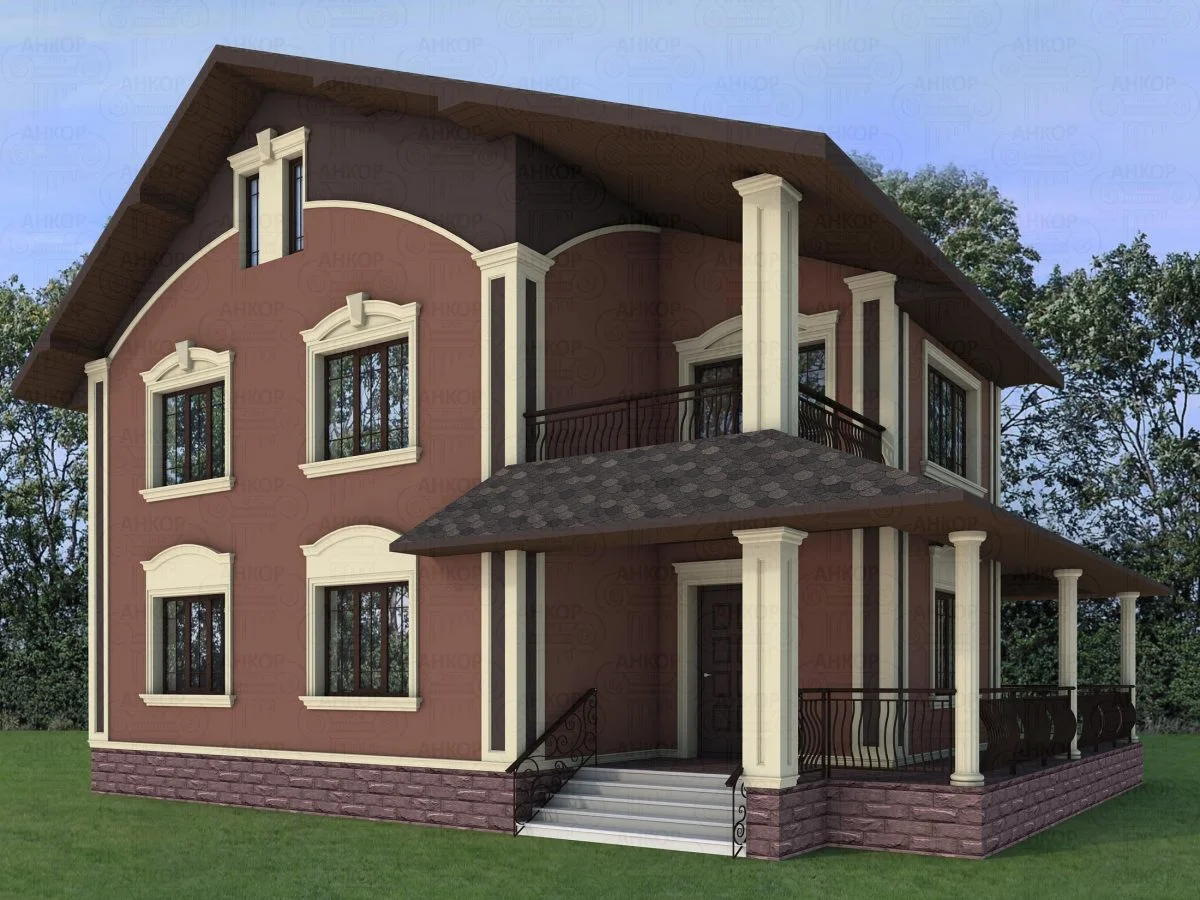
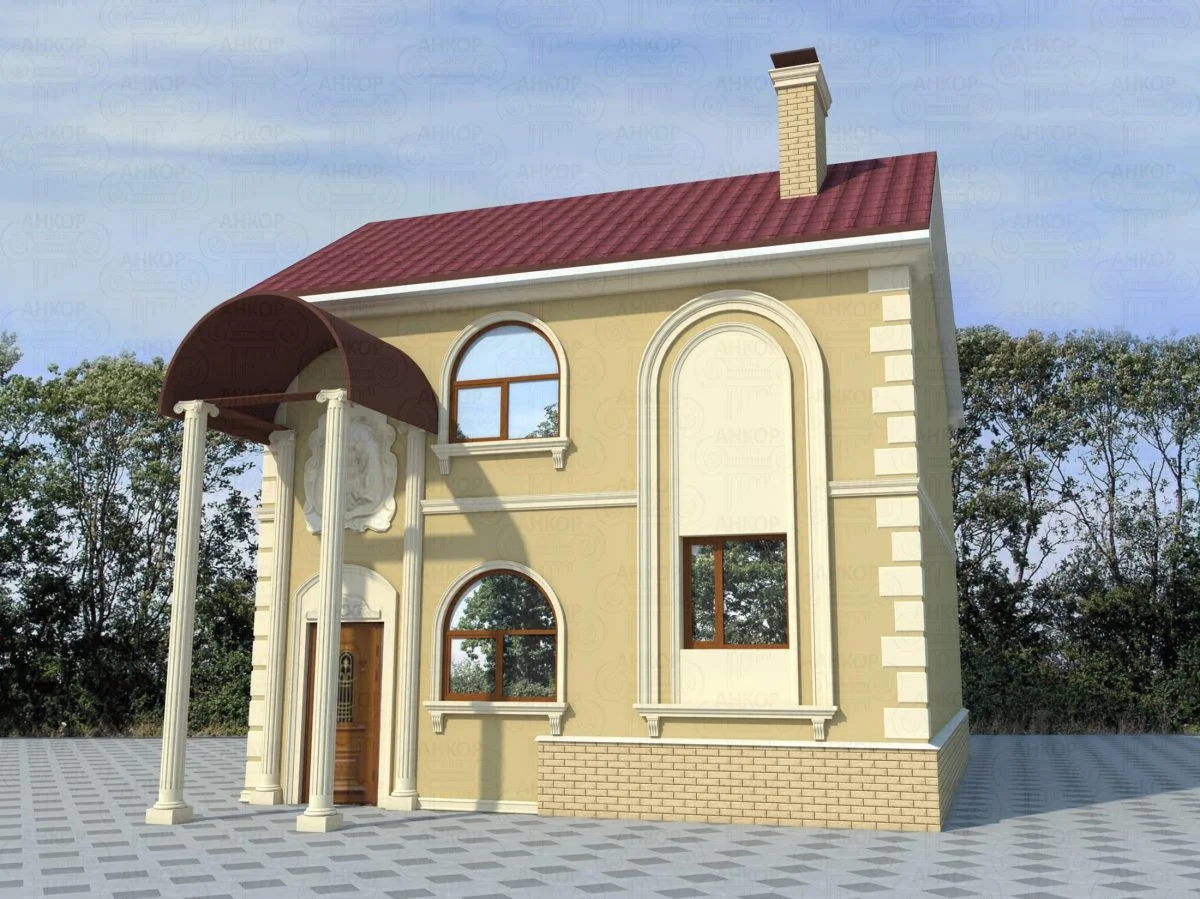
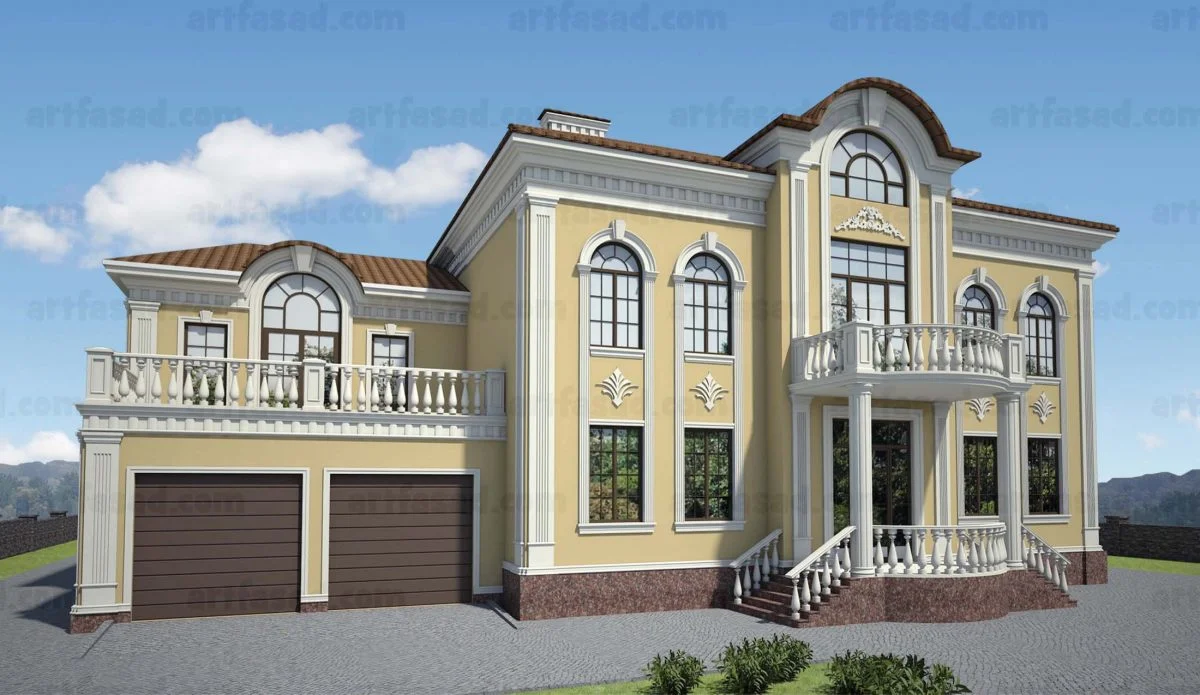
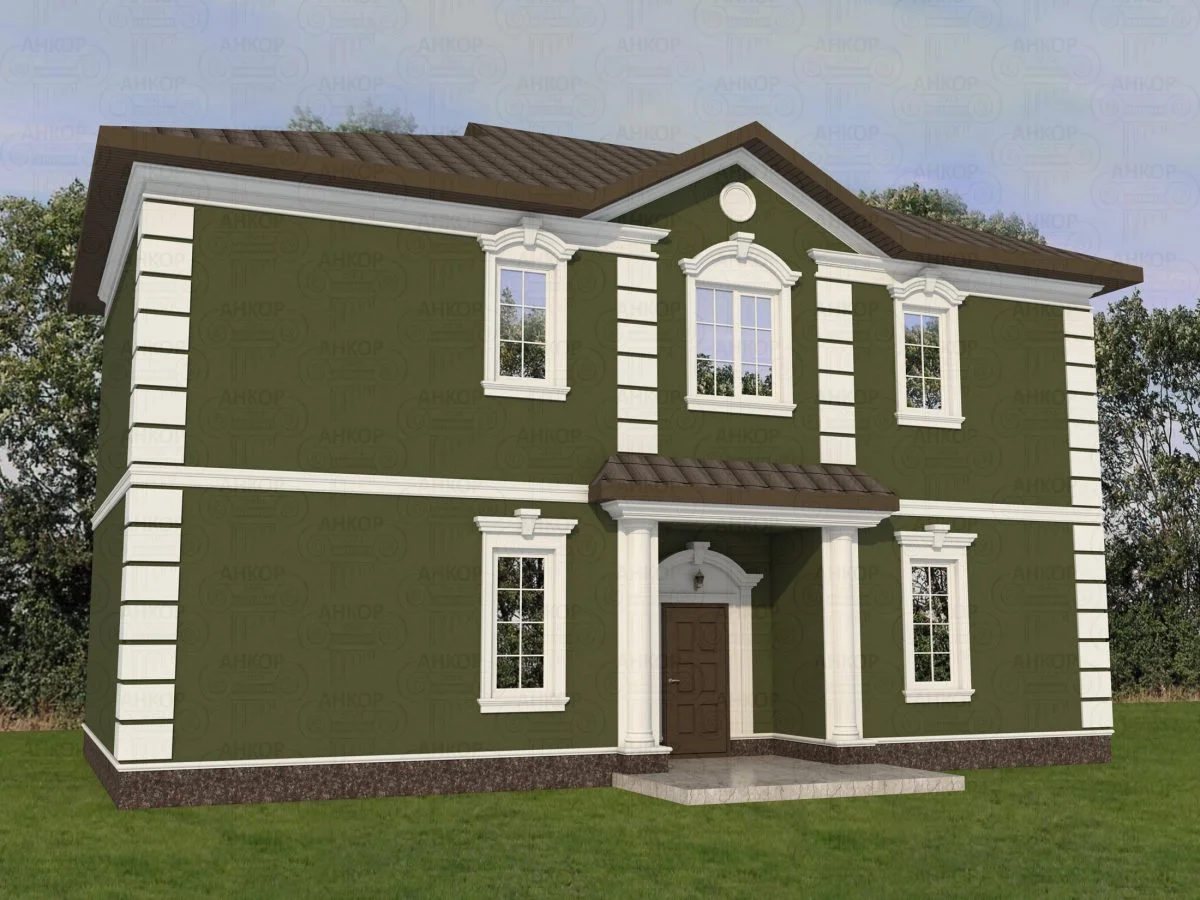
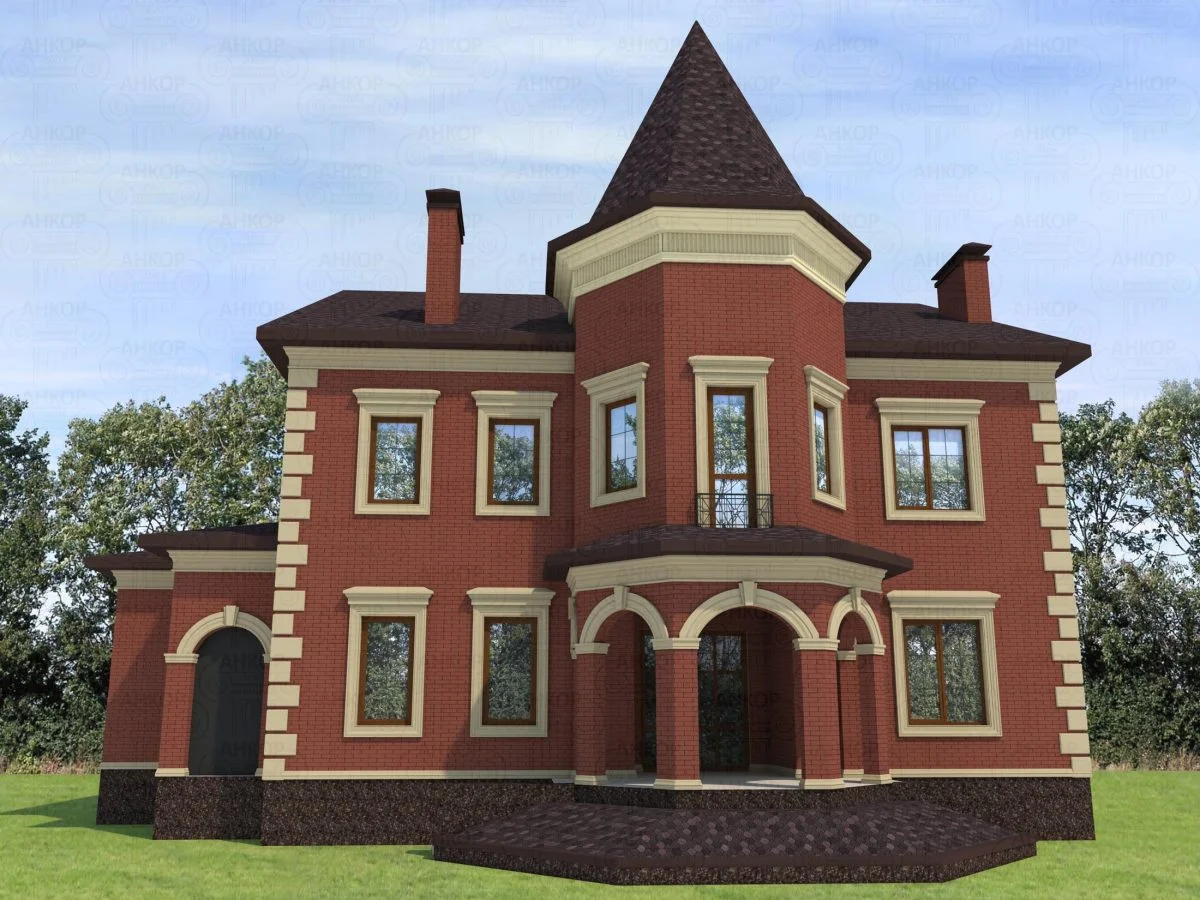
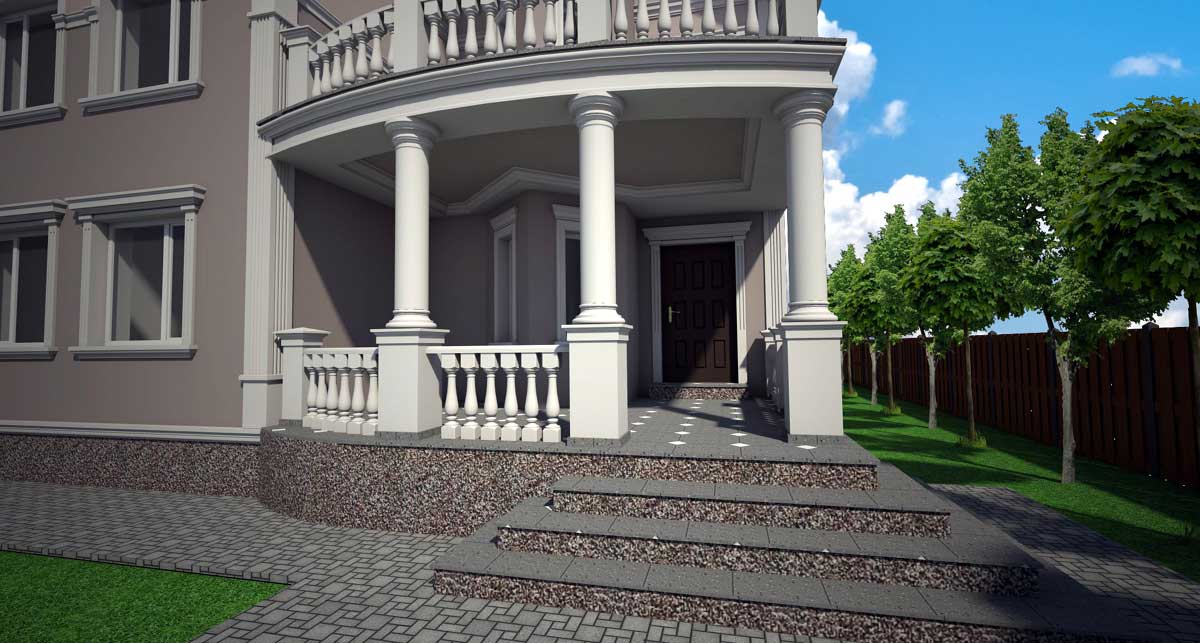
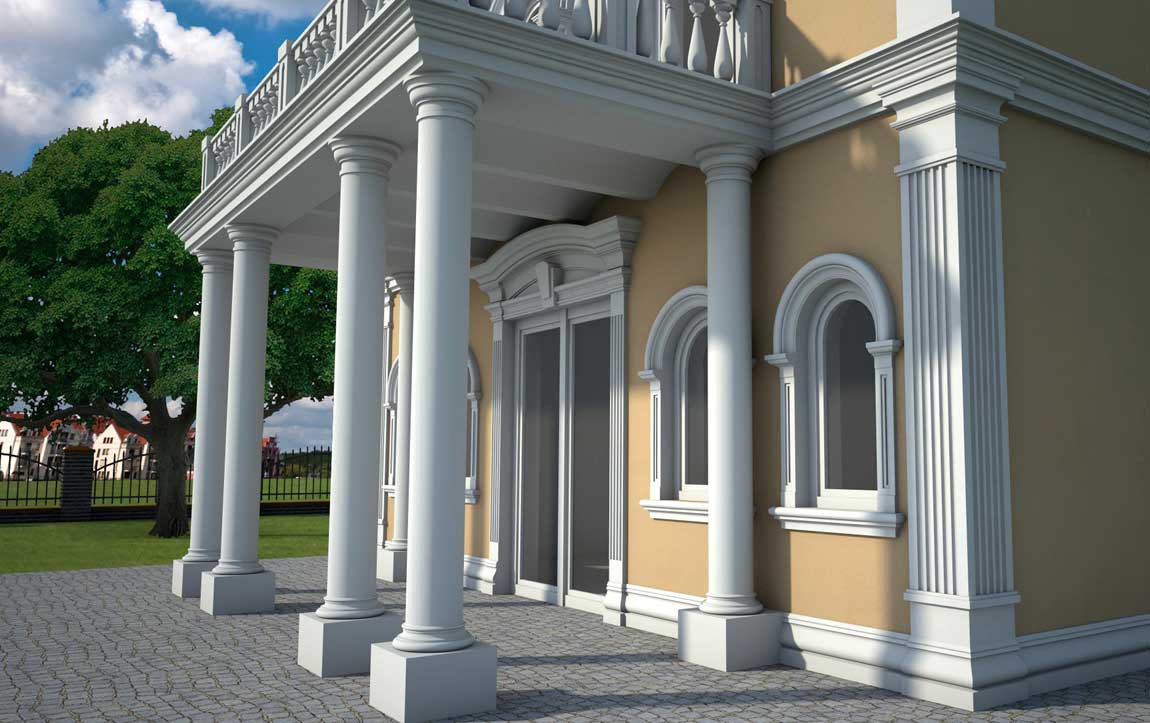
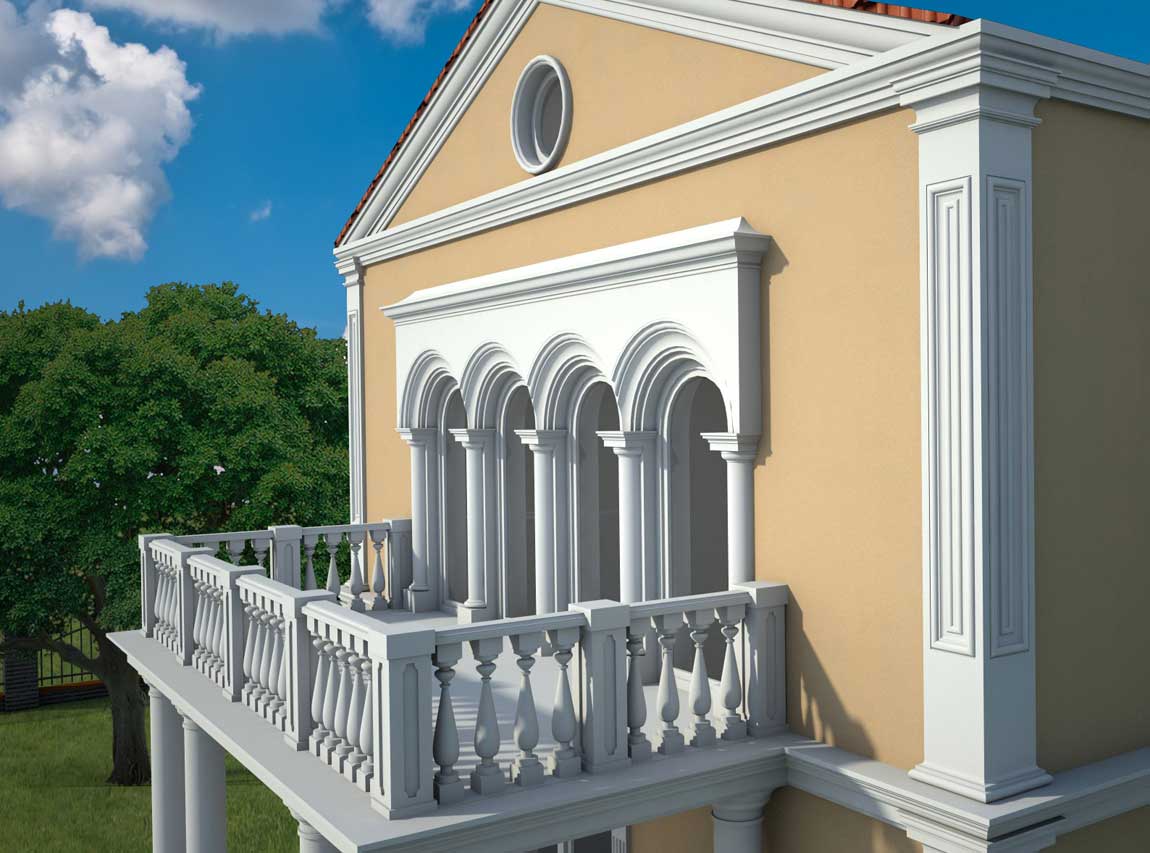
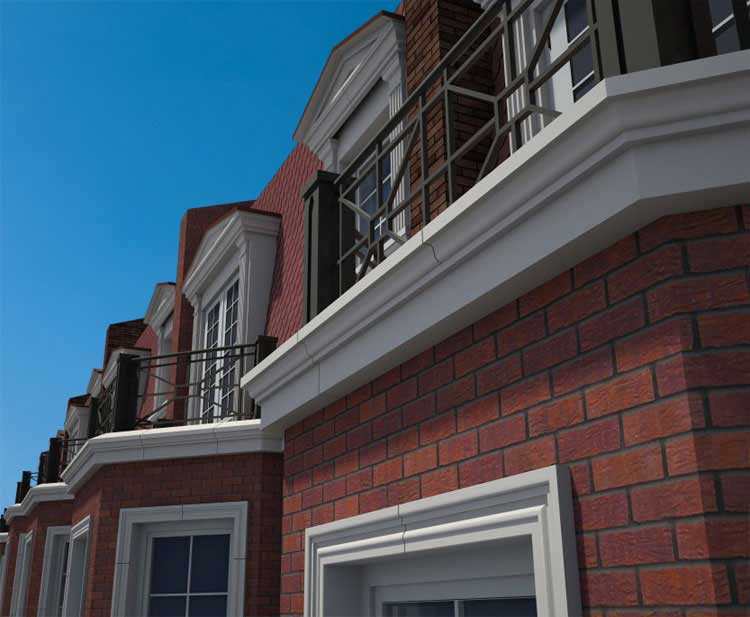
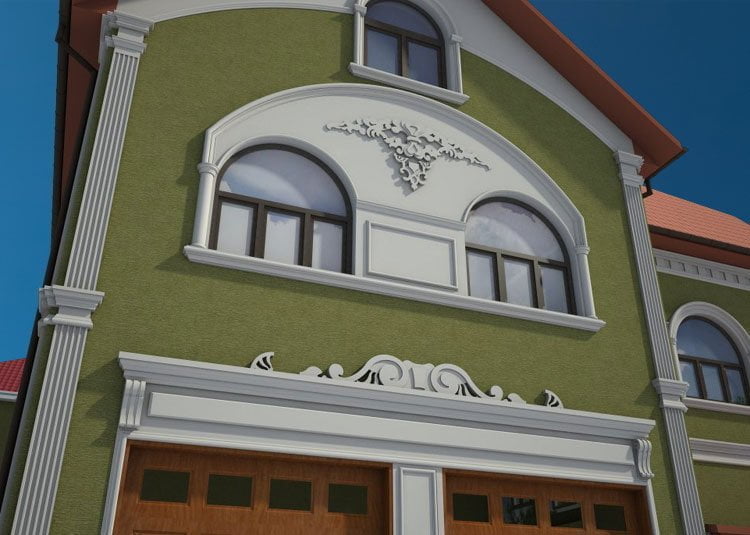
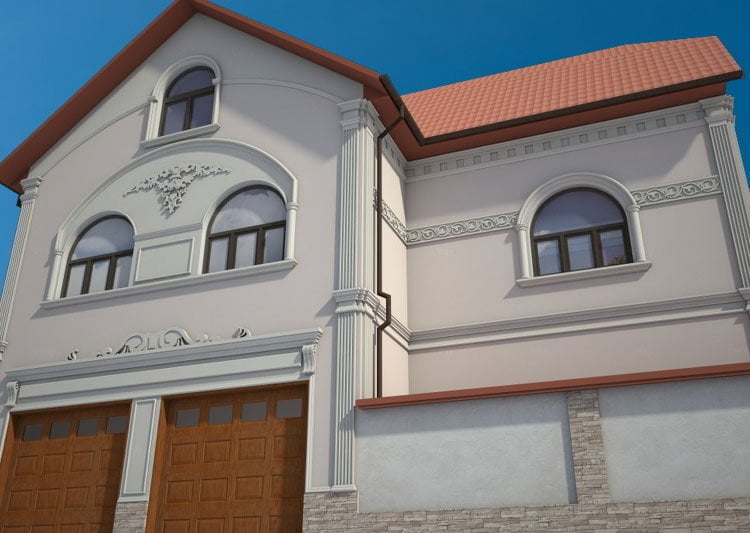
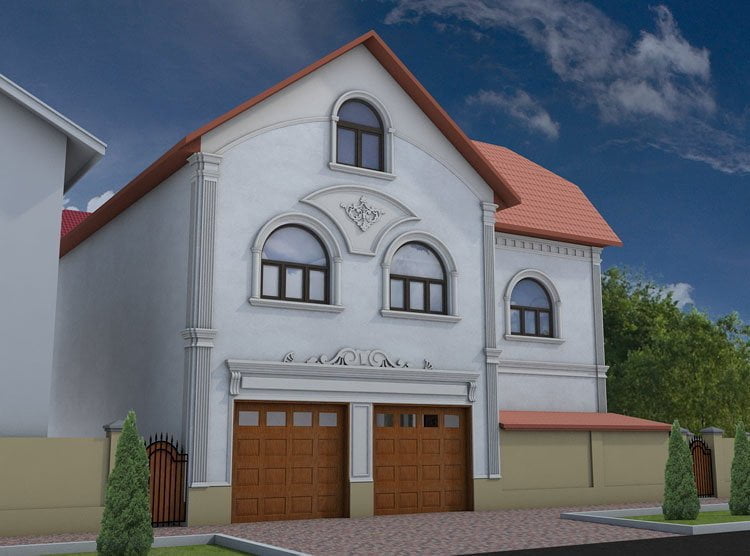
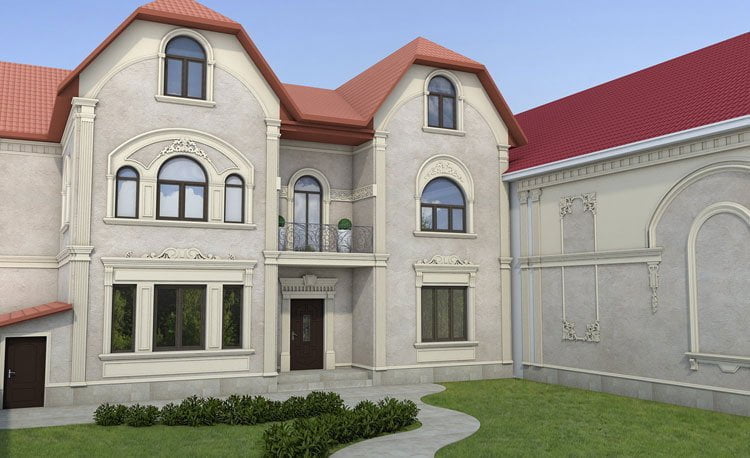
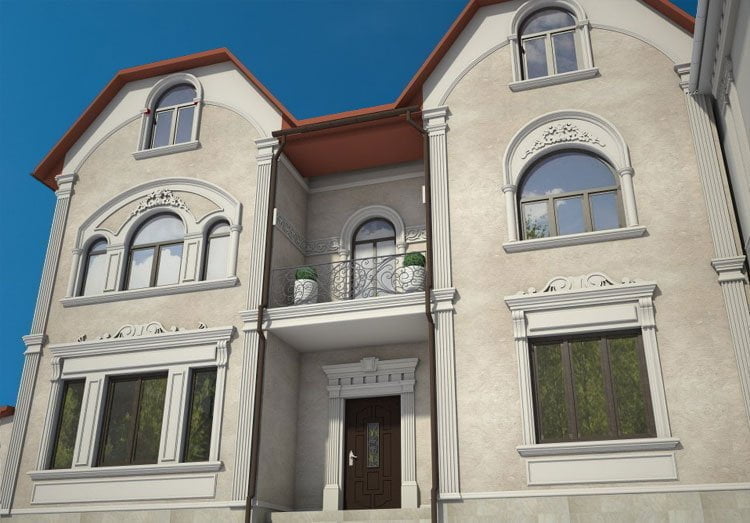
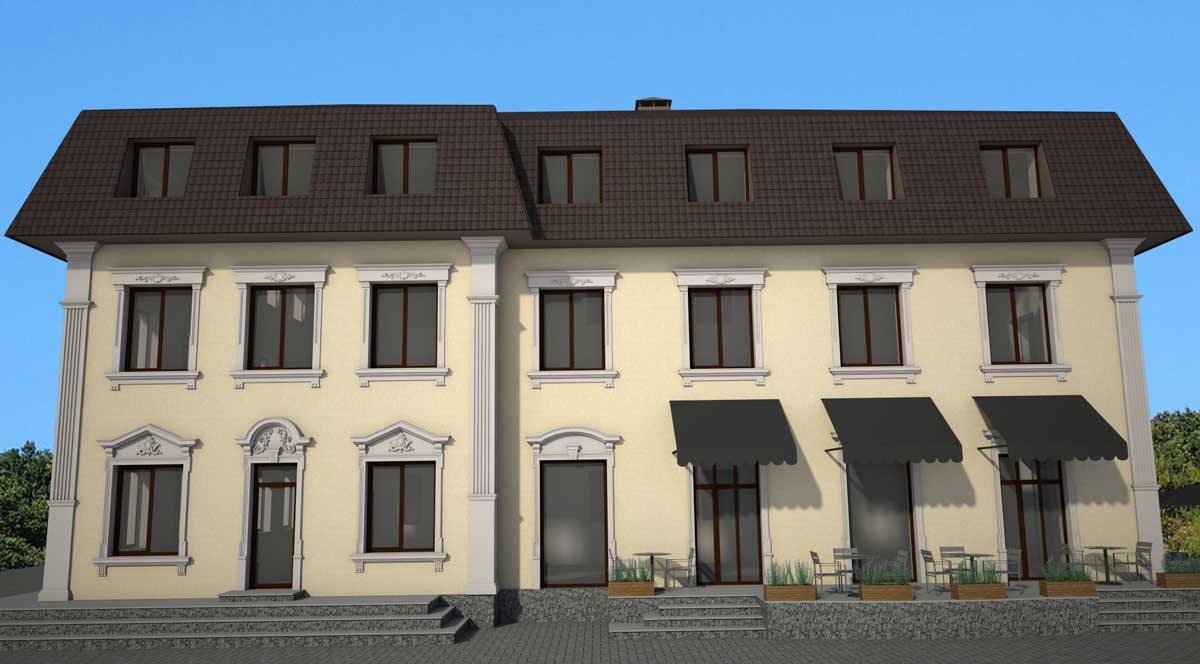
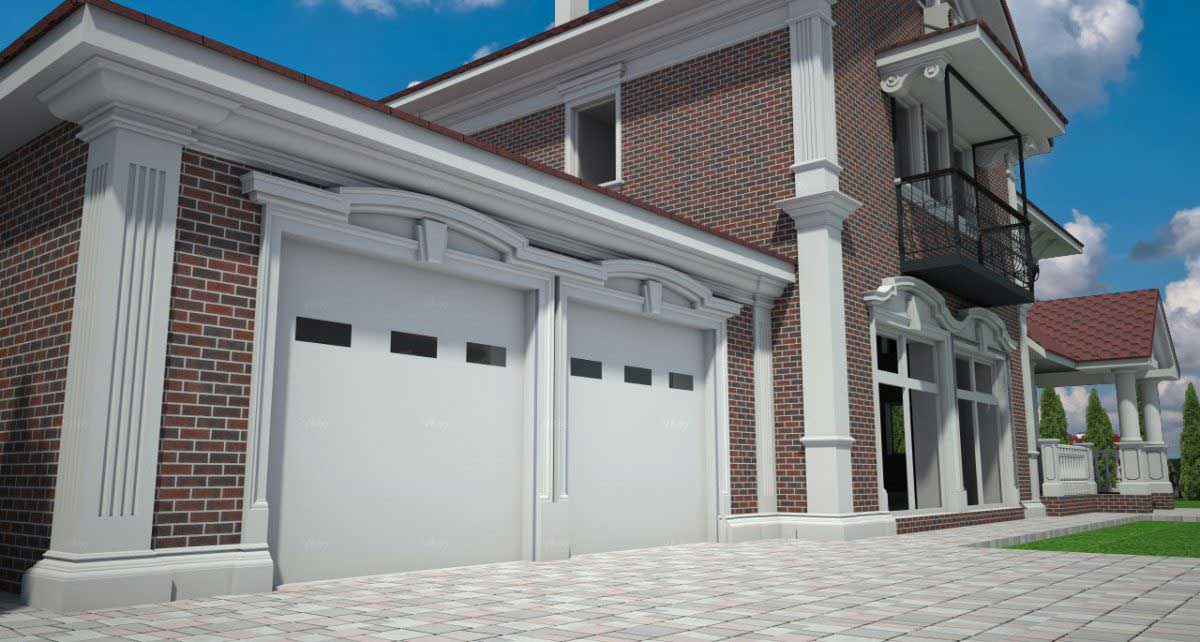
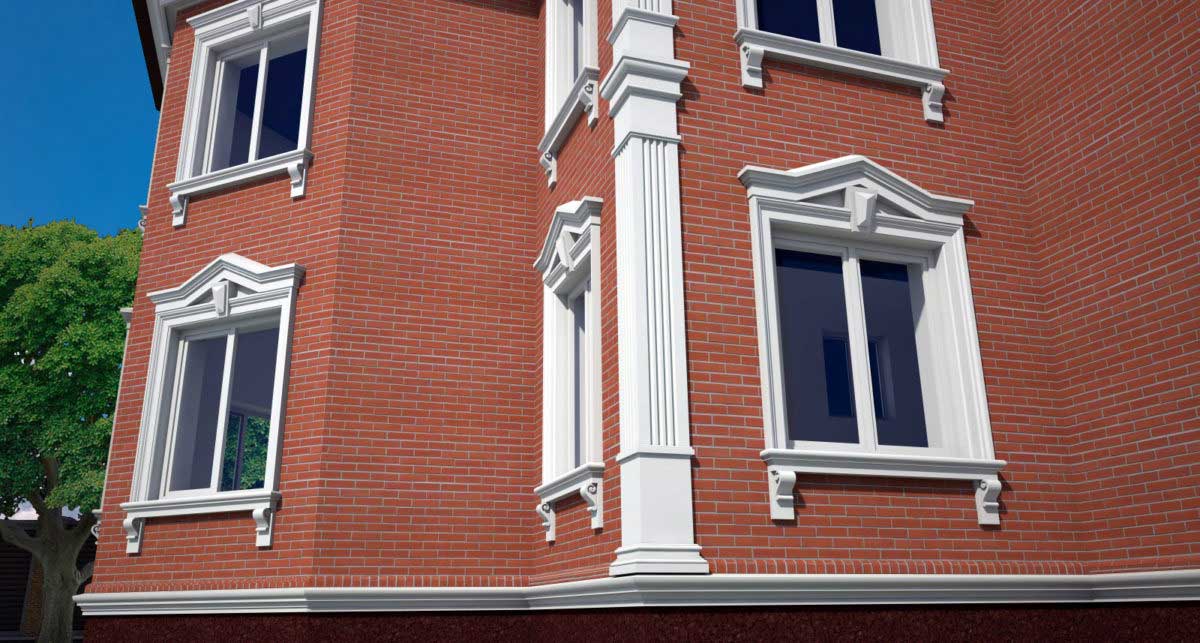
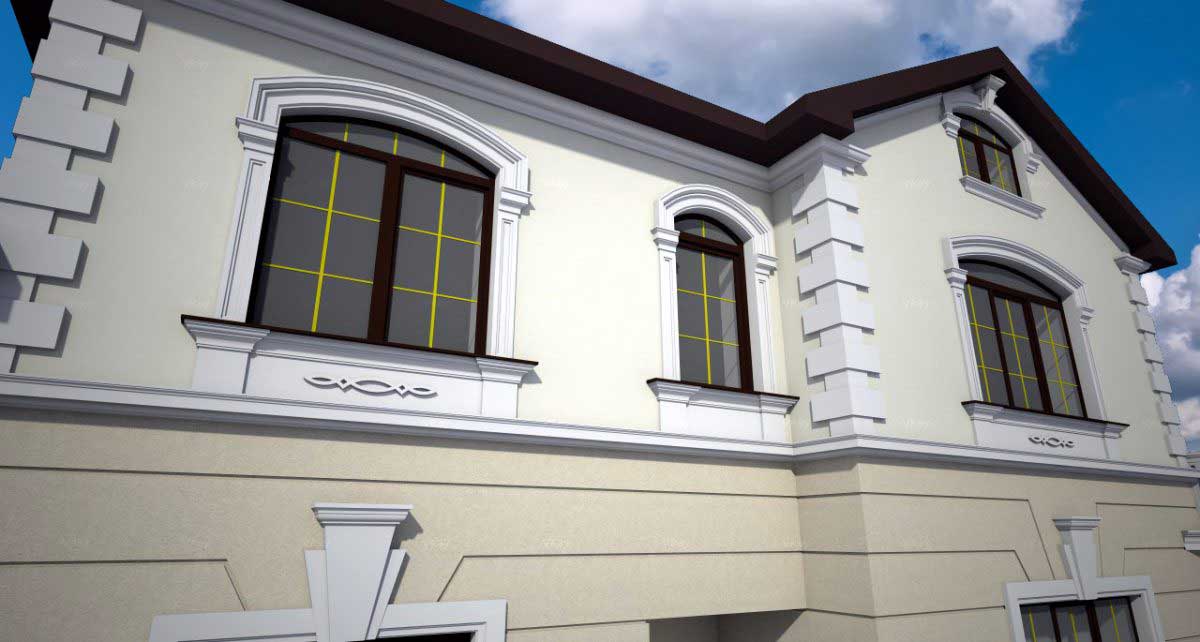
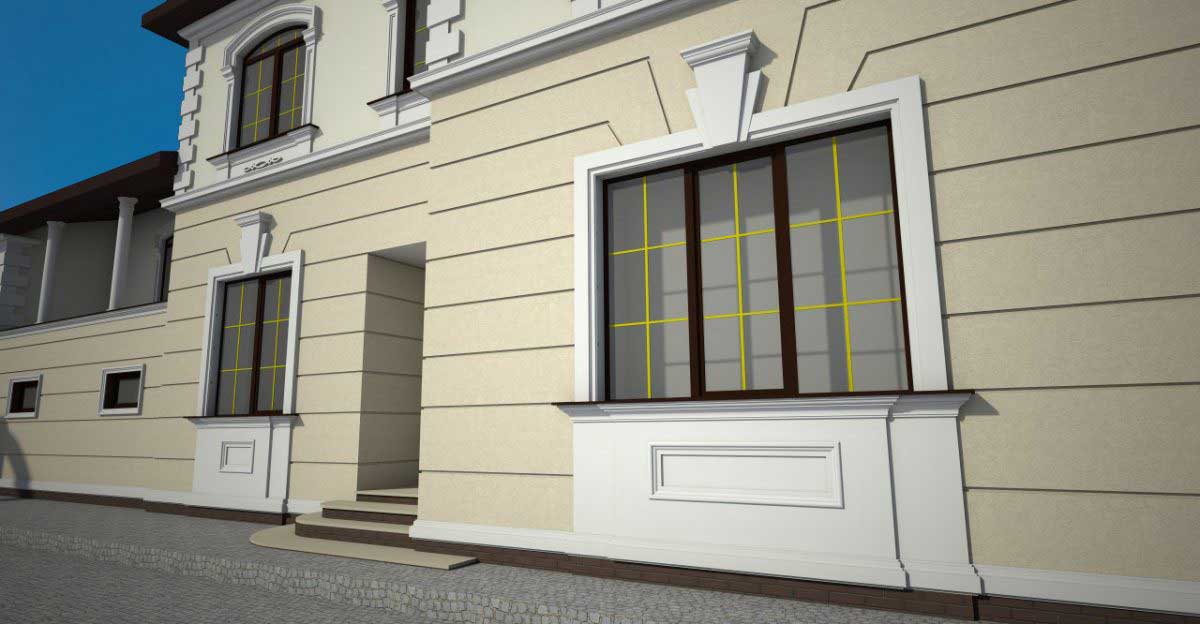
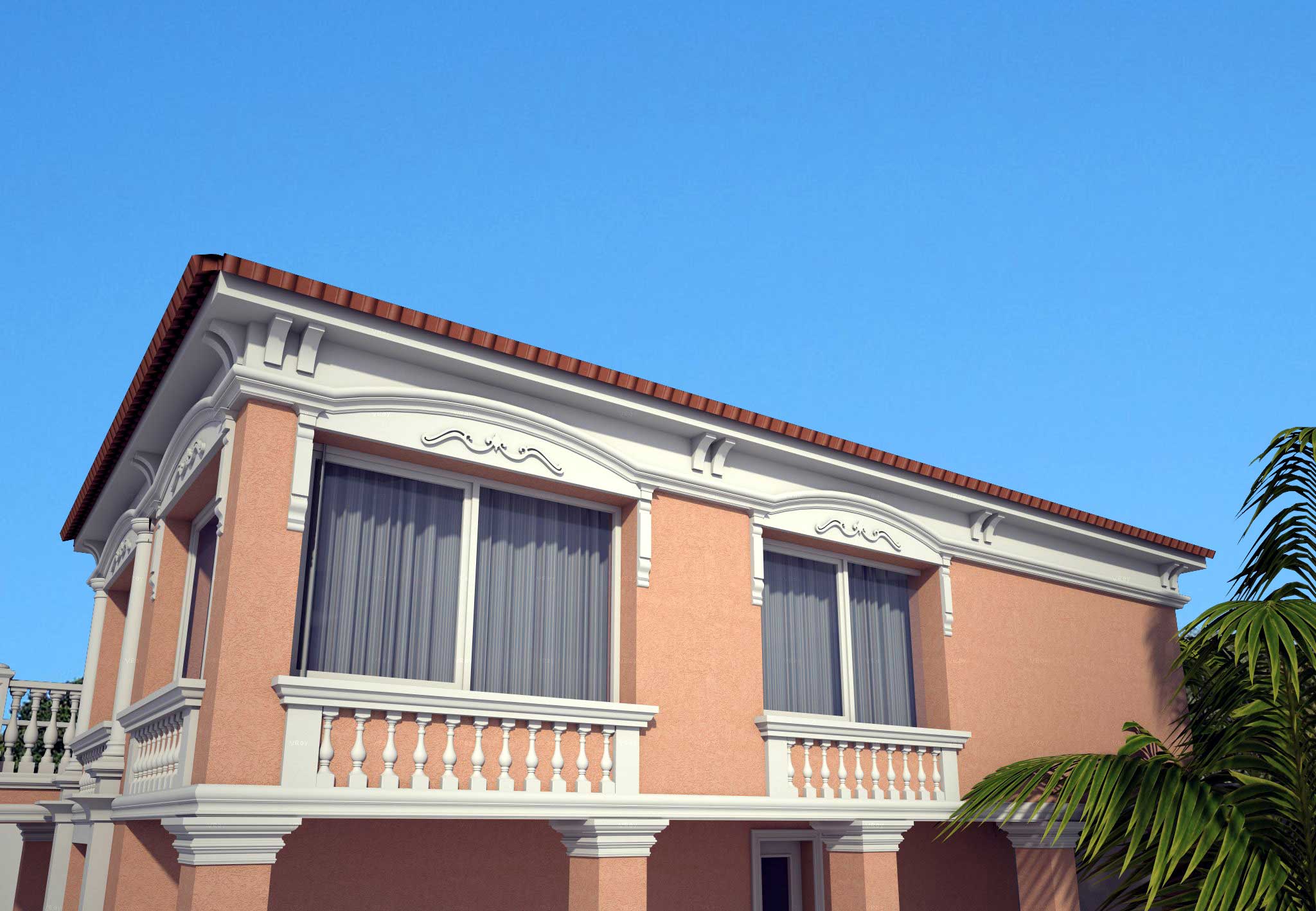
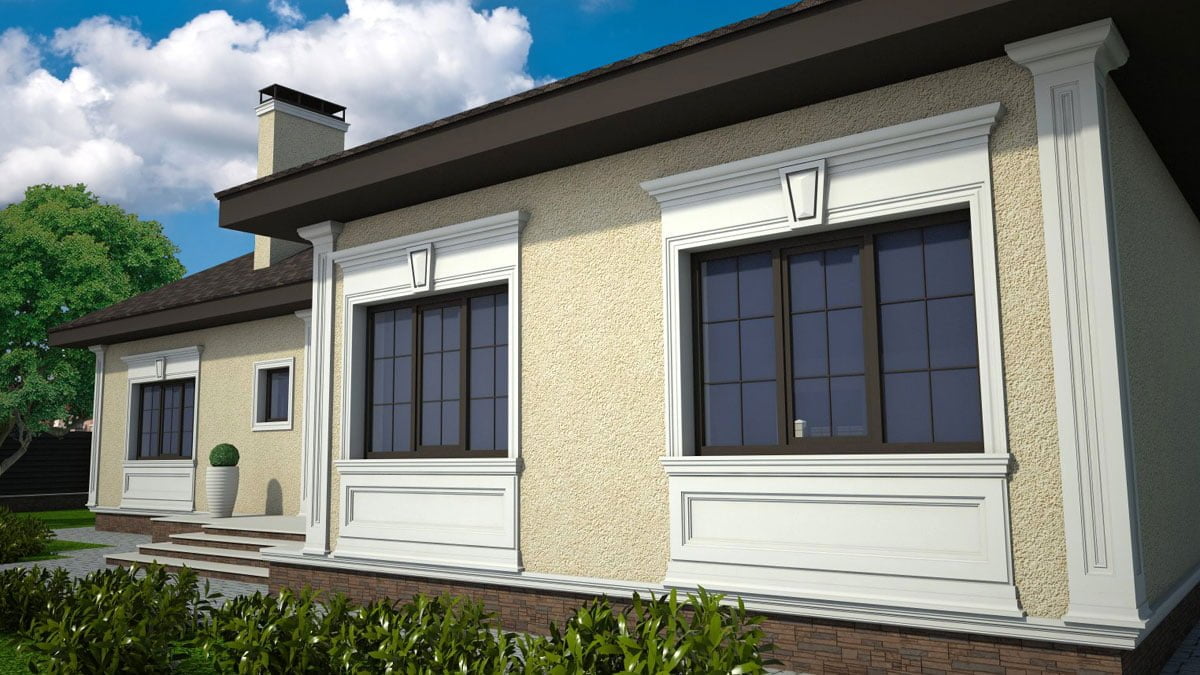
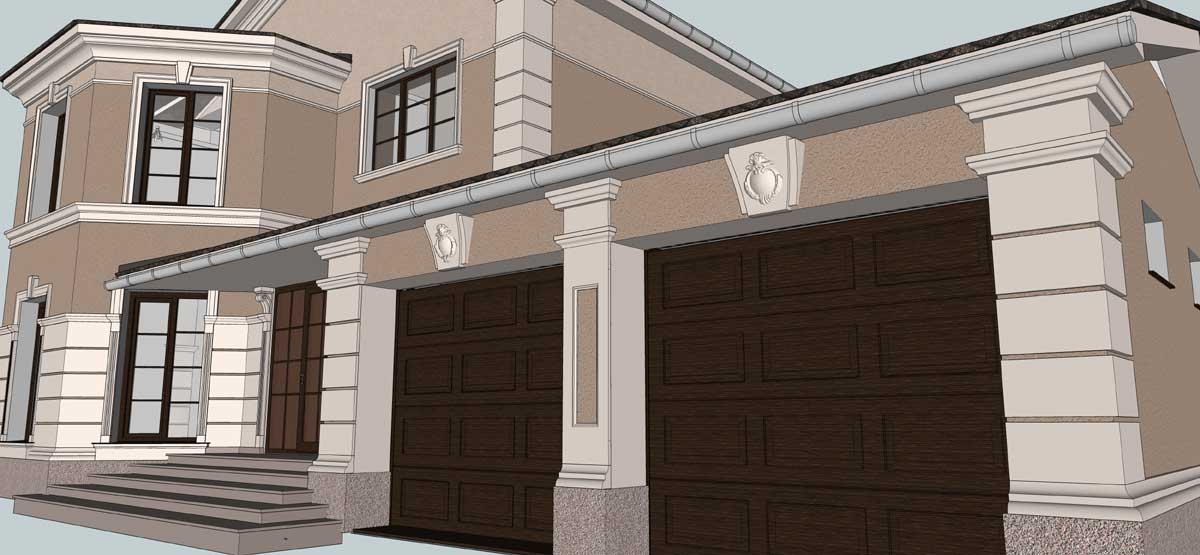
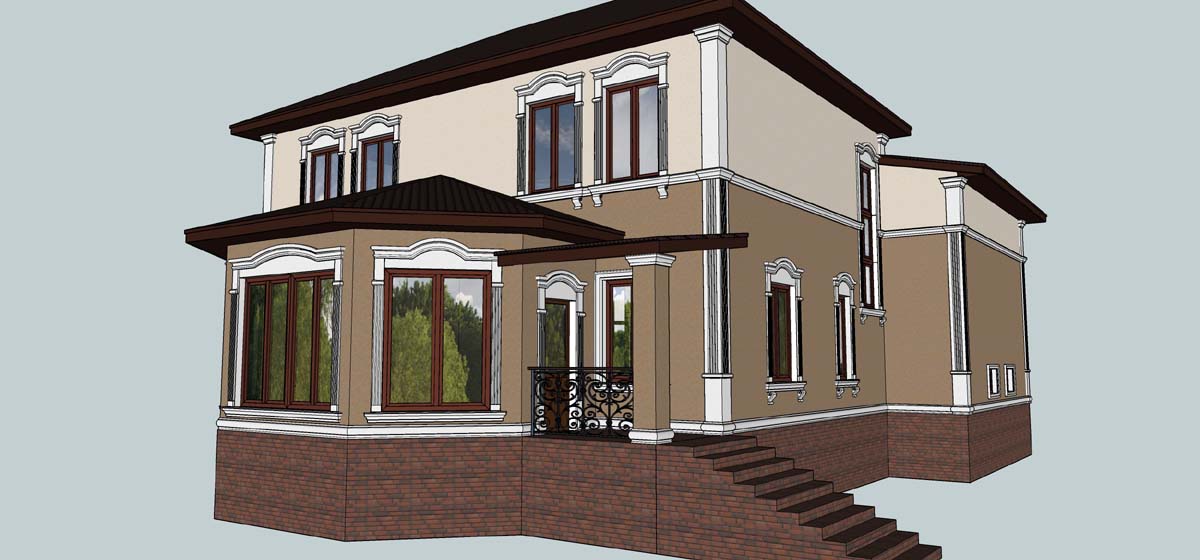
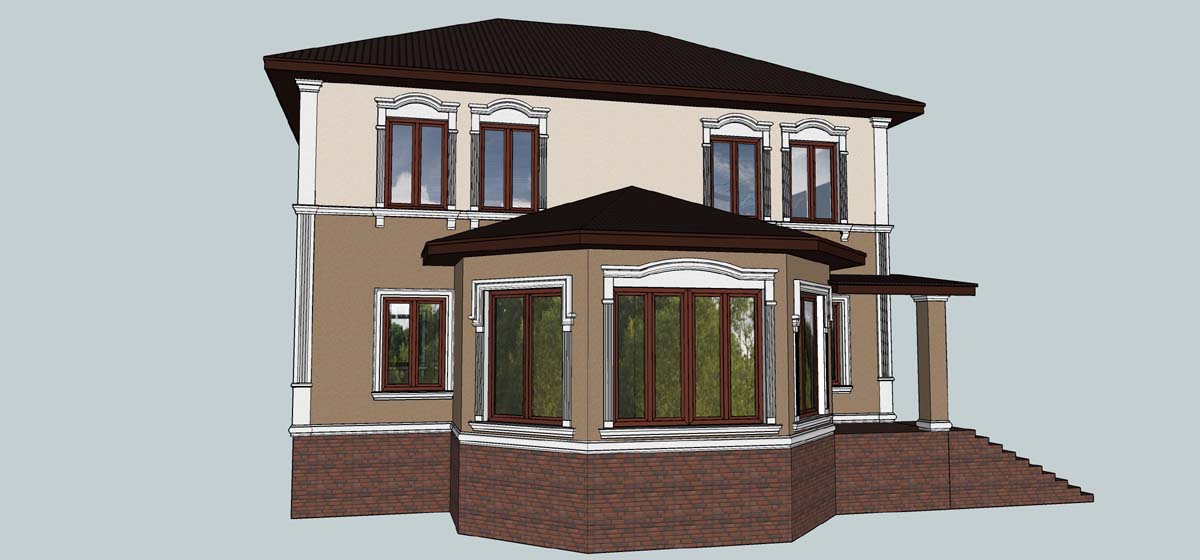
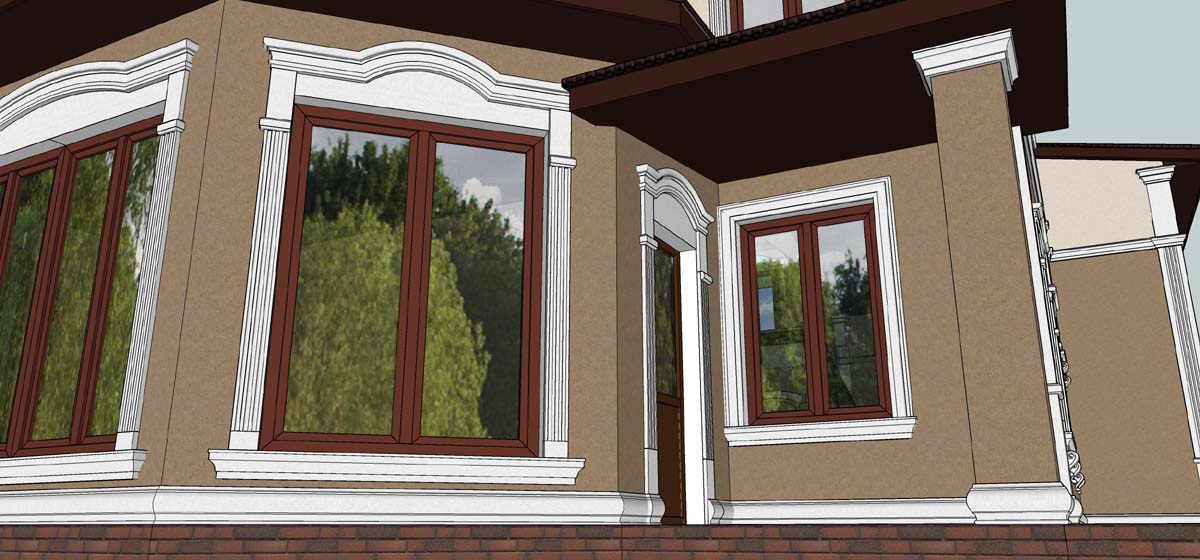
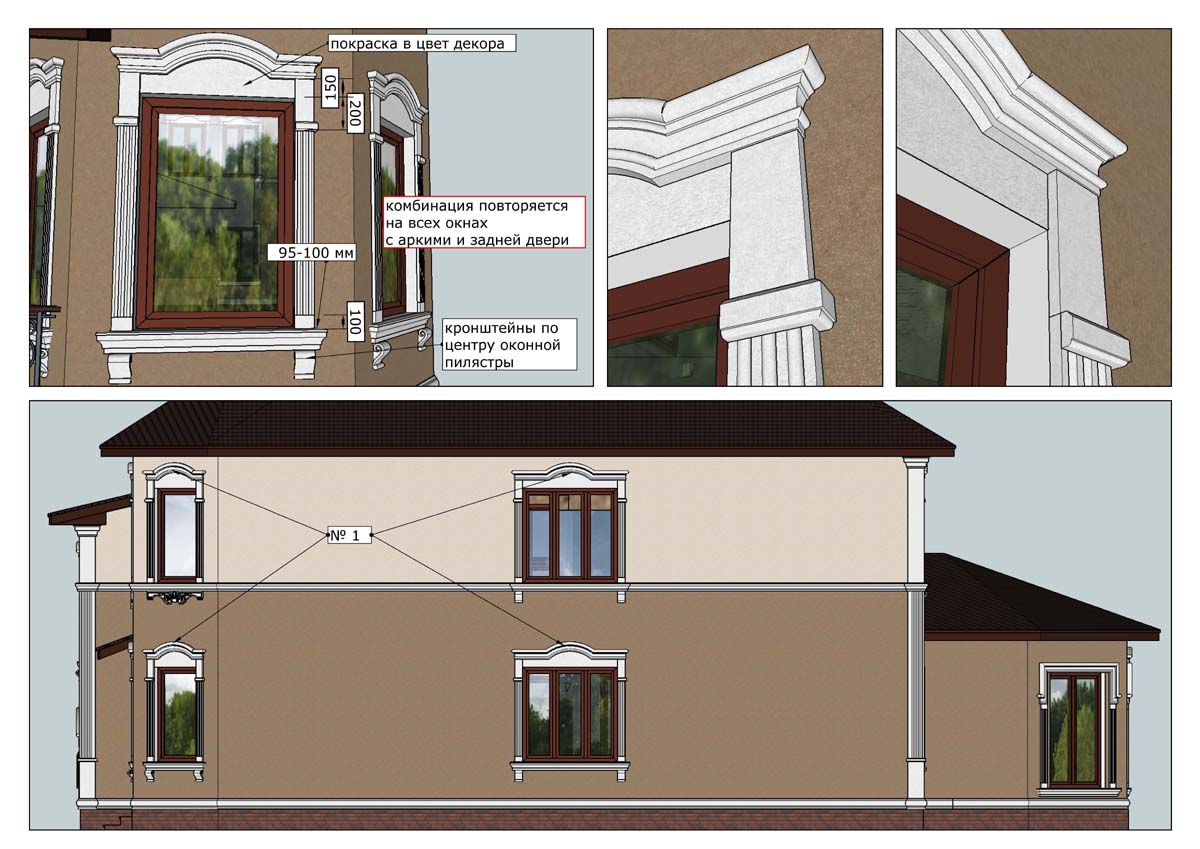
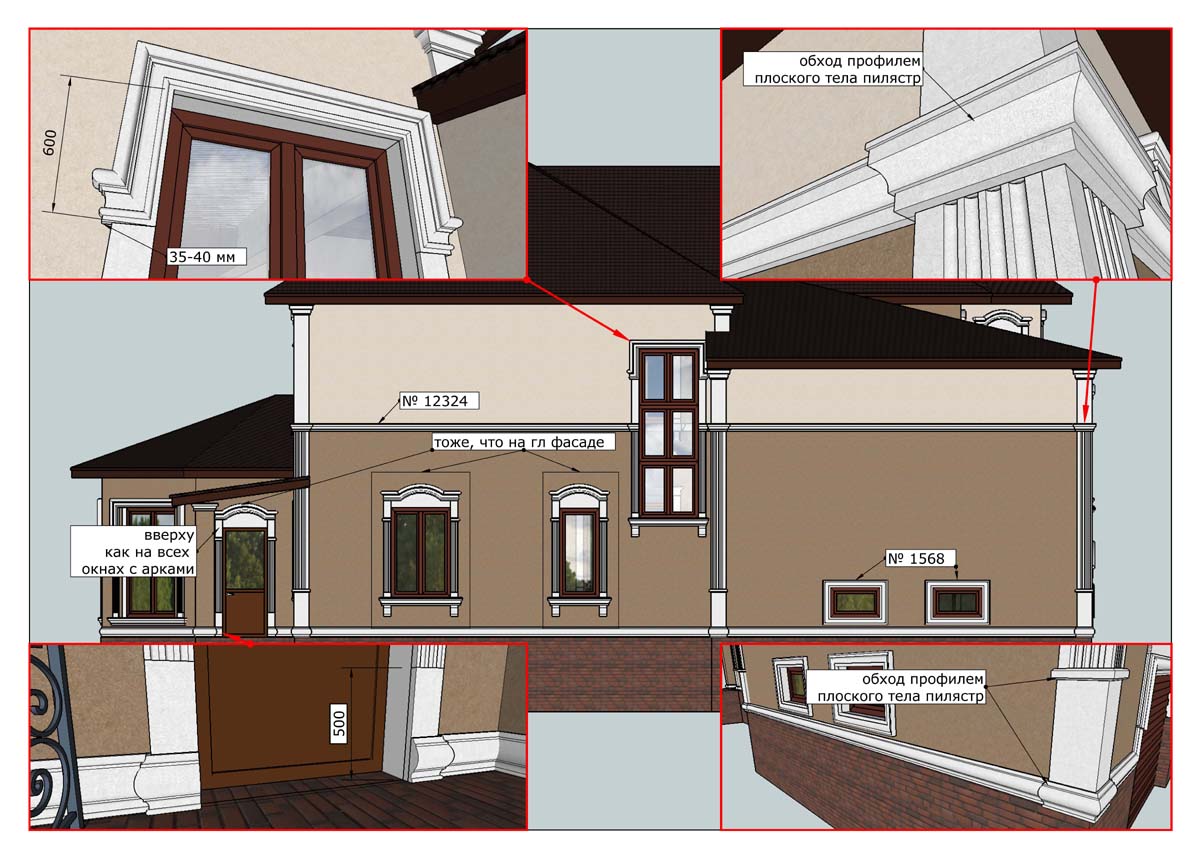
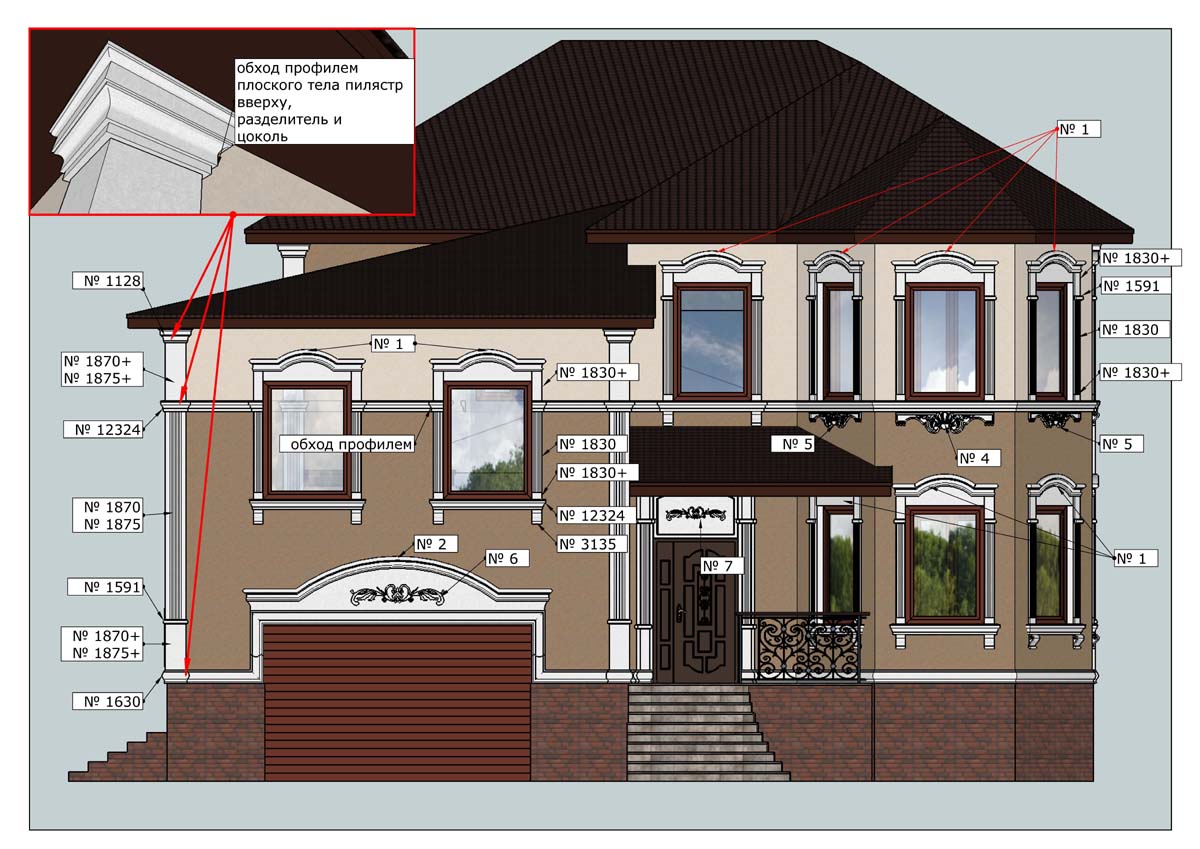
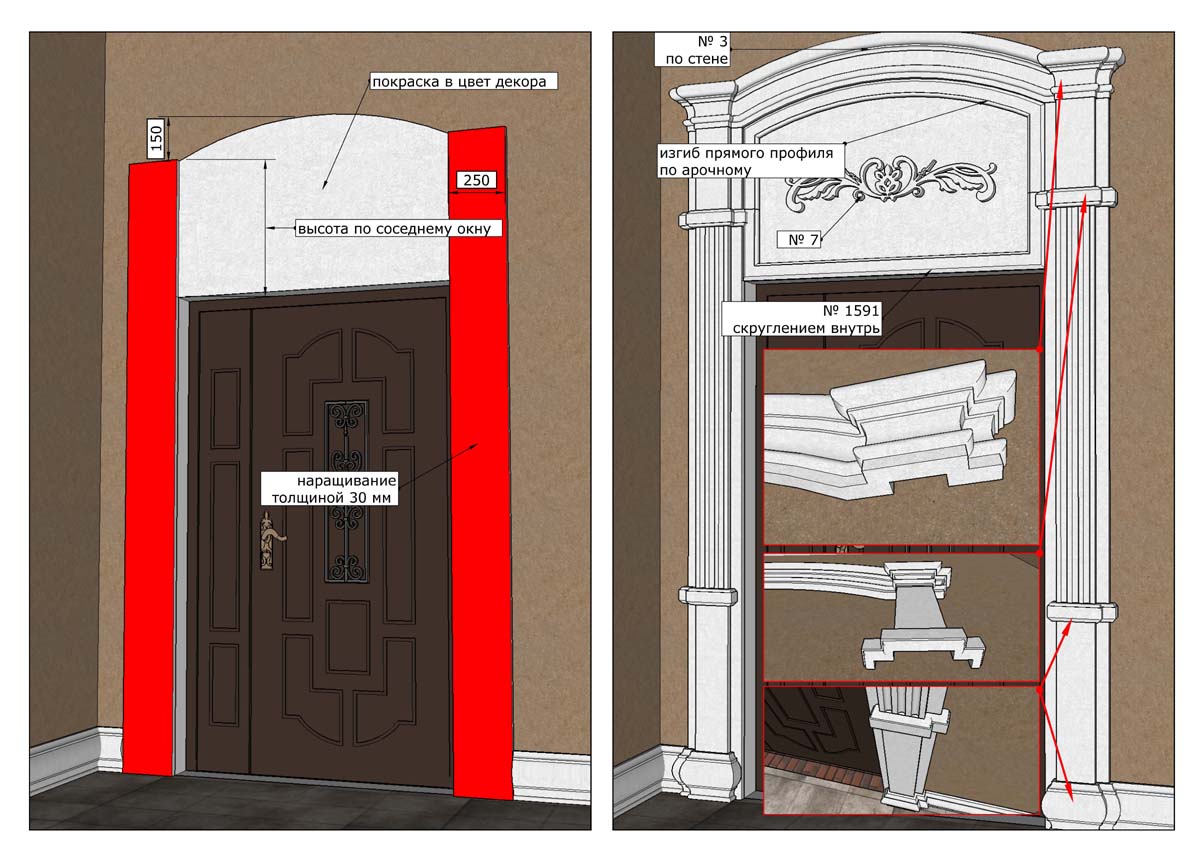
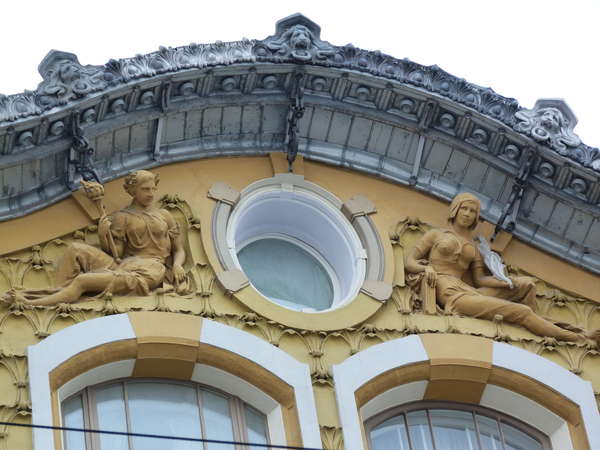
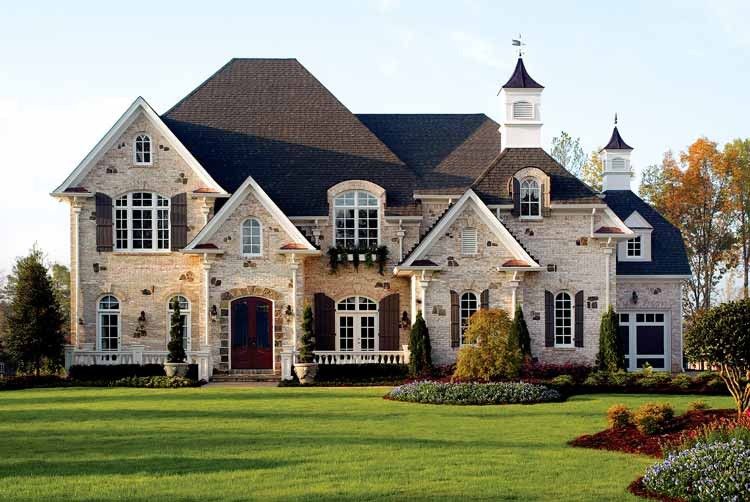
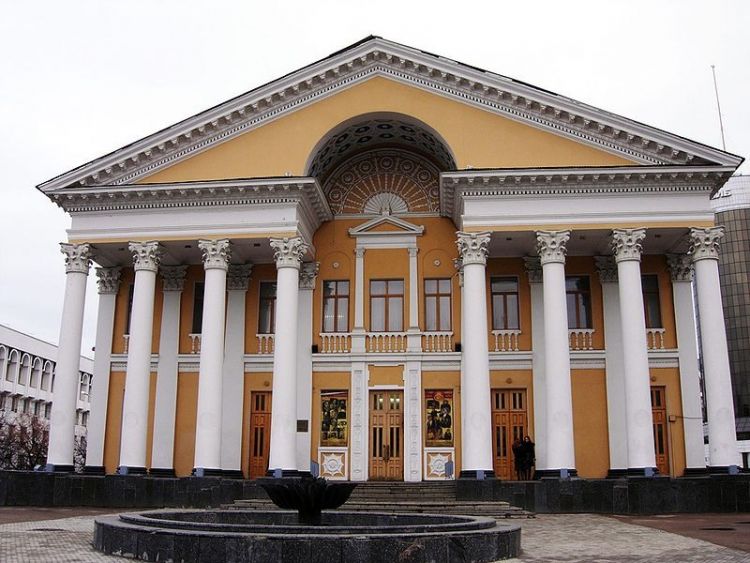
ONE OF OUR LATEST WORKS ON HOME EXTERIOR DESIGN


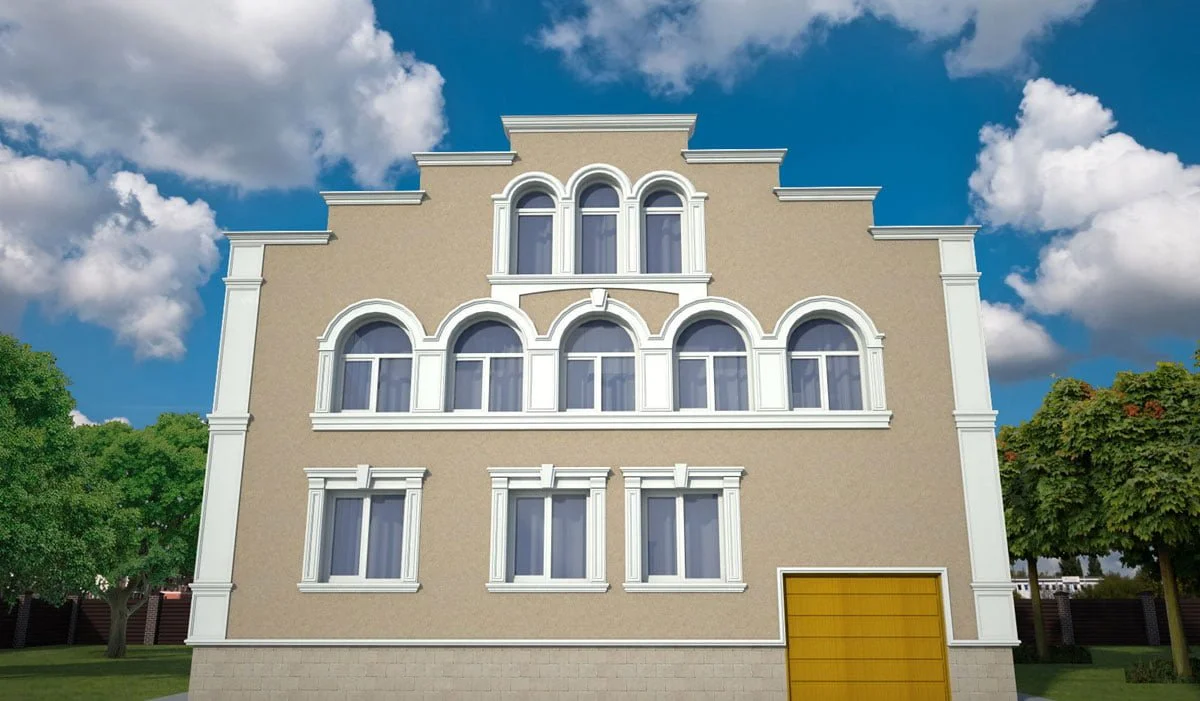
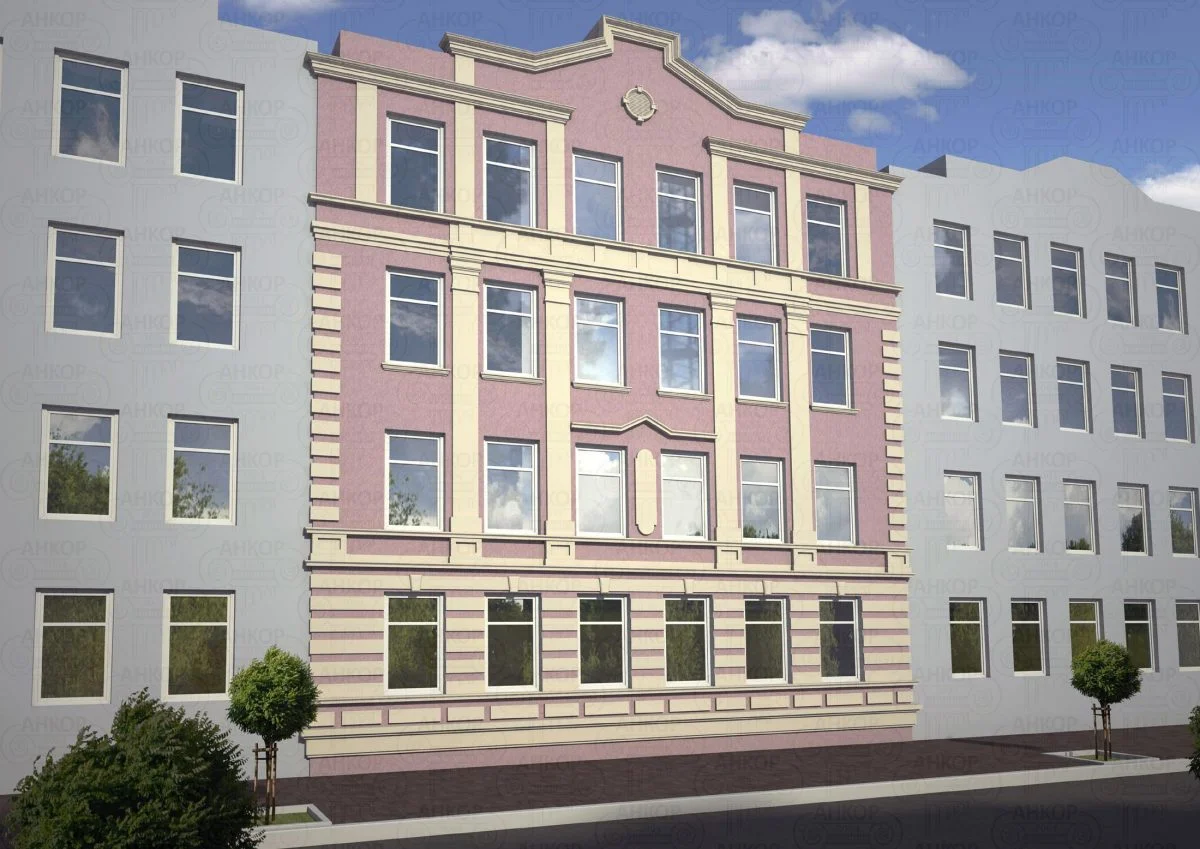
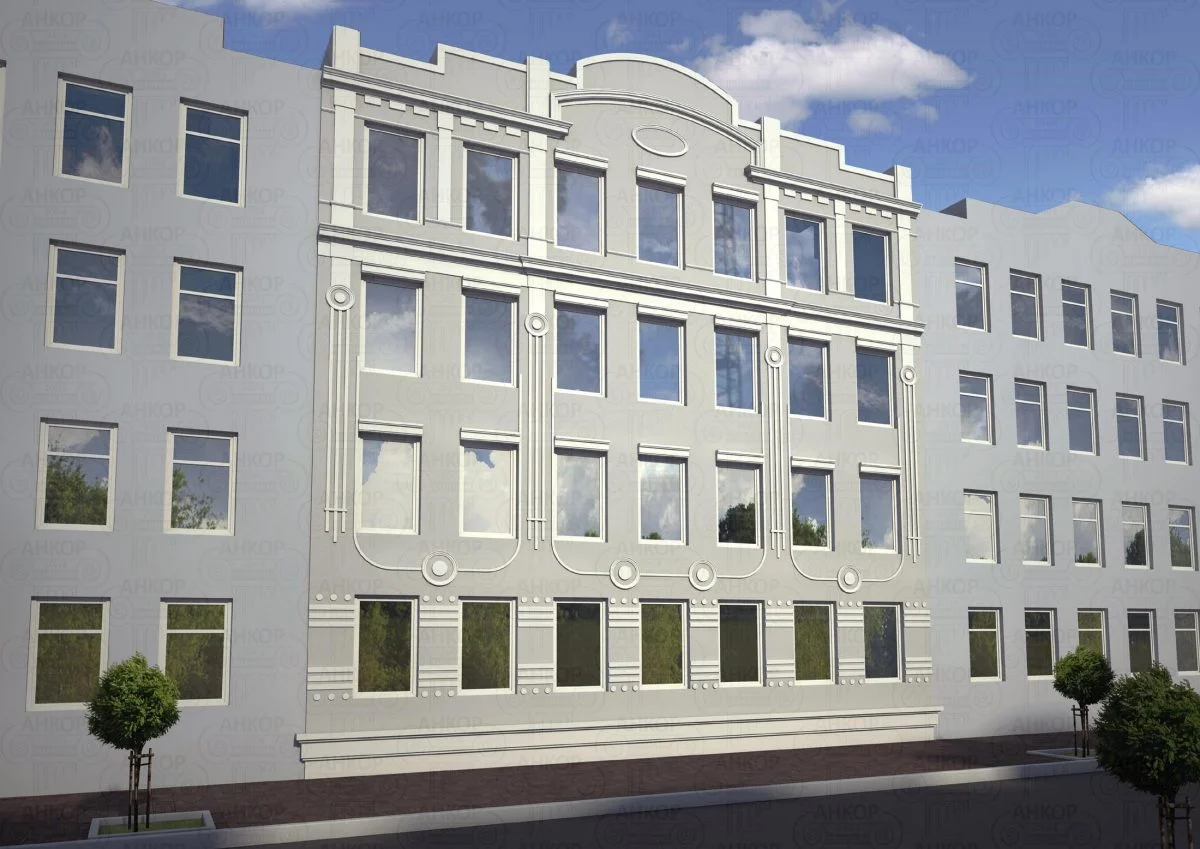
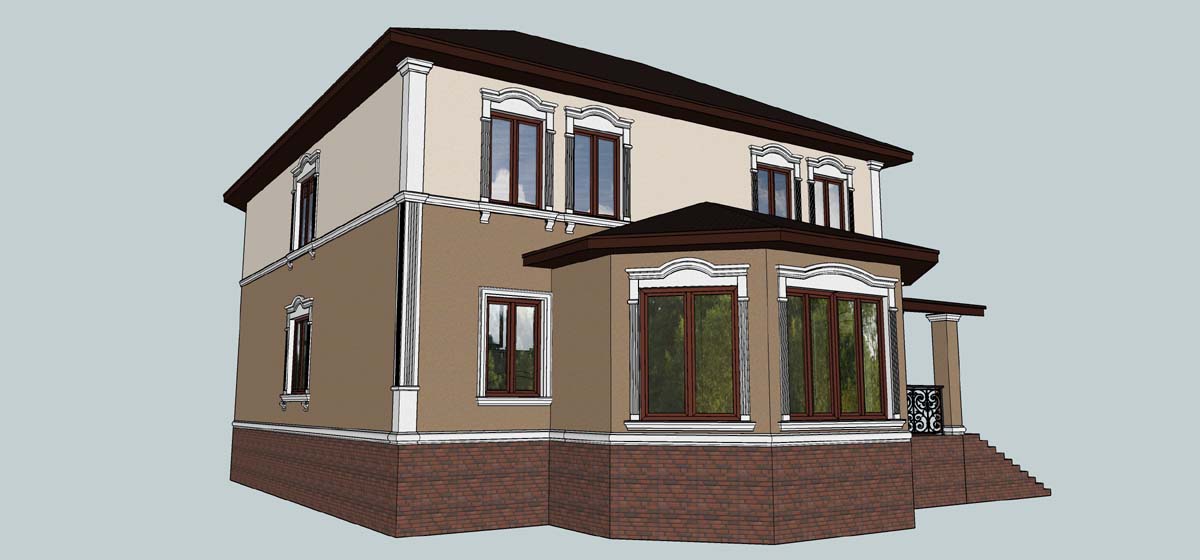
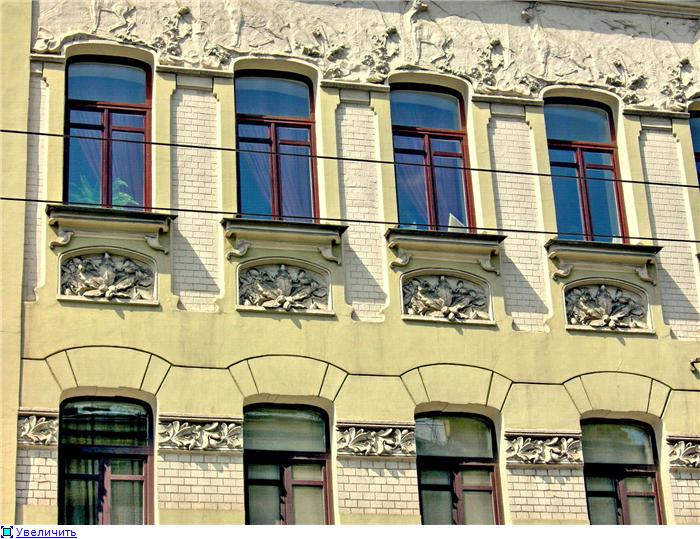
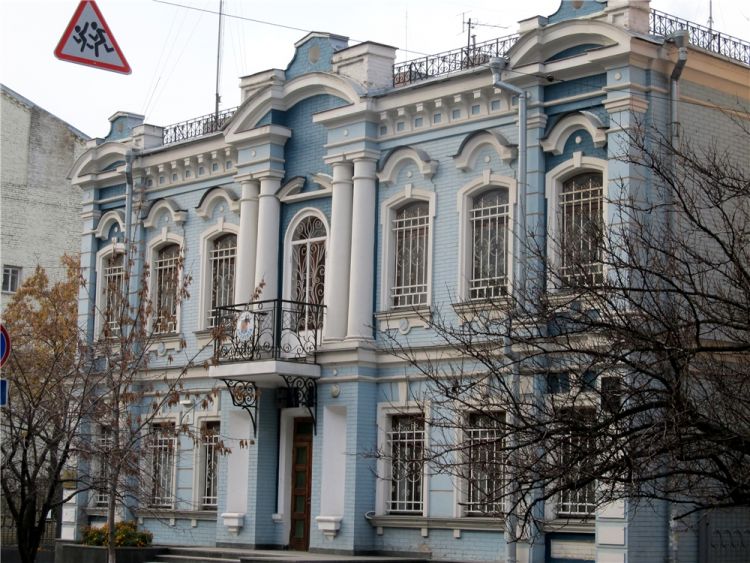
OUR OUTER WALL DESIGNS
In recent years, our team has been dedicated to utilizing cutting-edge technology to design visually stunning and functionally efficient 3D house exteriors. Our primary goal is to create unique and personalized homes that cater to our client’s individual lifestyles and preferences.
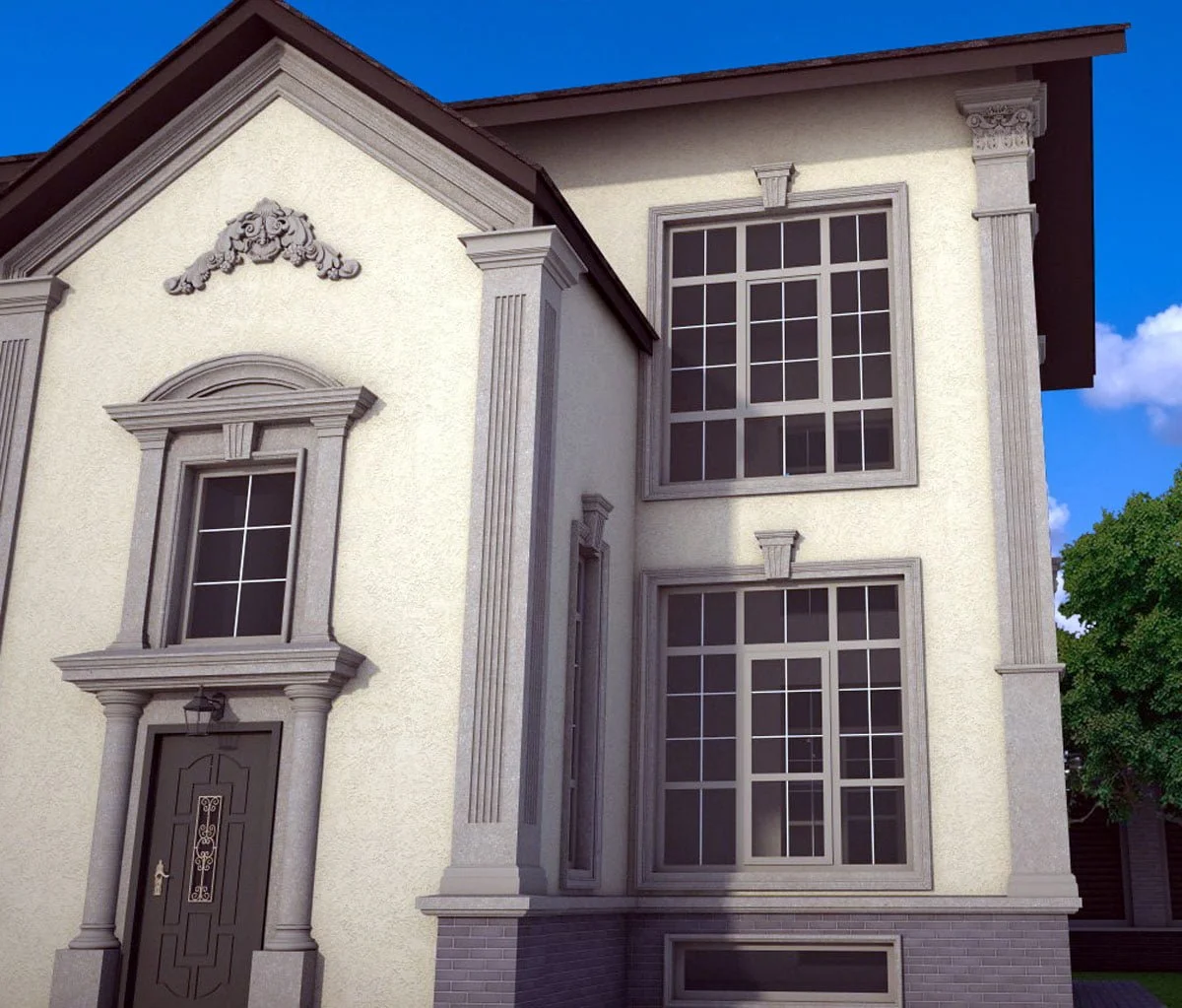
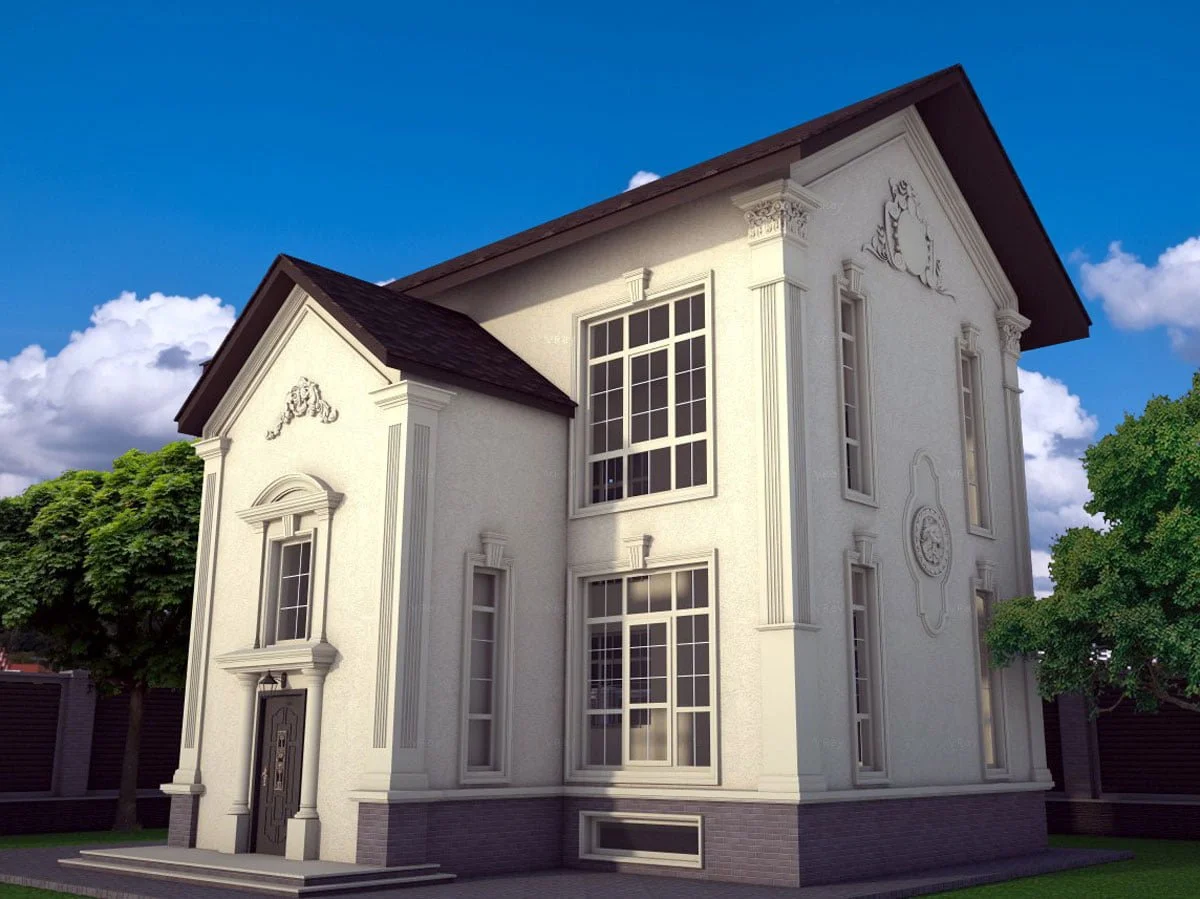
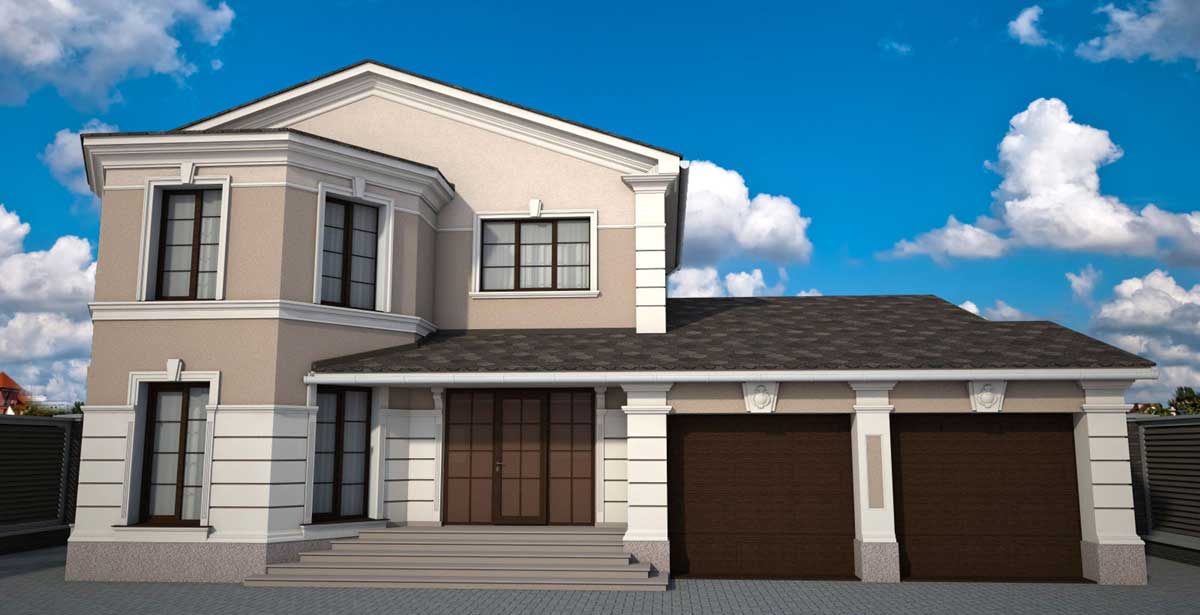
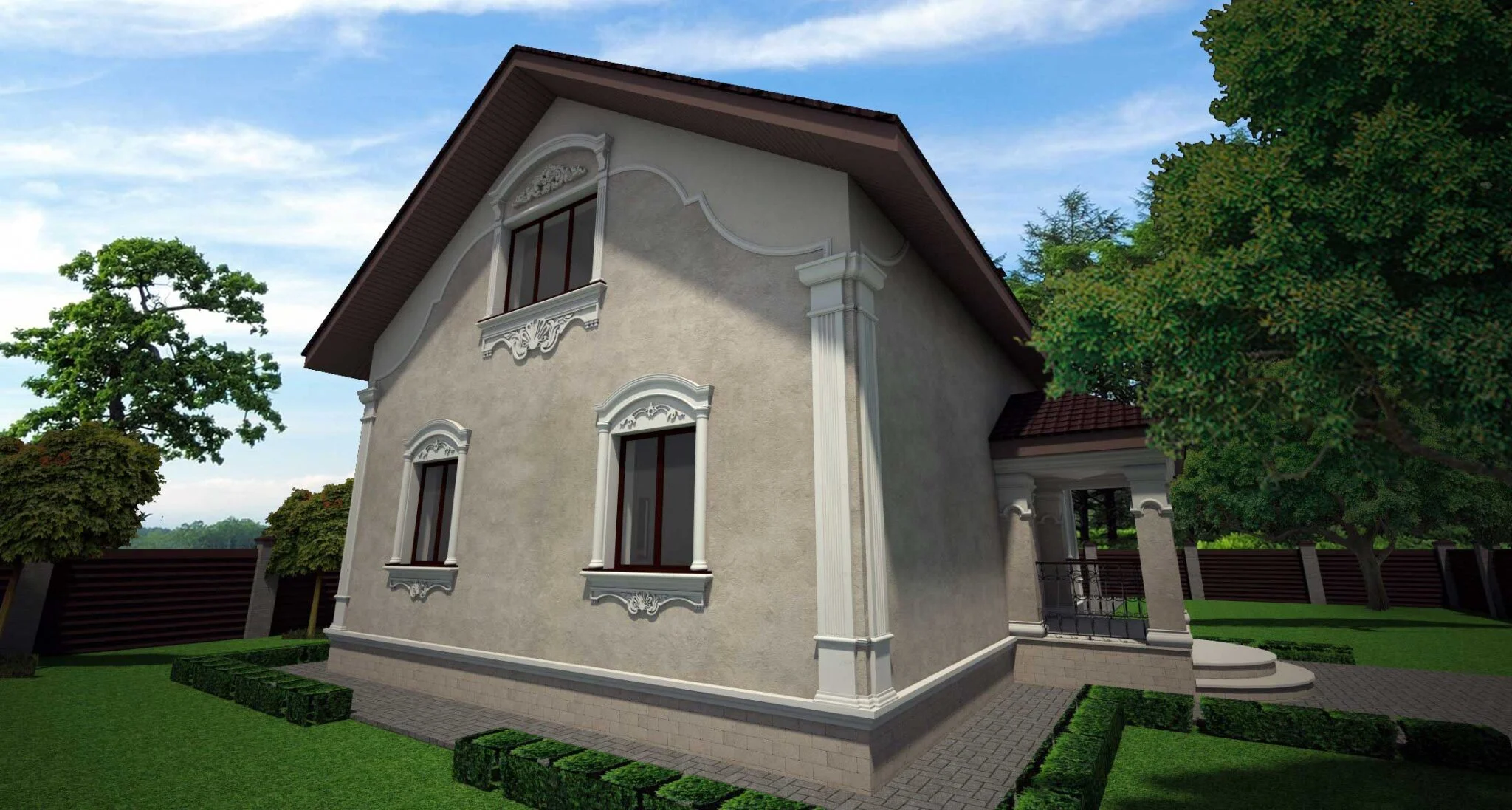
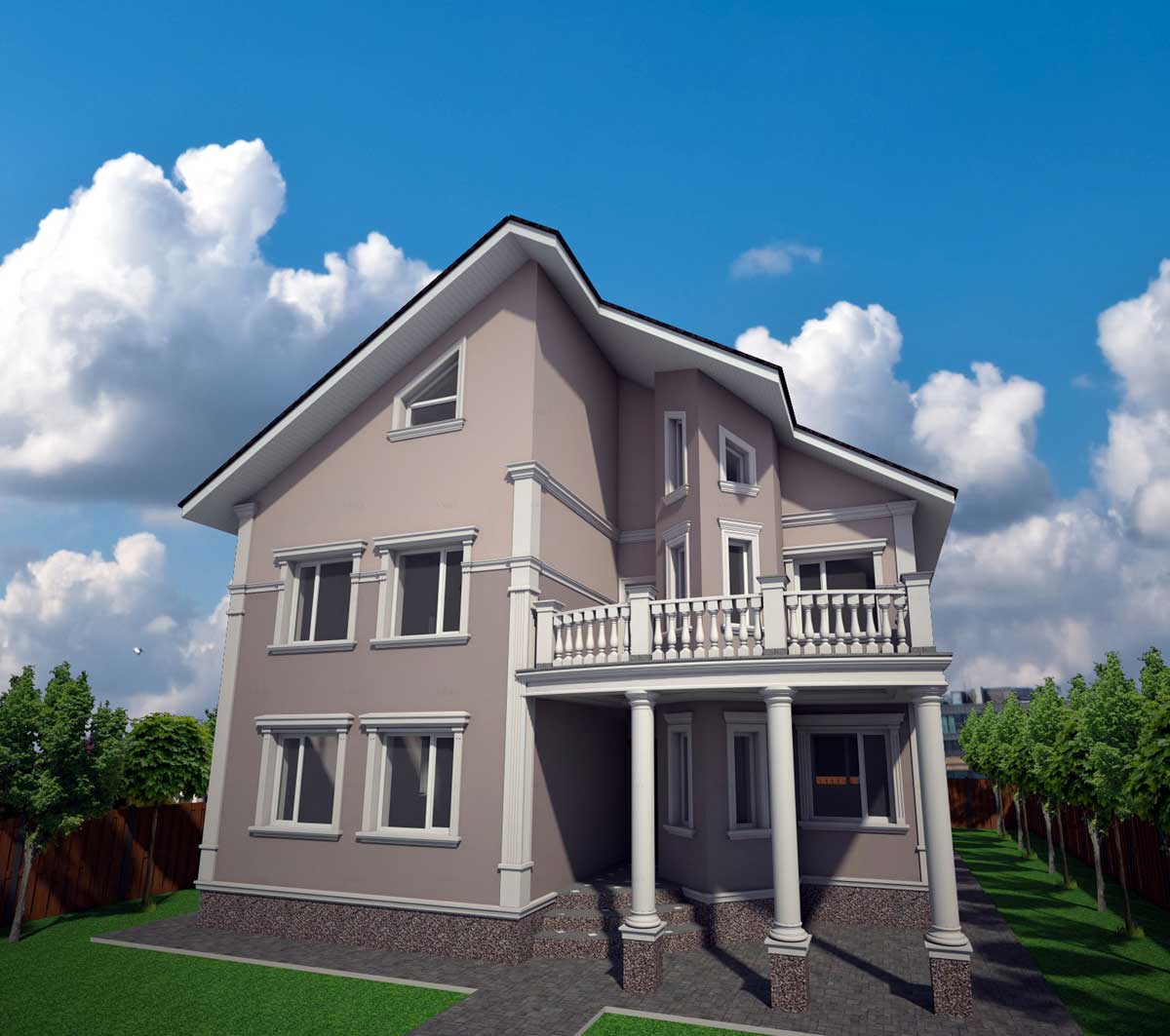
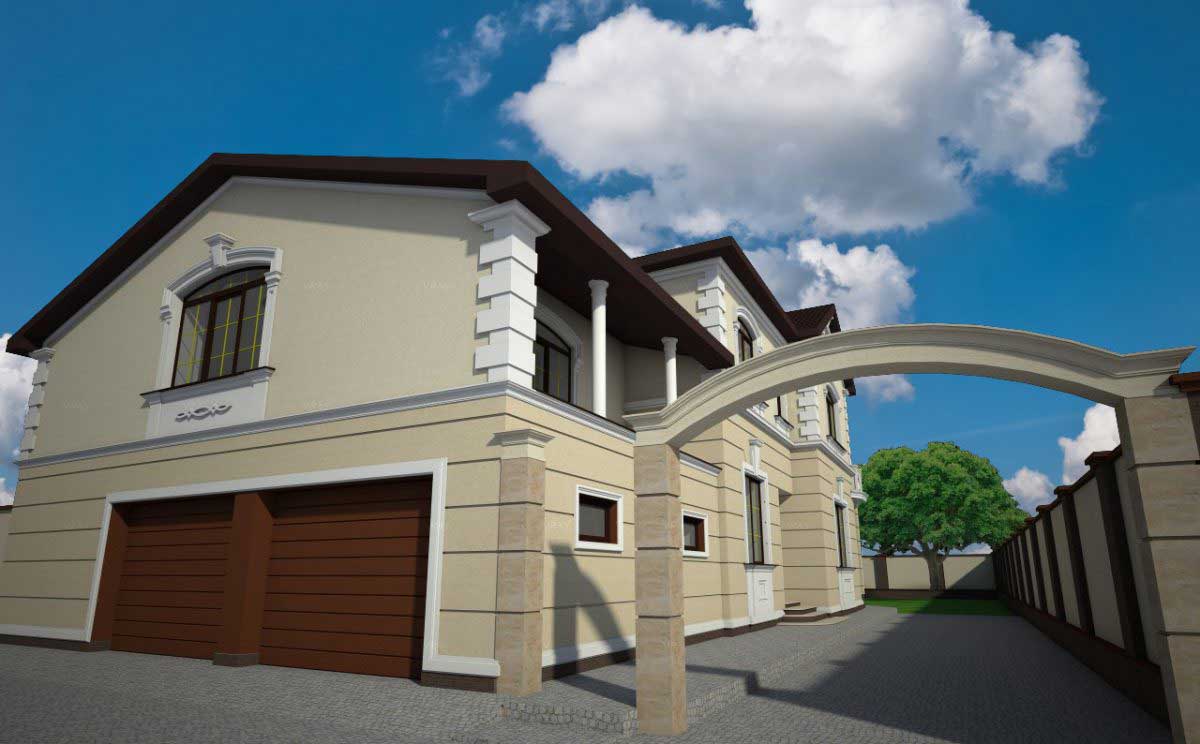
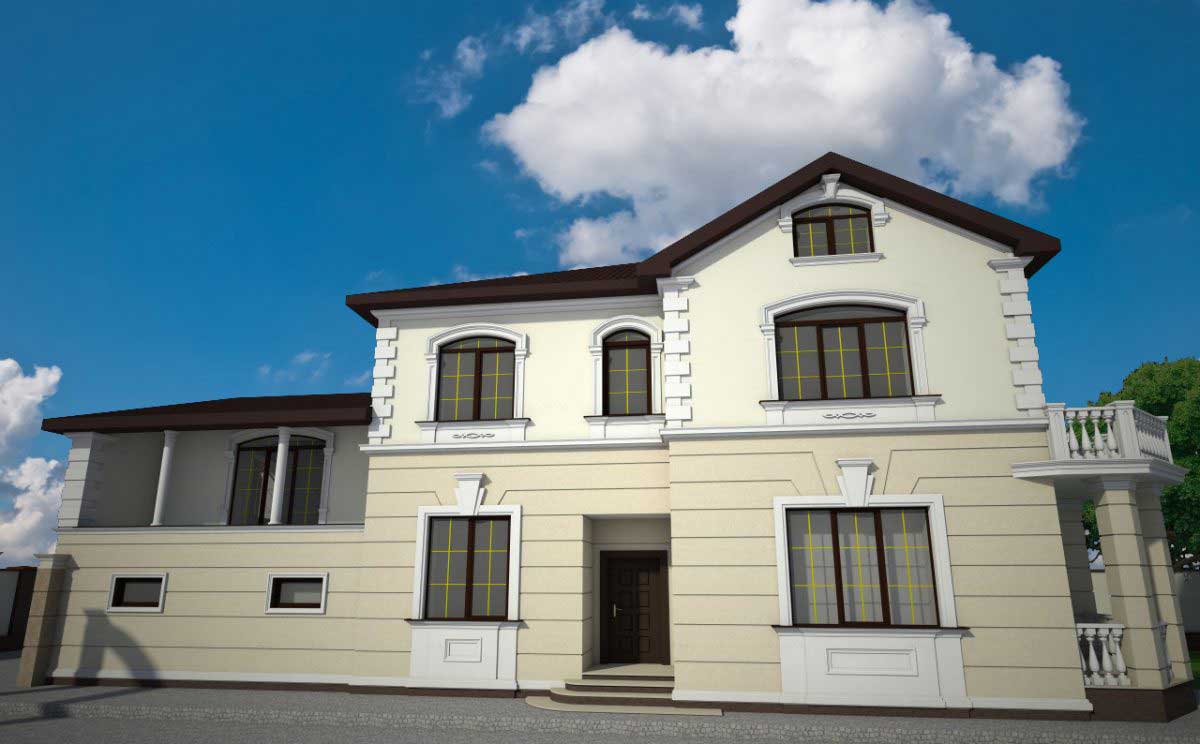
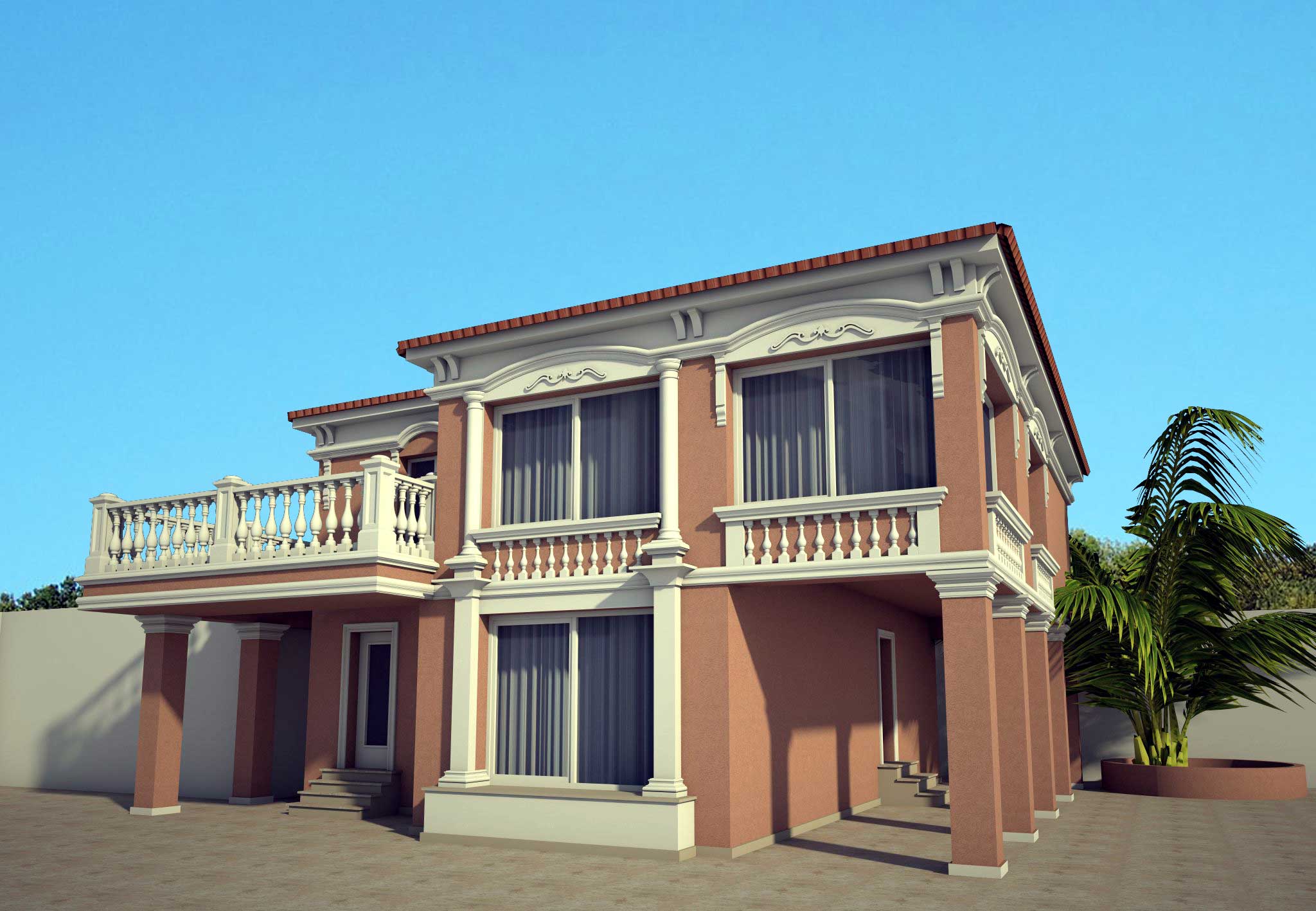
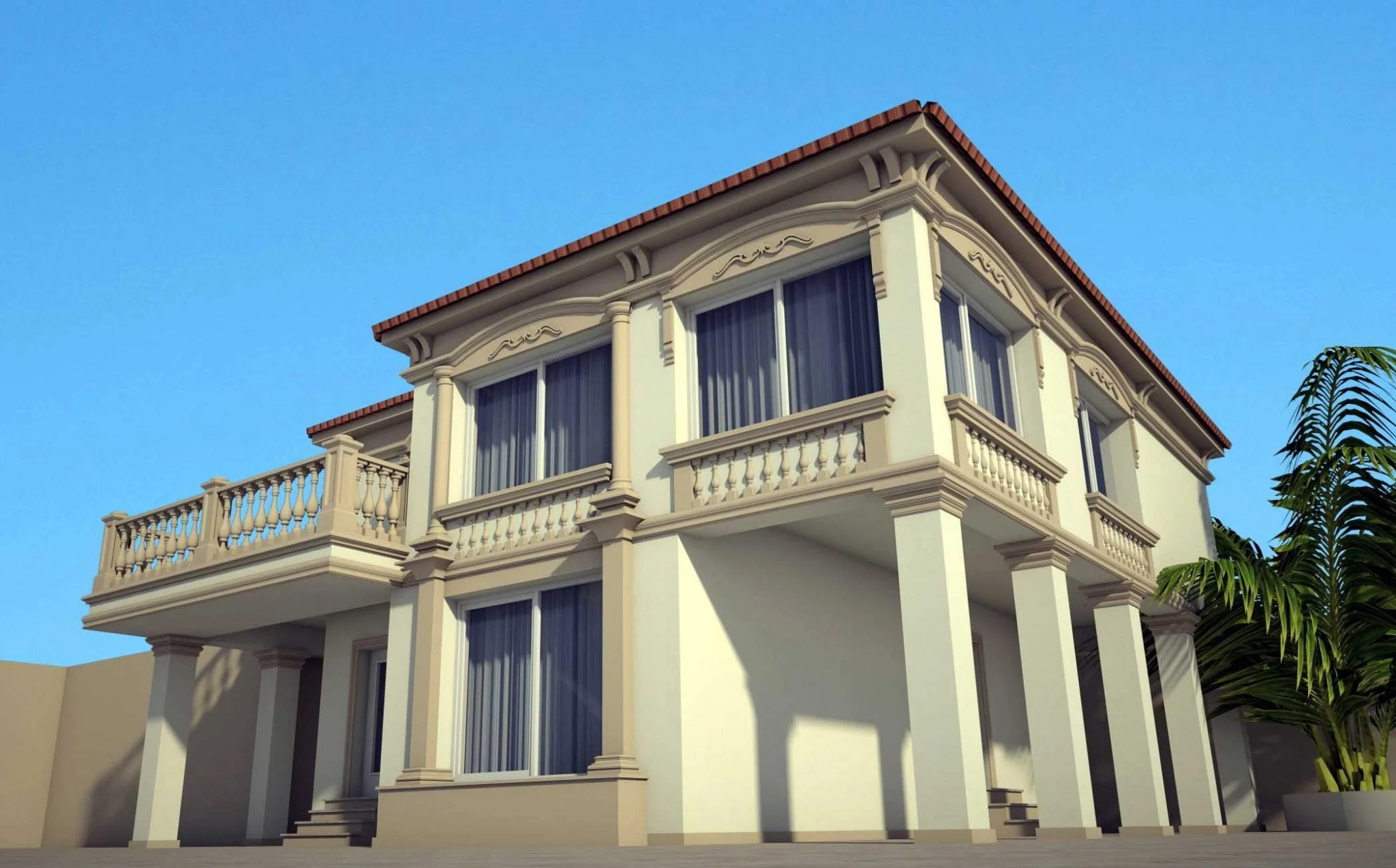
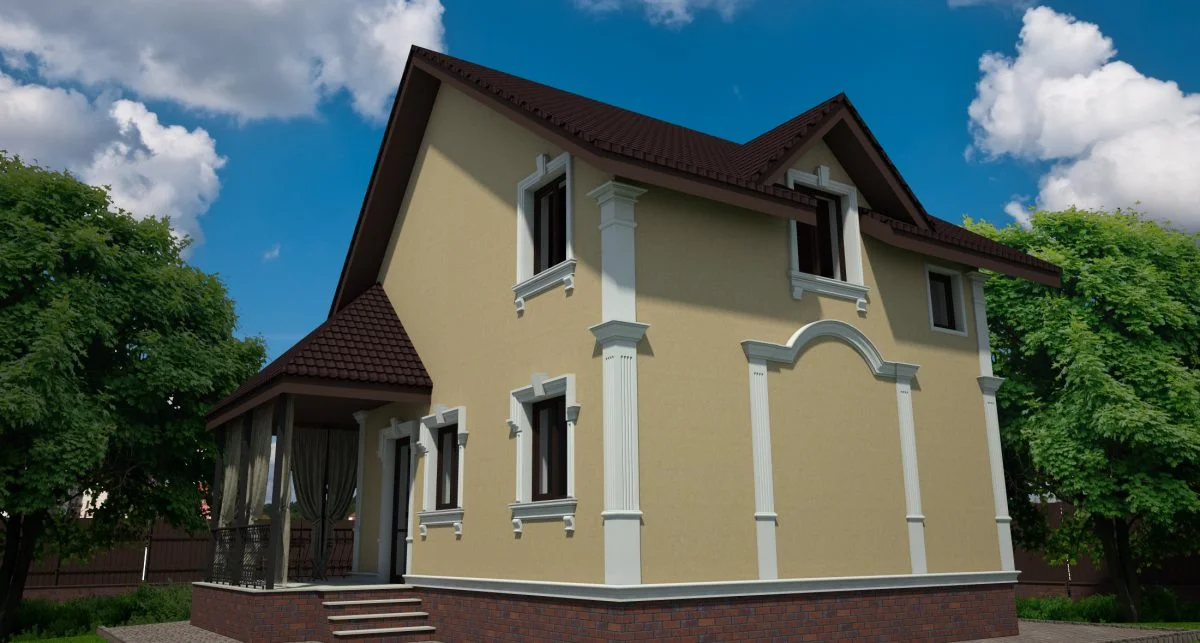























































































































One of the key aspects of our work is the seamless integration of advanced software and design tools, which allows us to create highly detailed and accurate 3D models of house exteriors. By employing state-of-the-art programs such as AutoCAD, SketchUp, and Lumion, we can easily manipulate and adjust various design elements, including the choice of materials, colors, and textures. This level of flexibility enables us to experiment with different styles and approaches, fostering a collaborative environment where clients can provide input and feedback in real-time.
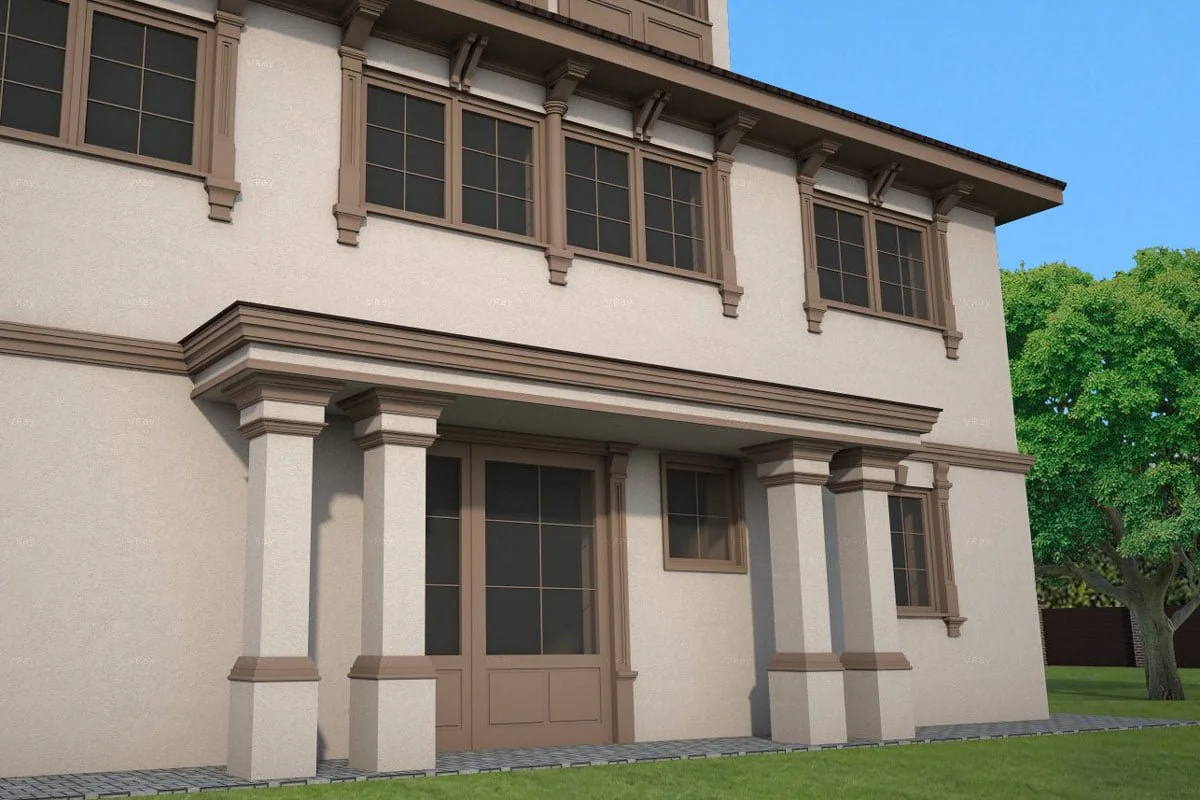
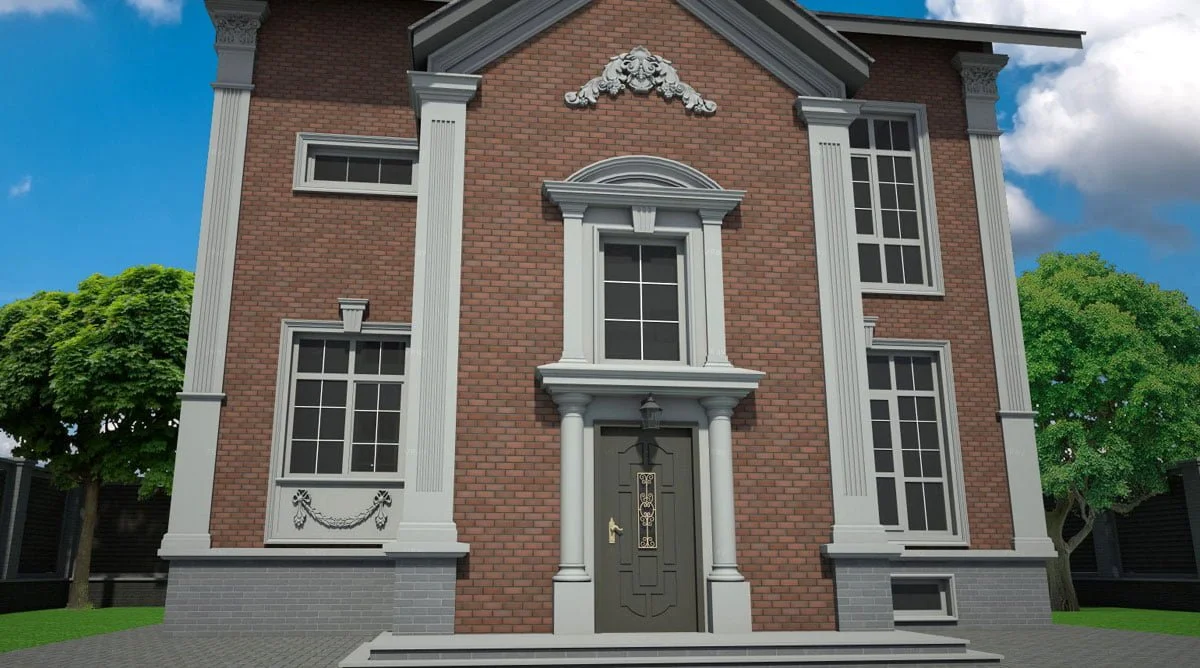
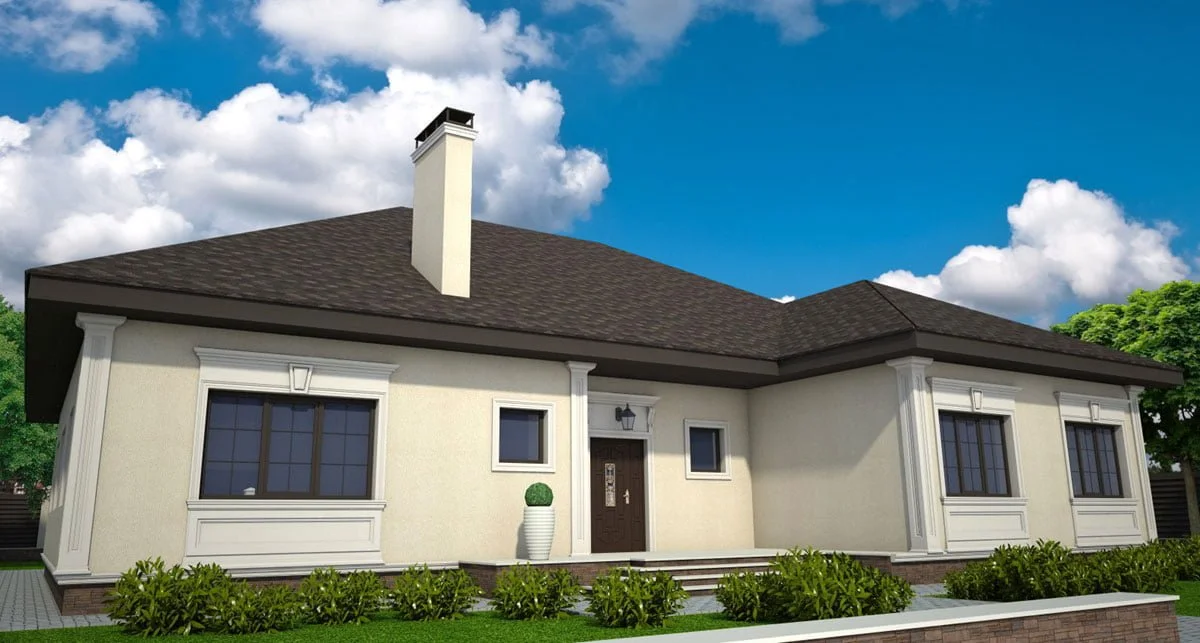
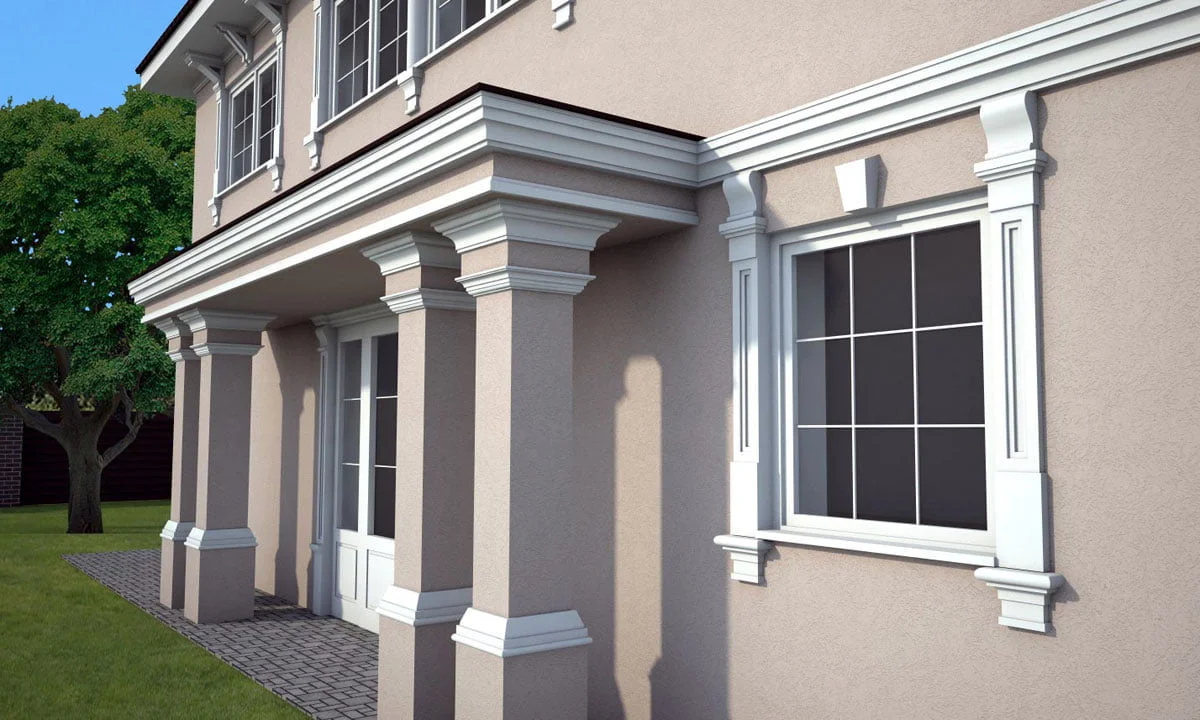
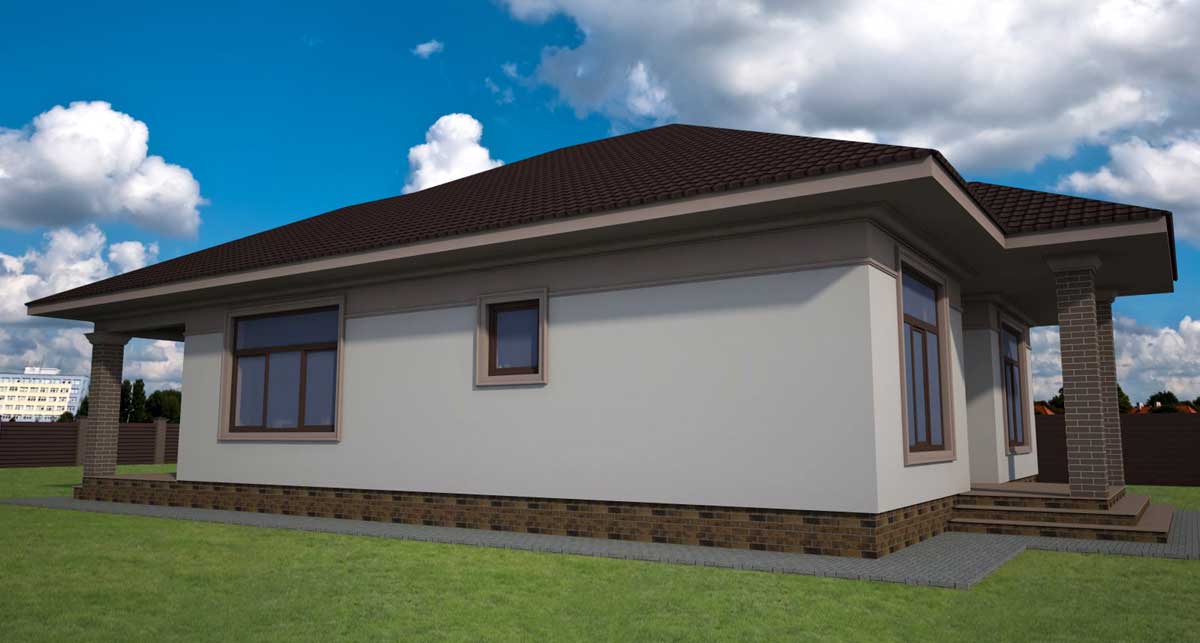
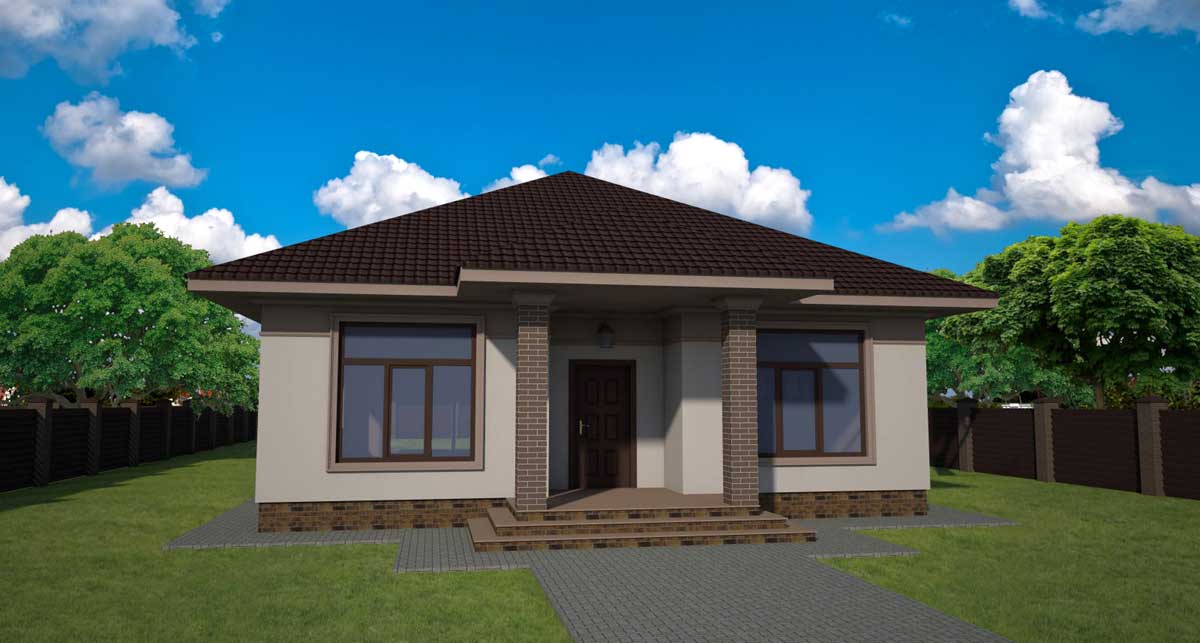
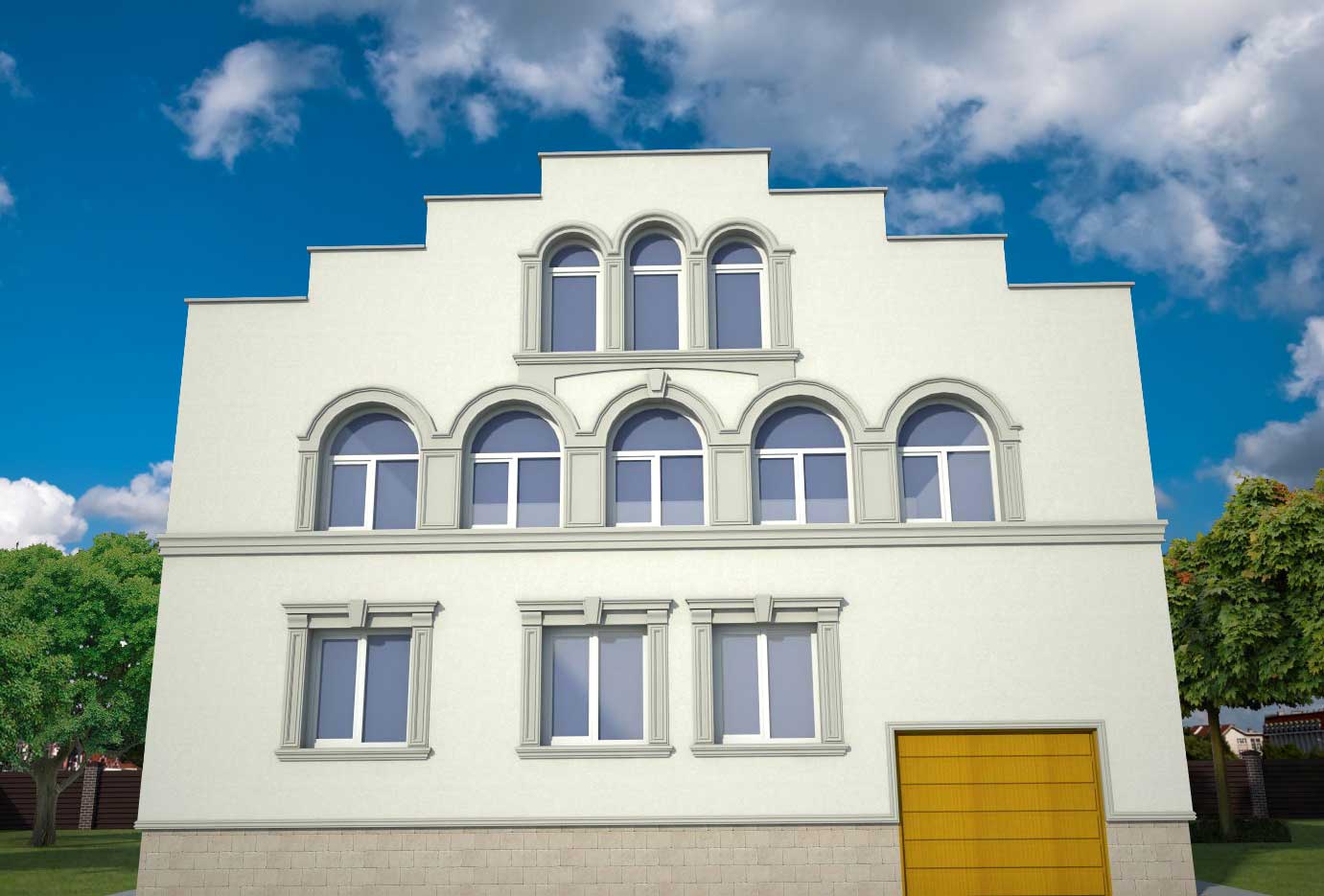
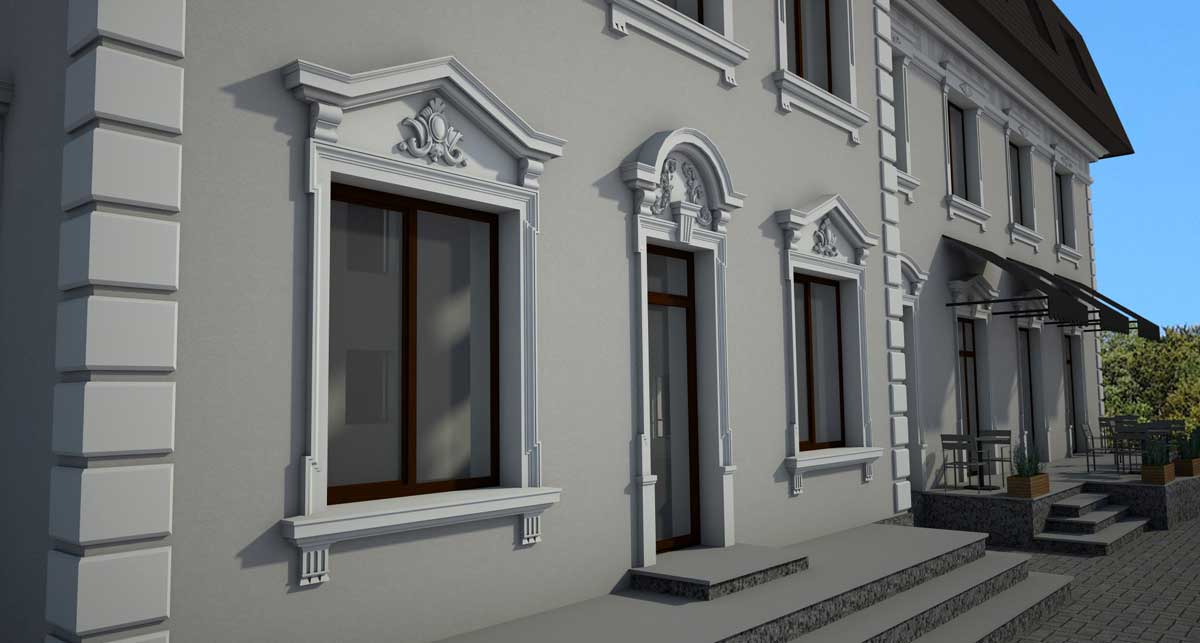
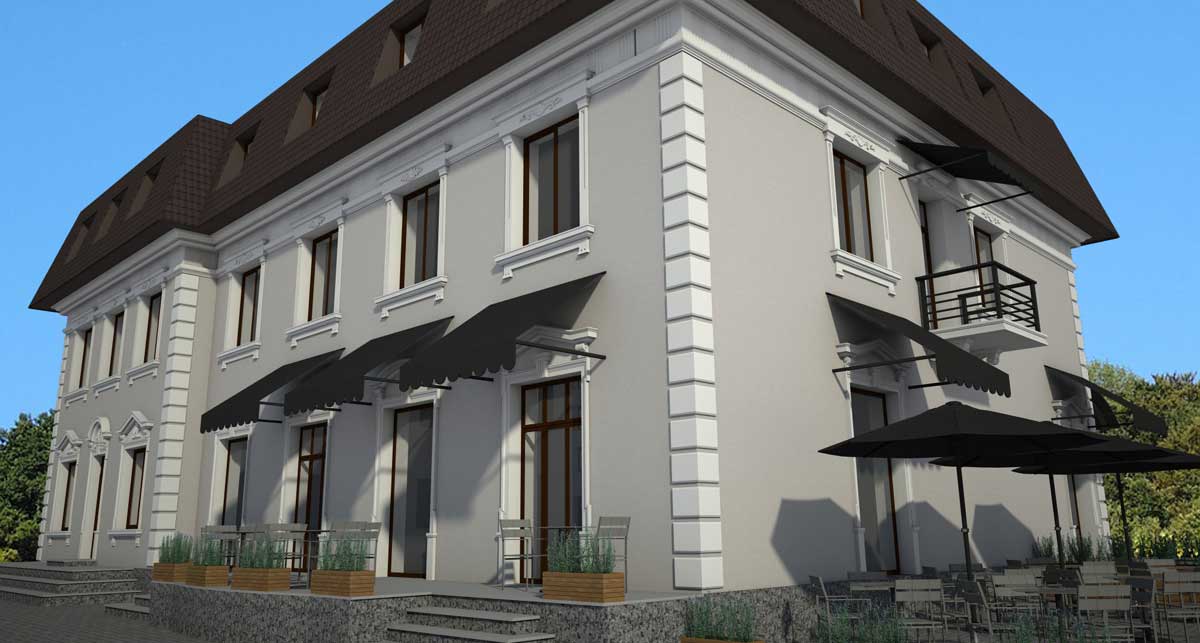
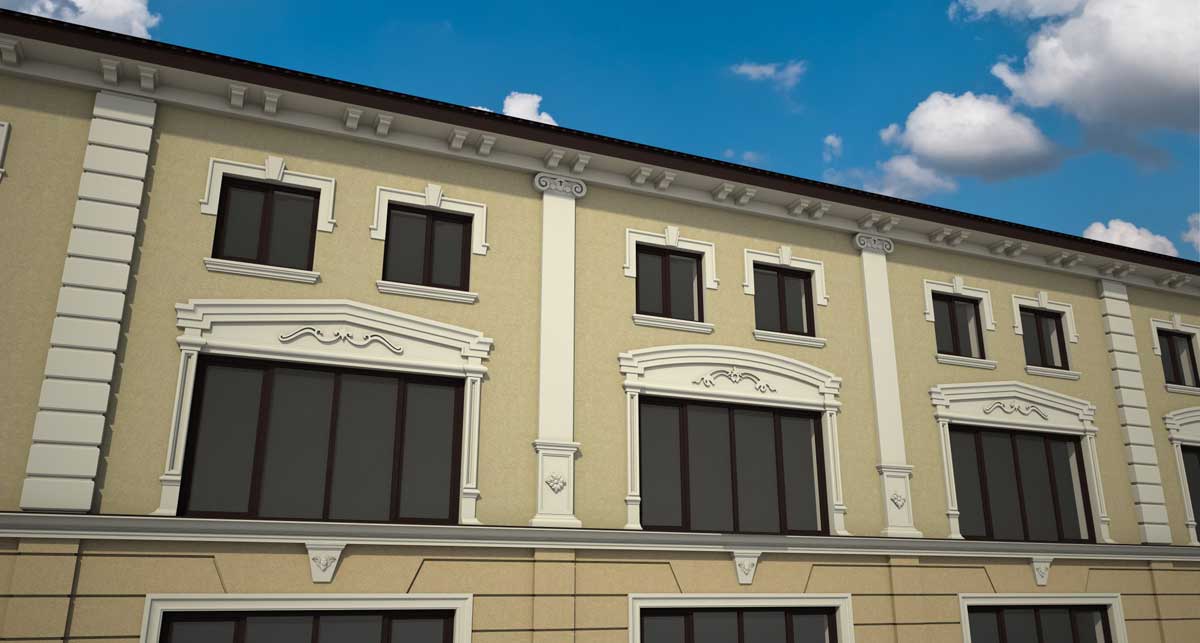
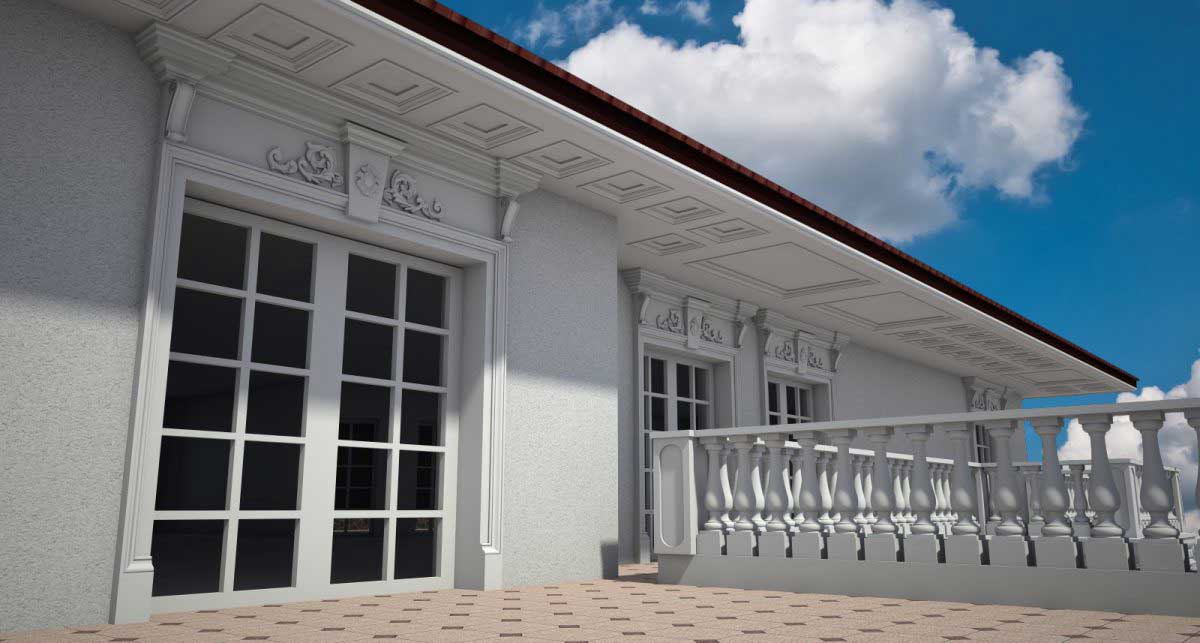
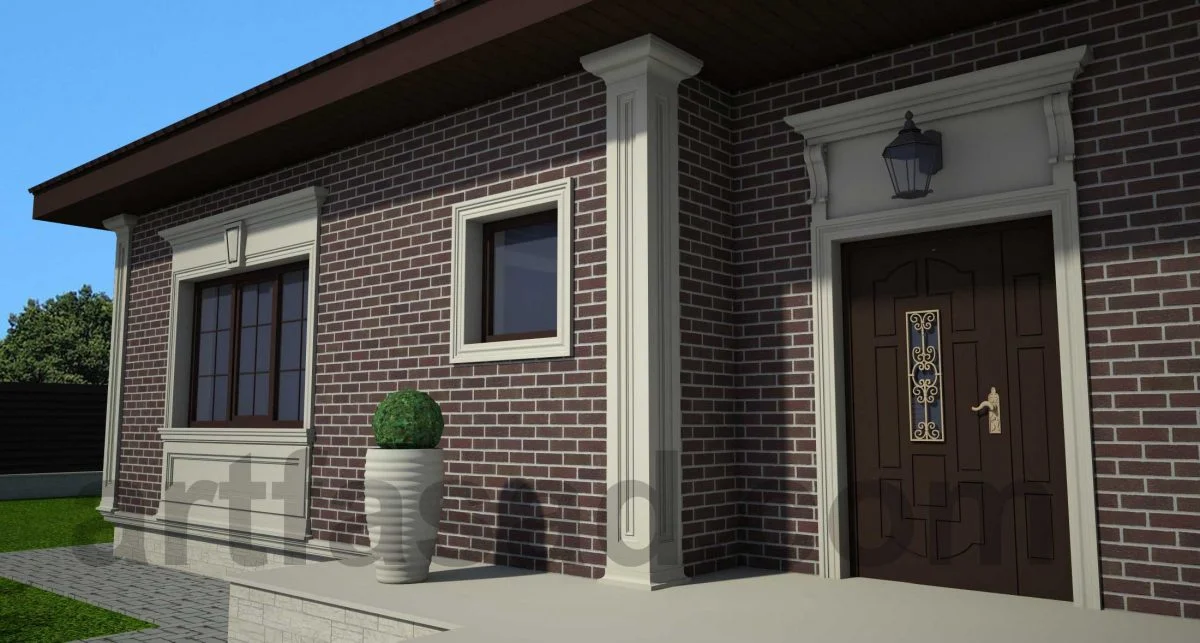
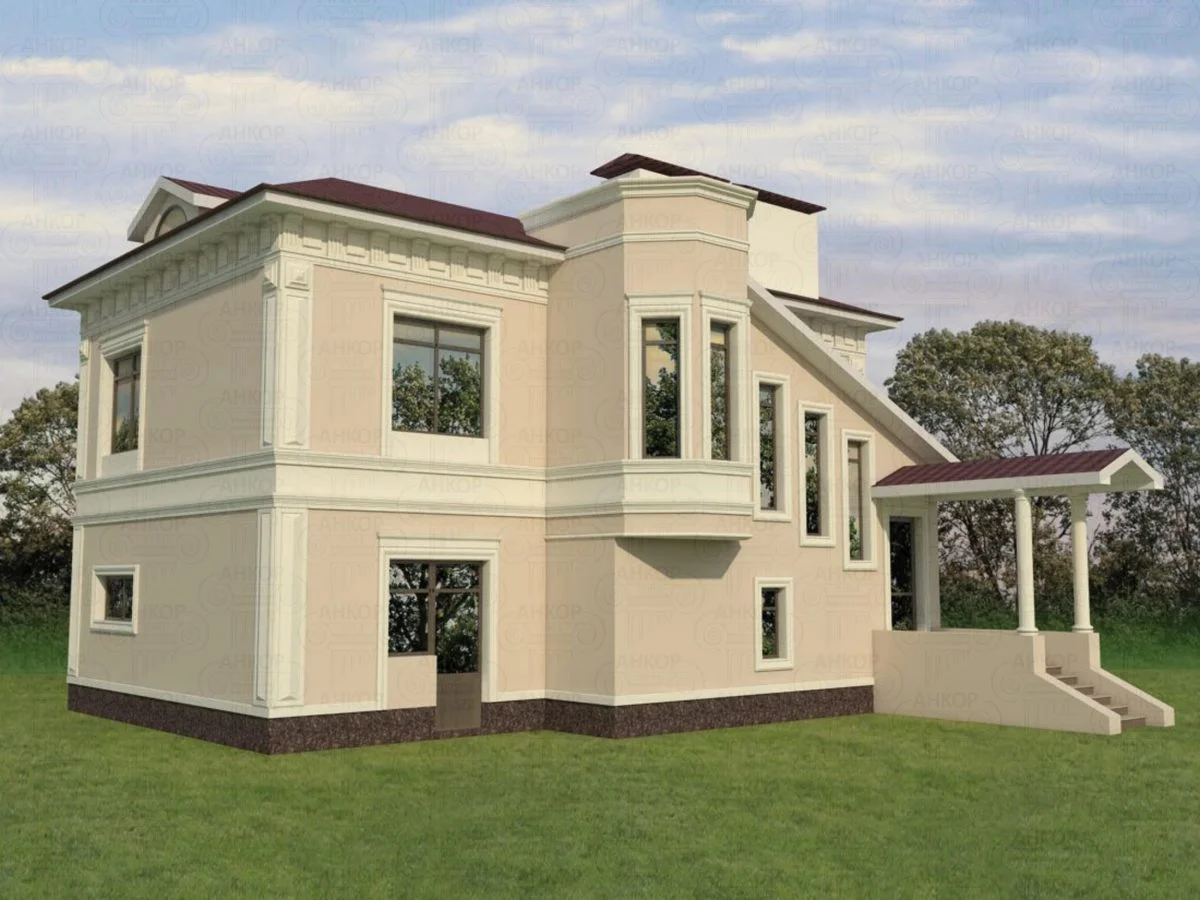
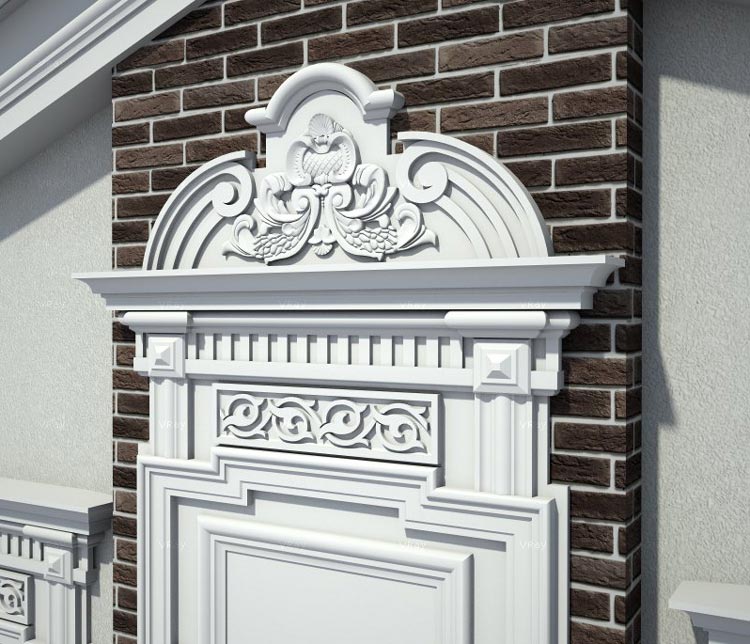
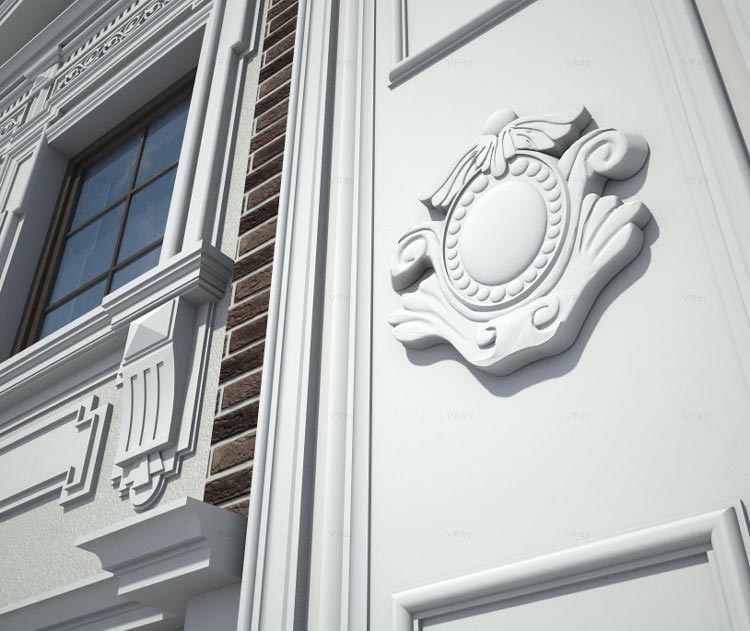
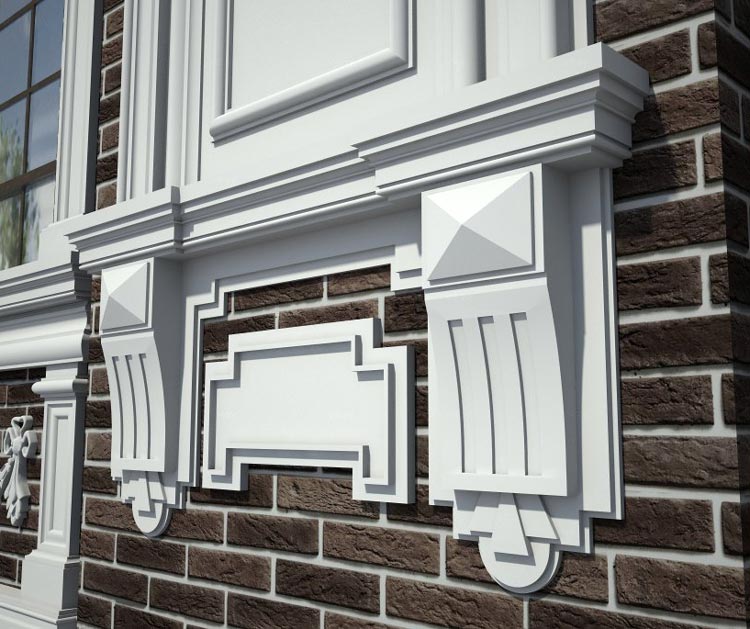
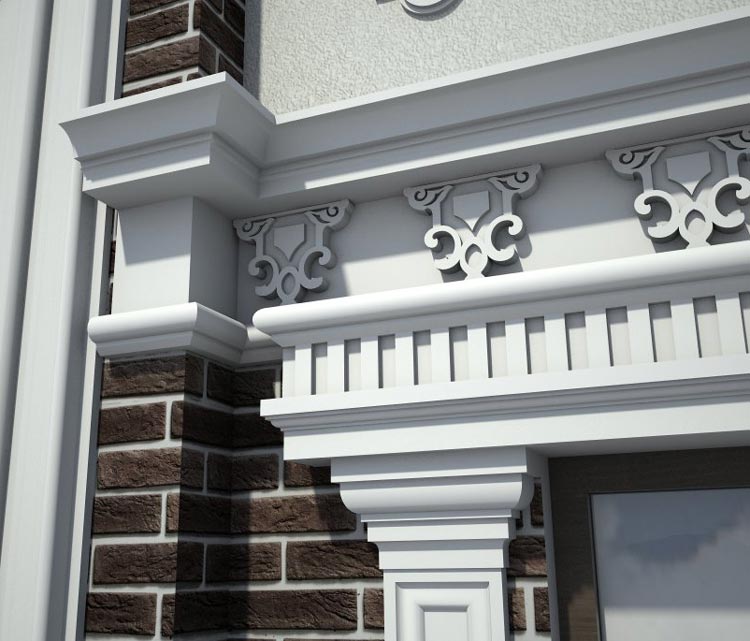
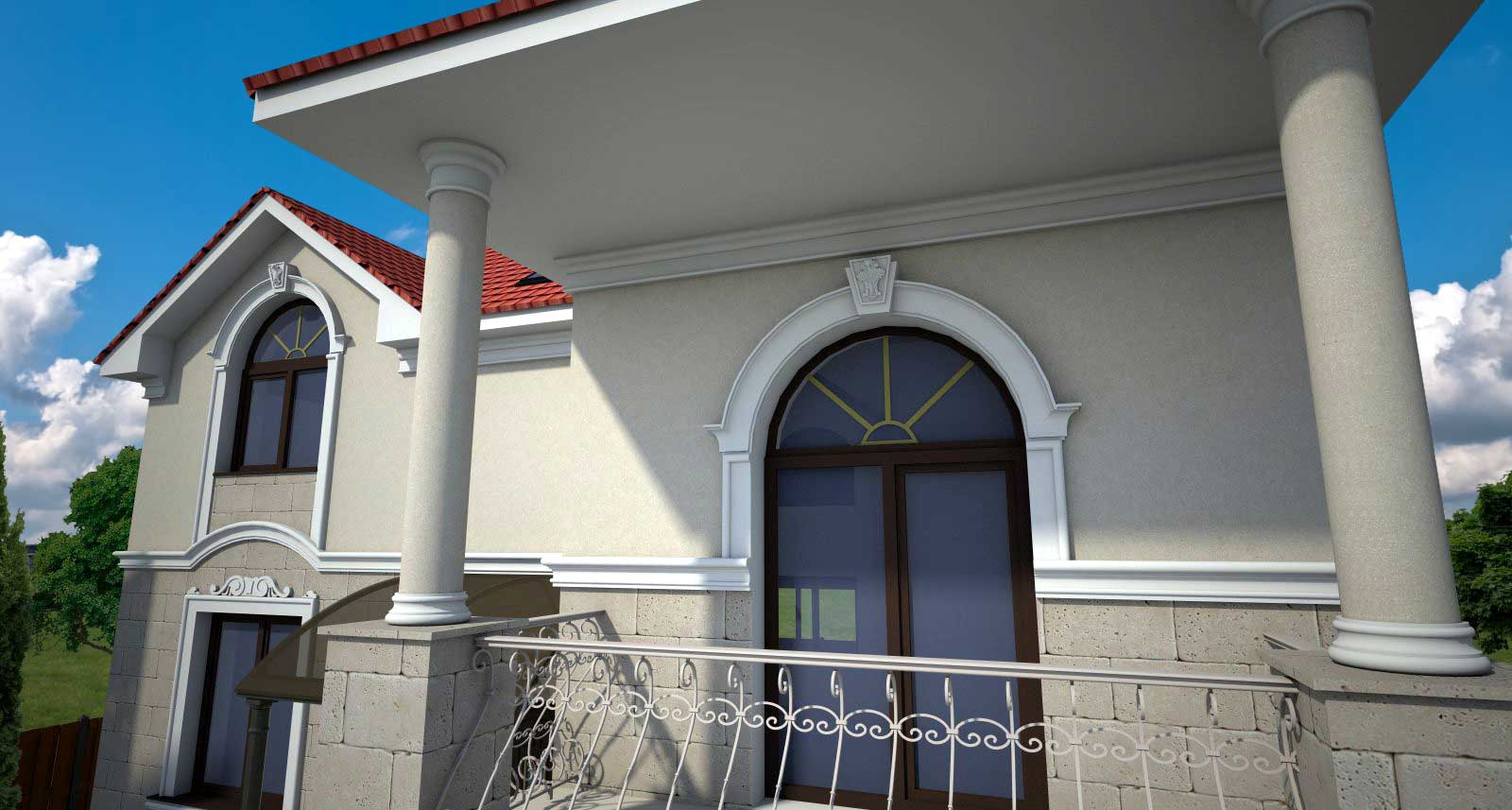
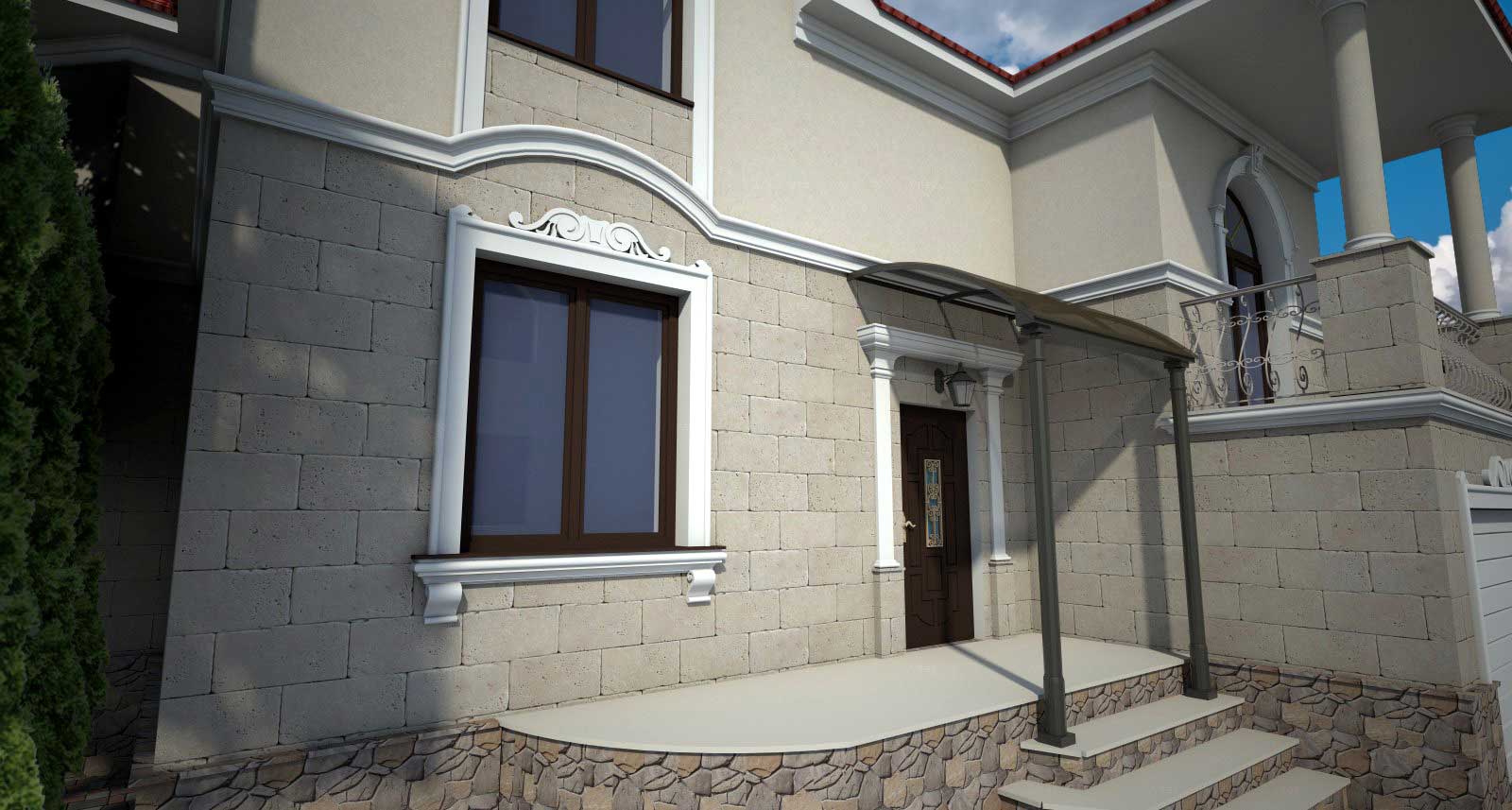
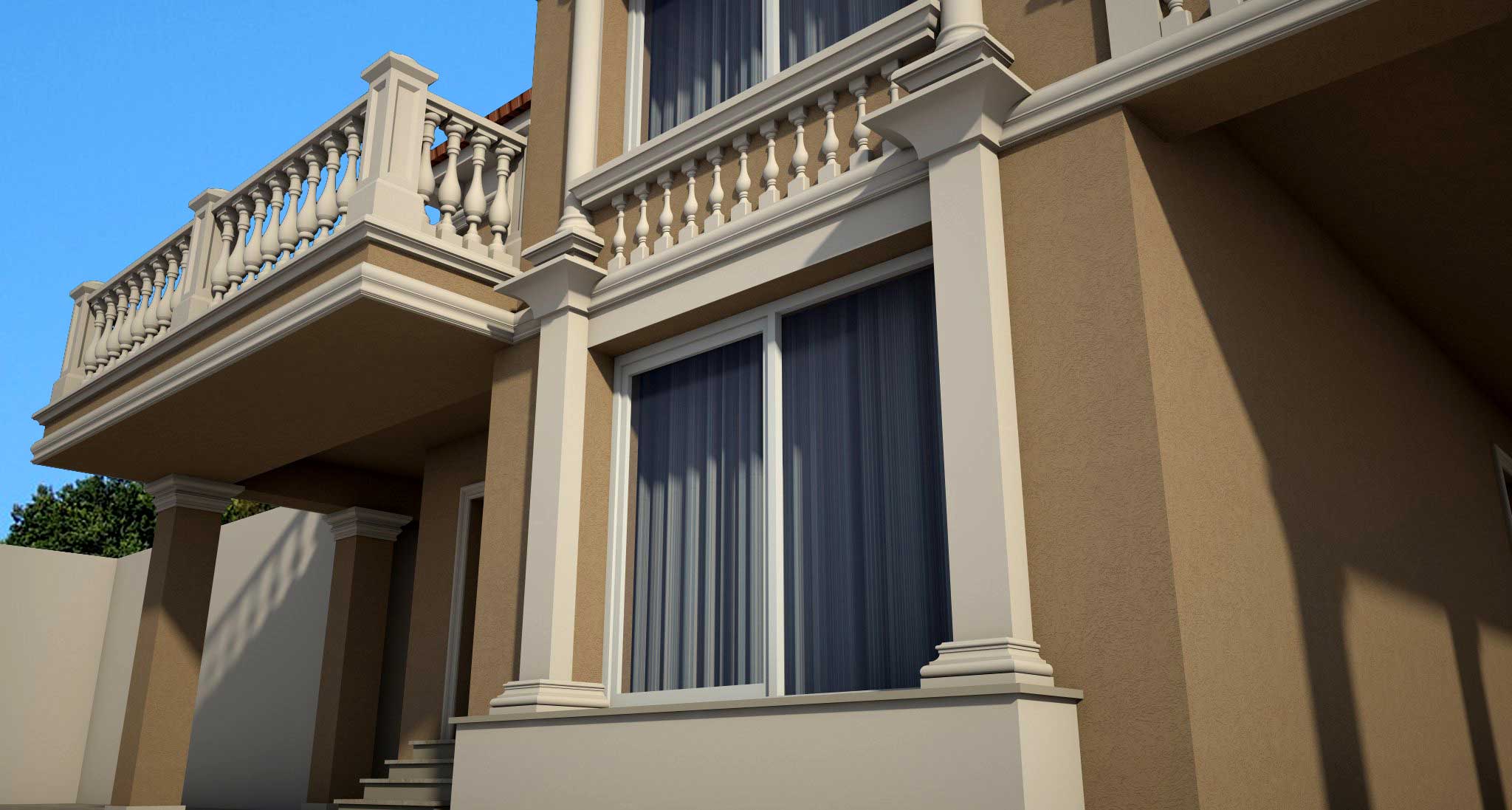
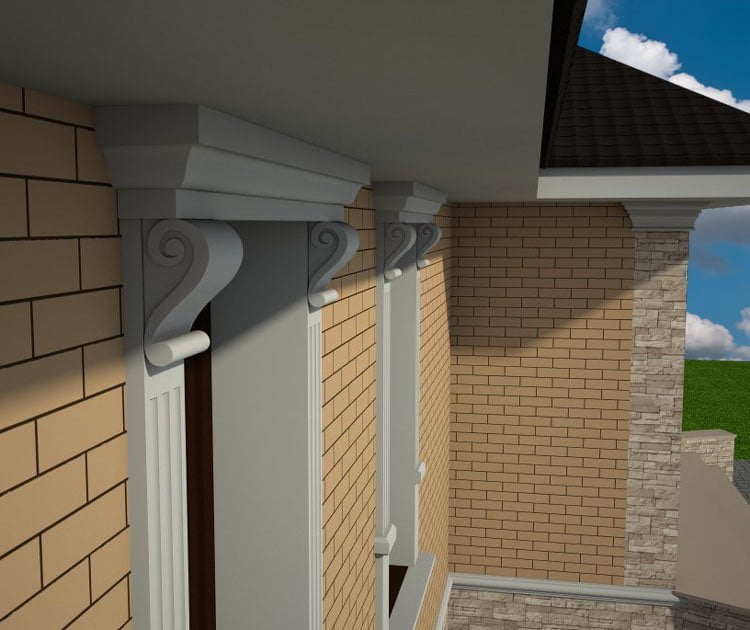
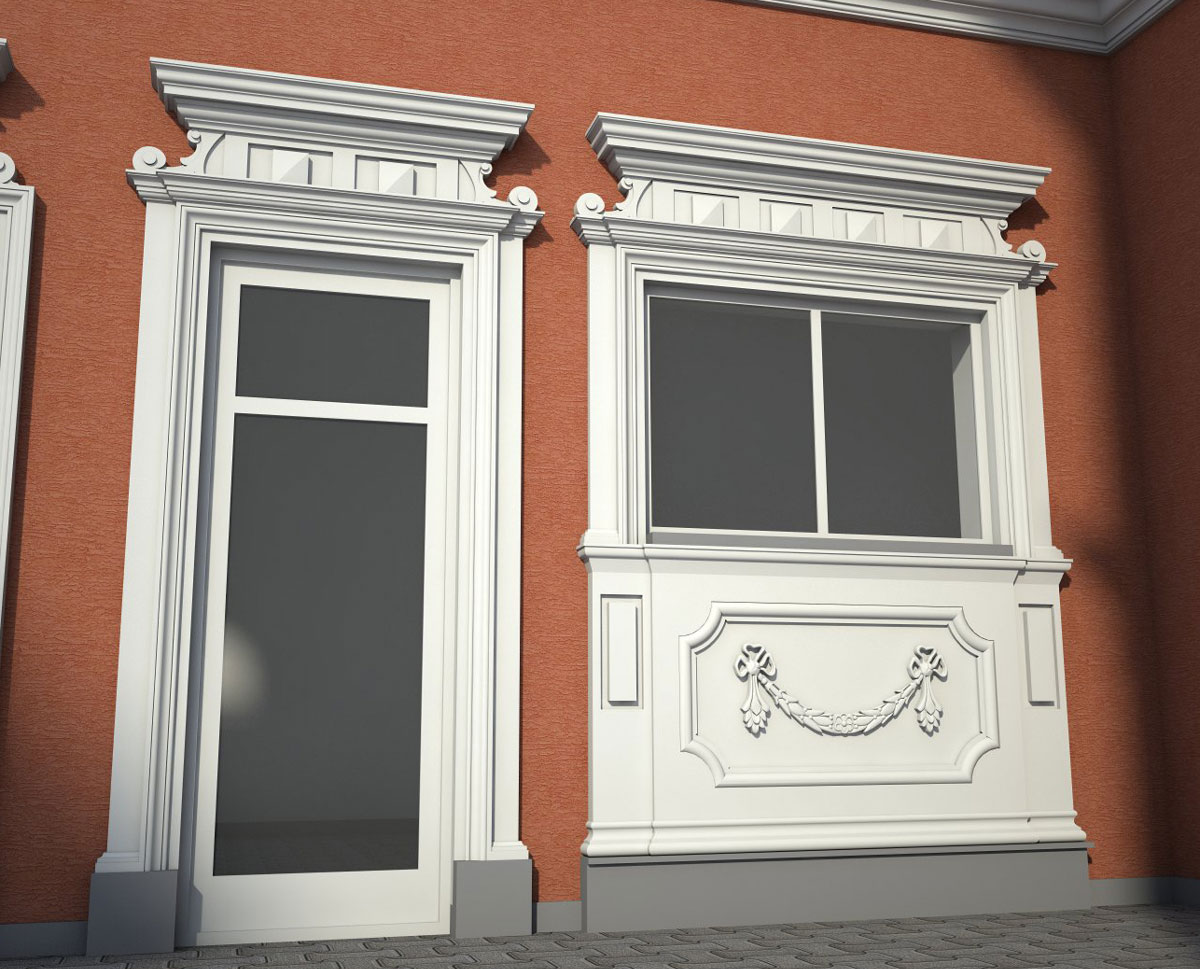
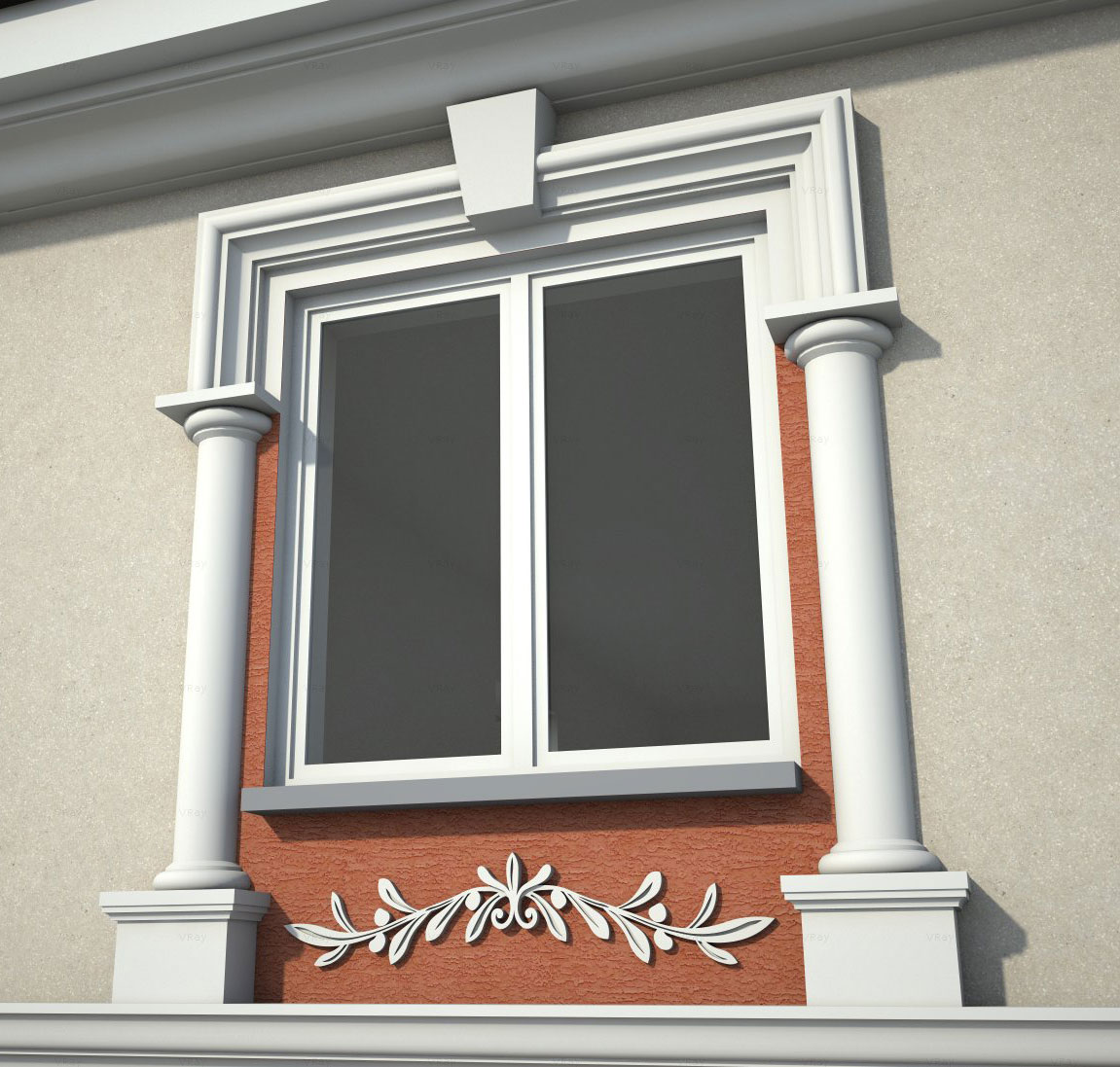
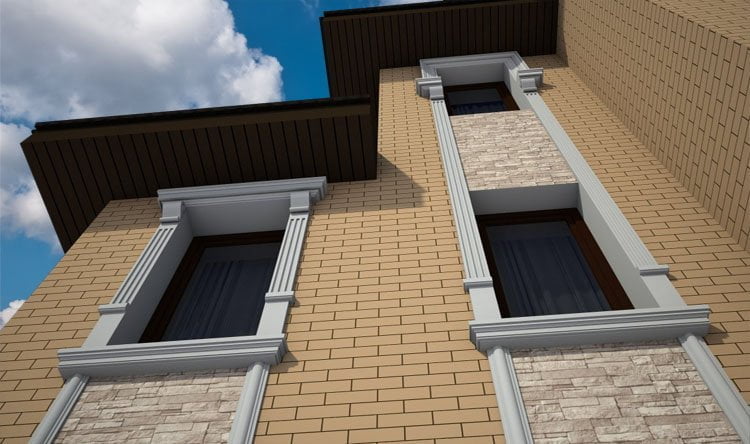
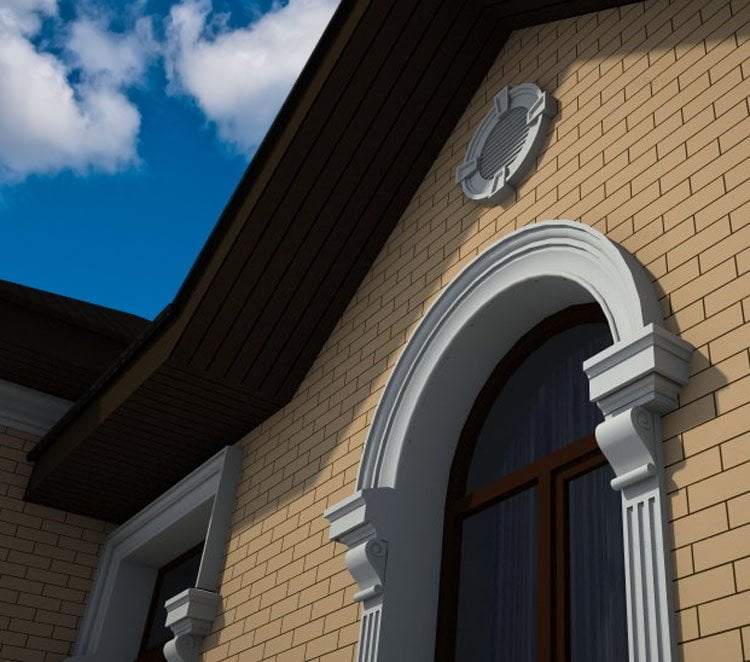
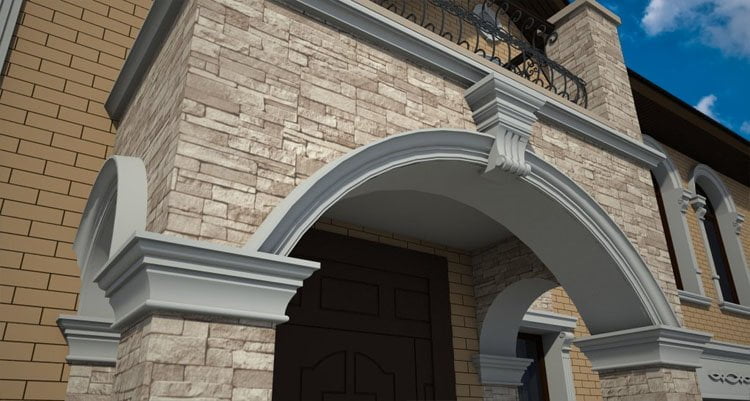
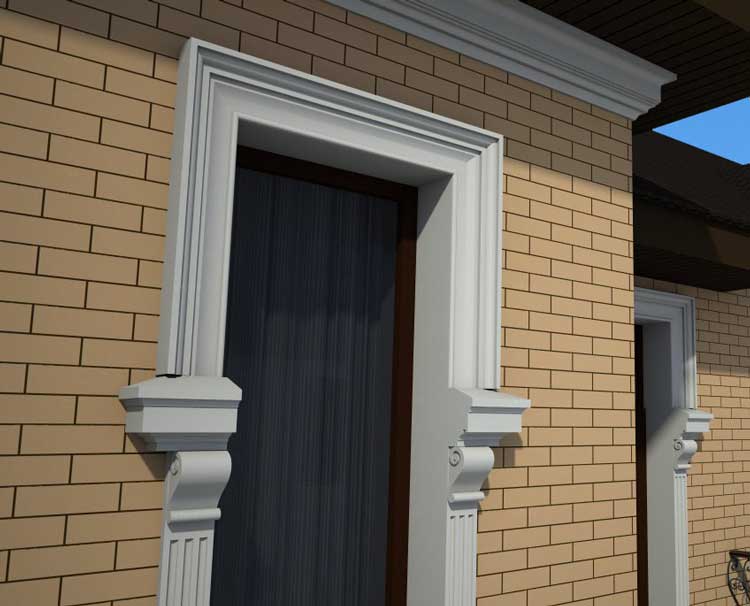
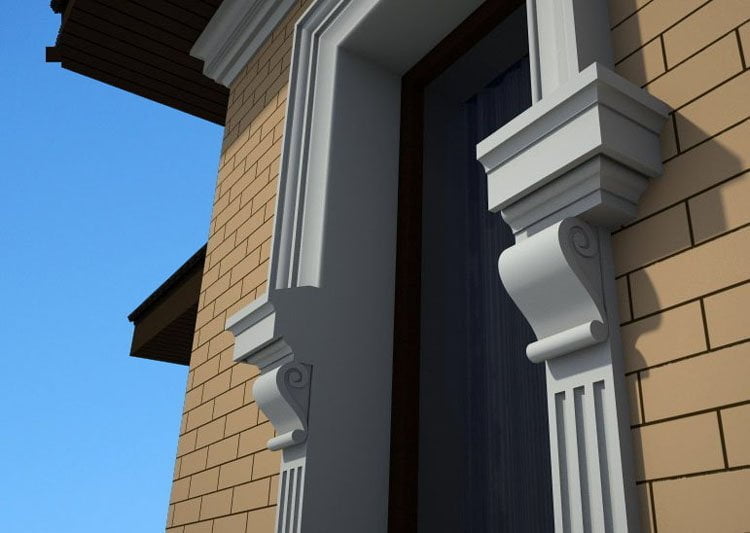
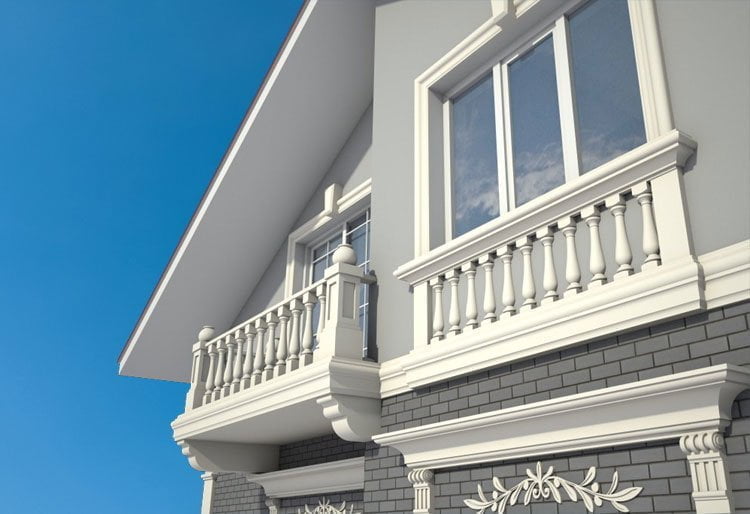
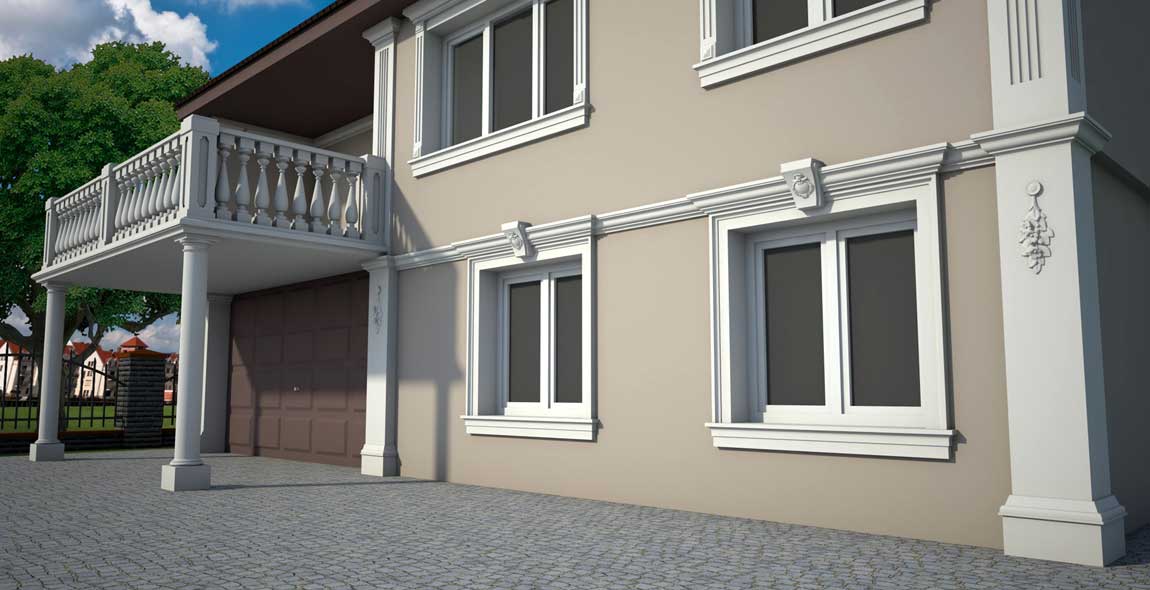
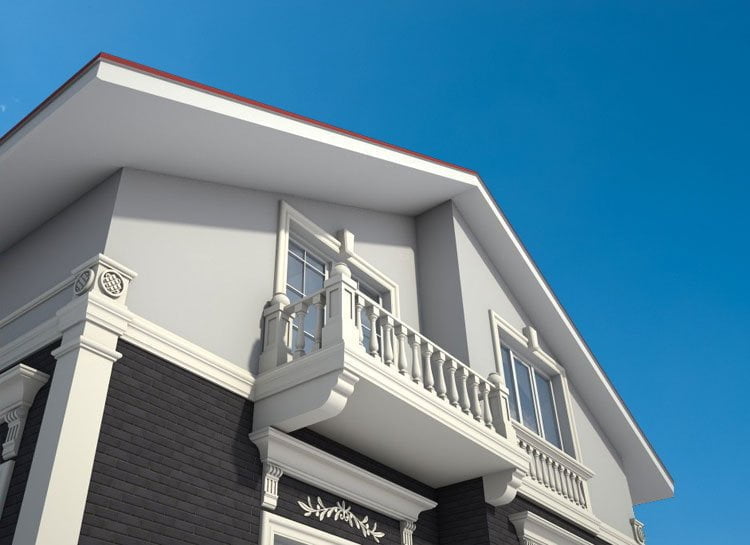
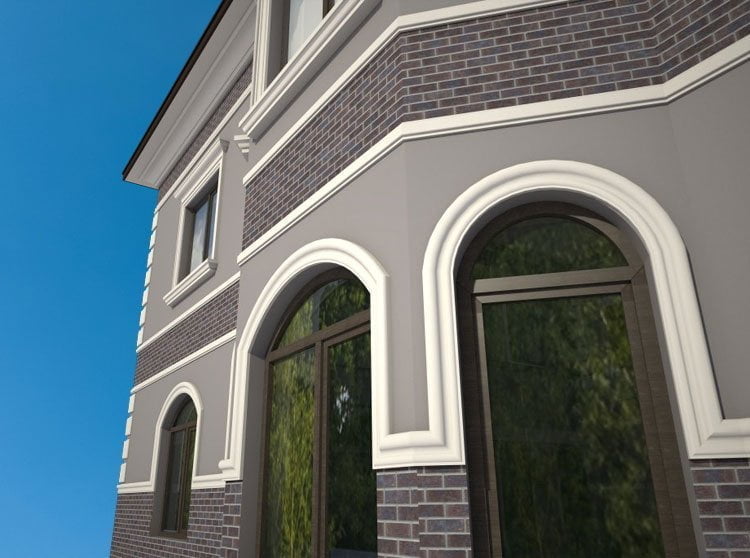
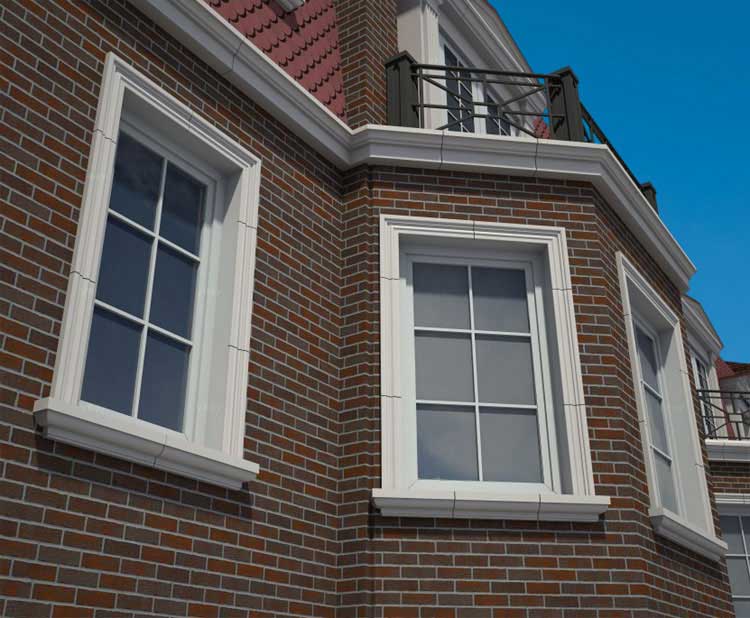
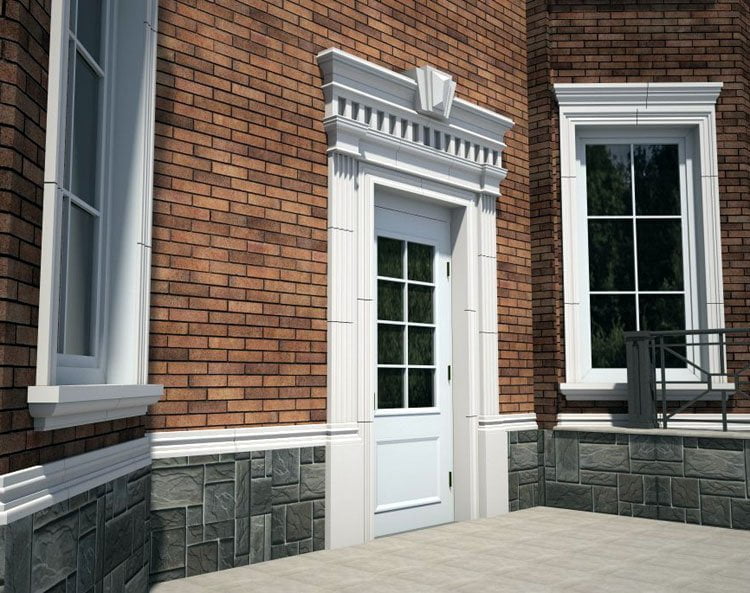
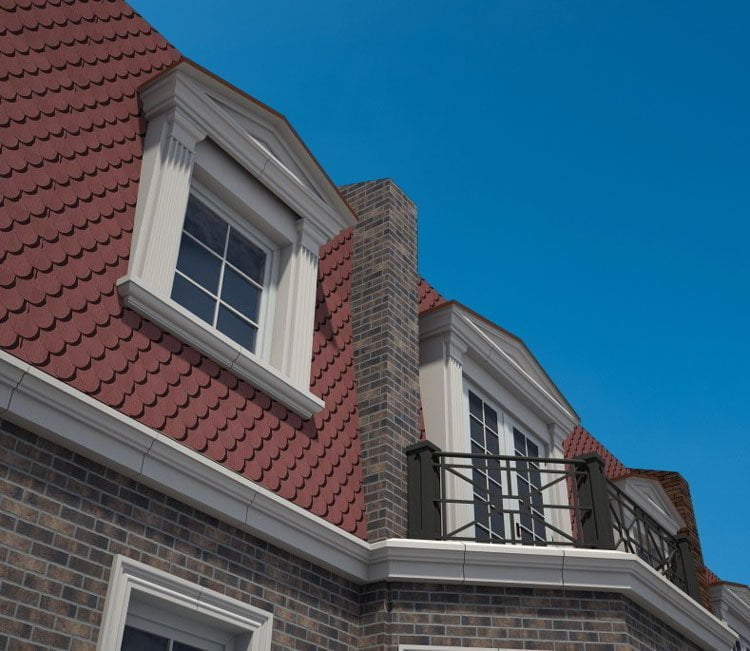
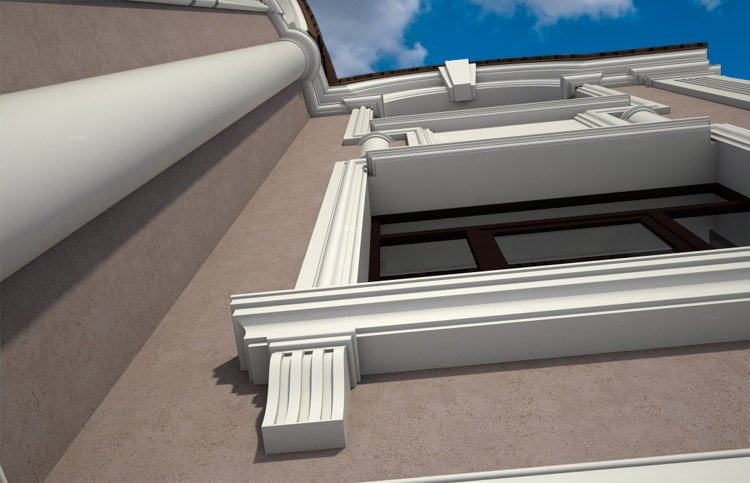
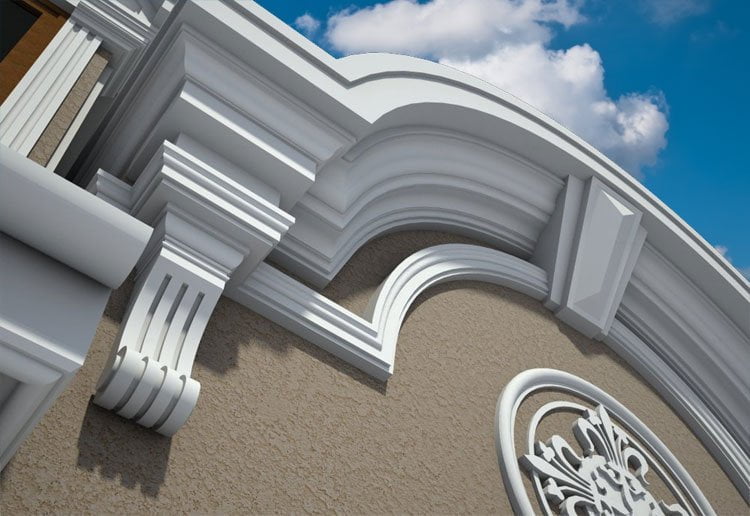
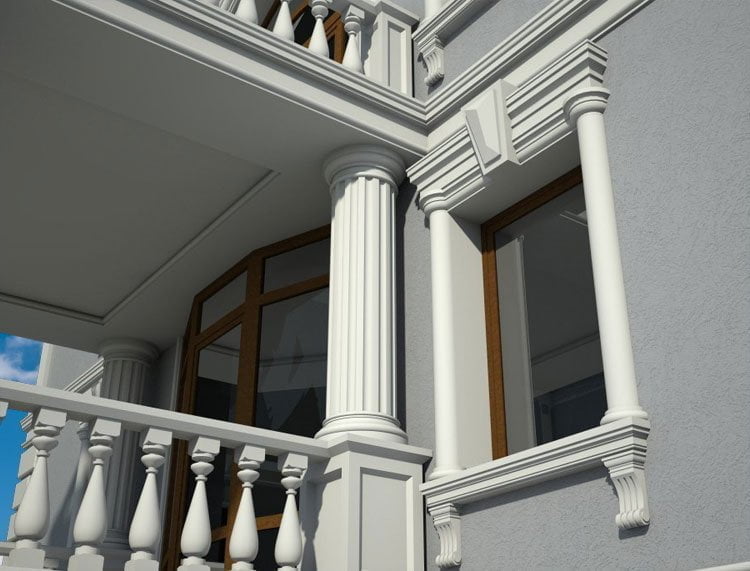
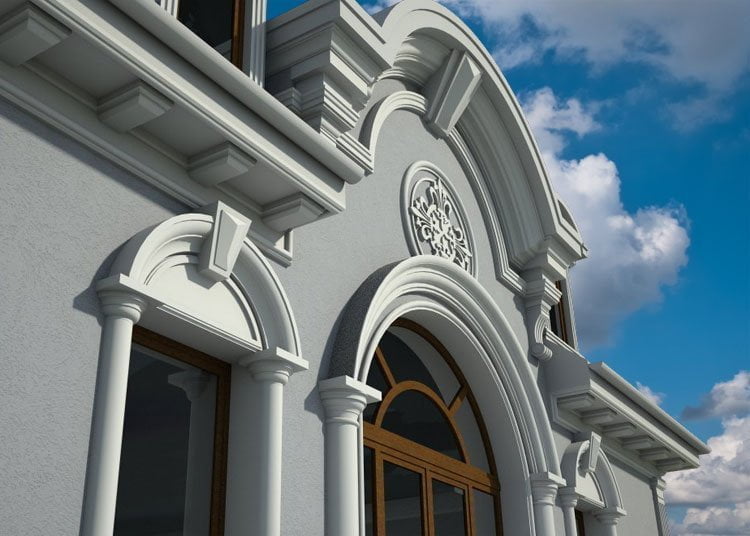
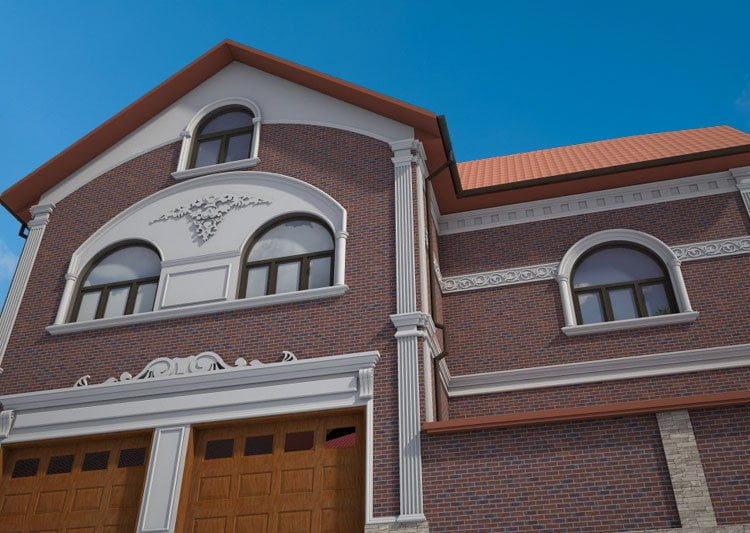
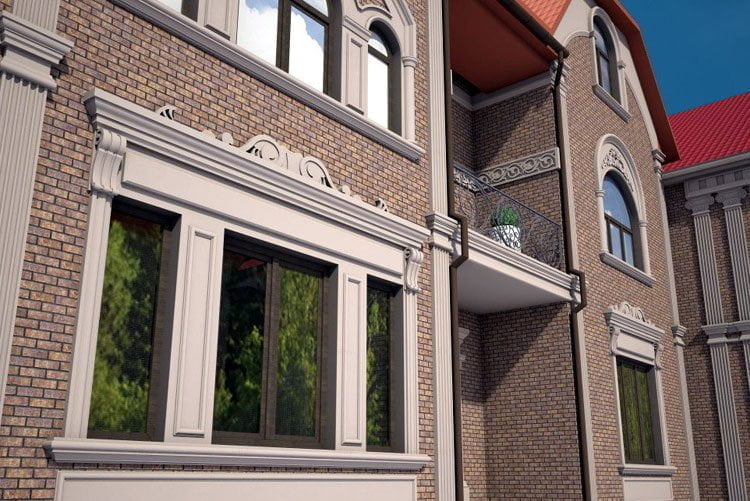
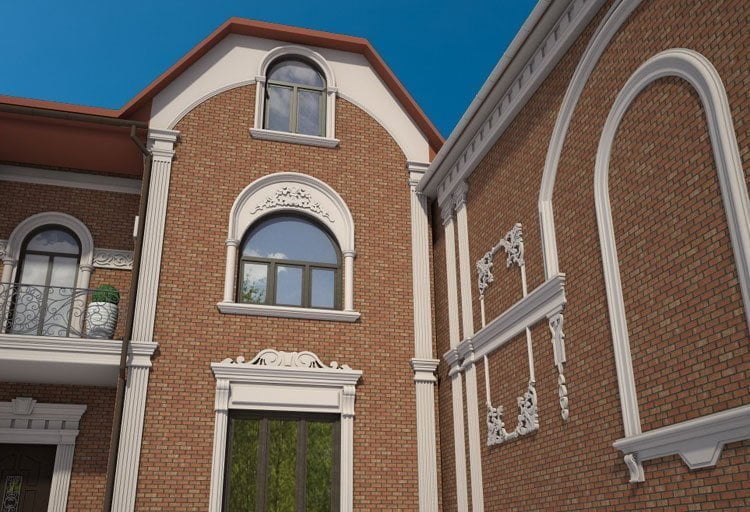
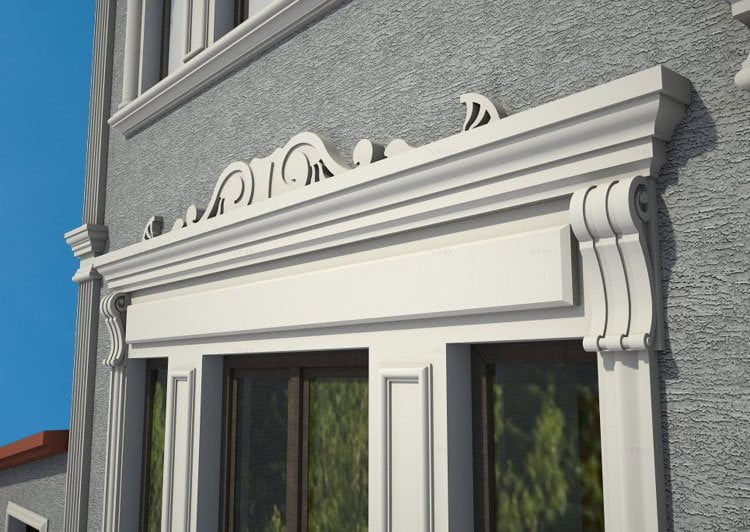
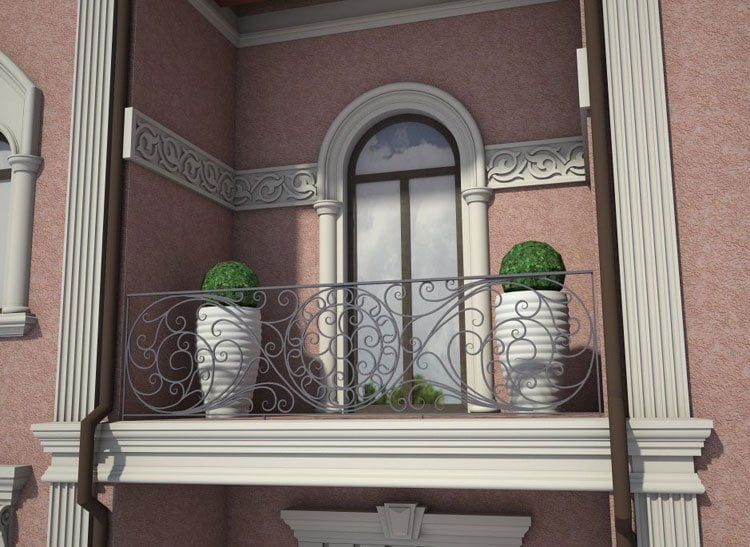
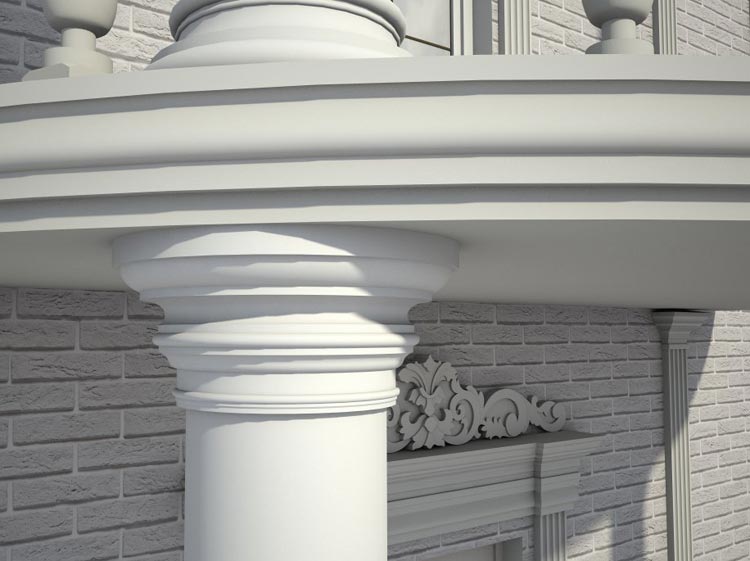
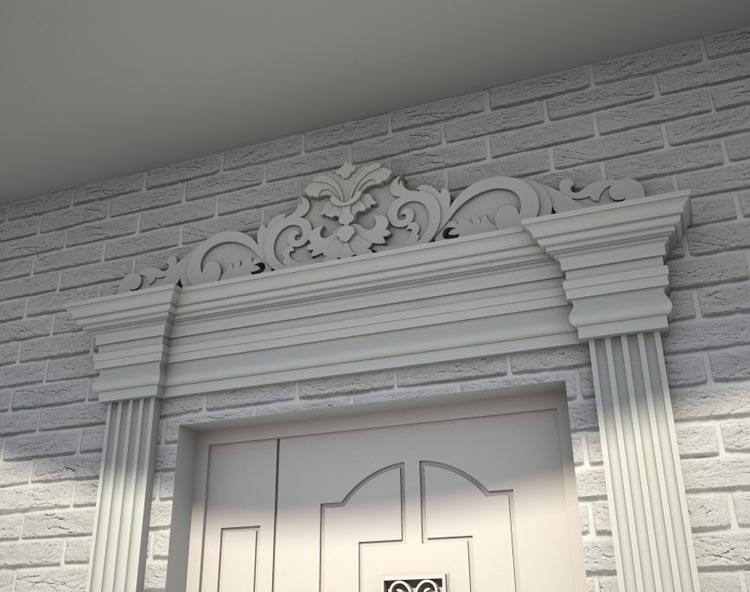
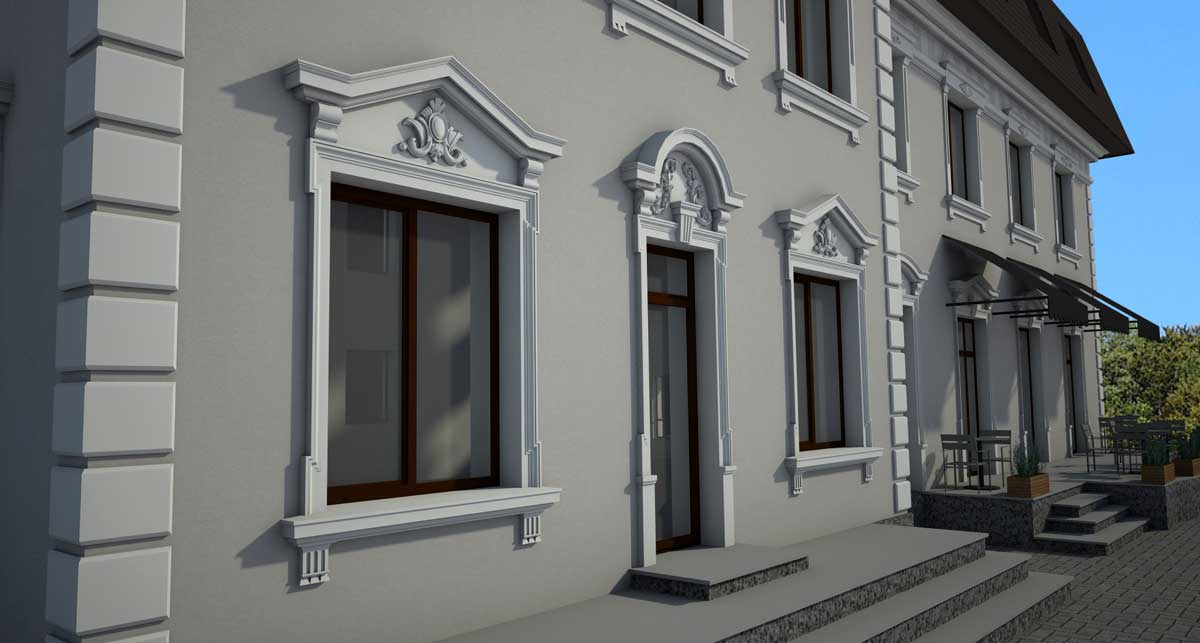
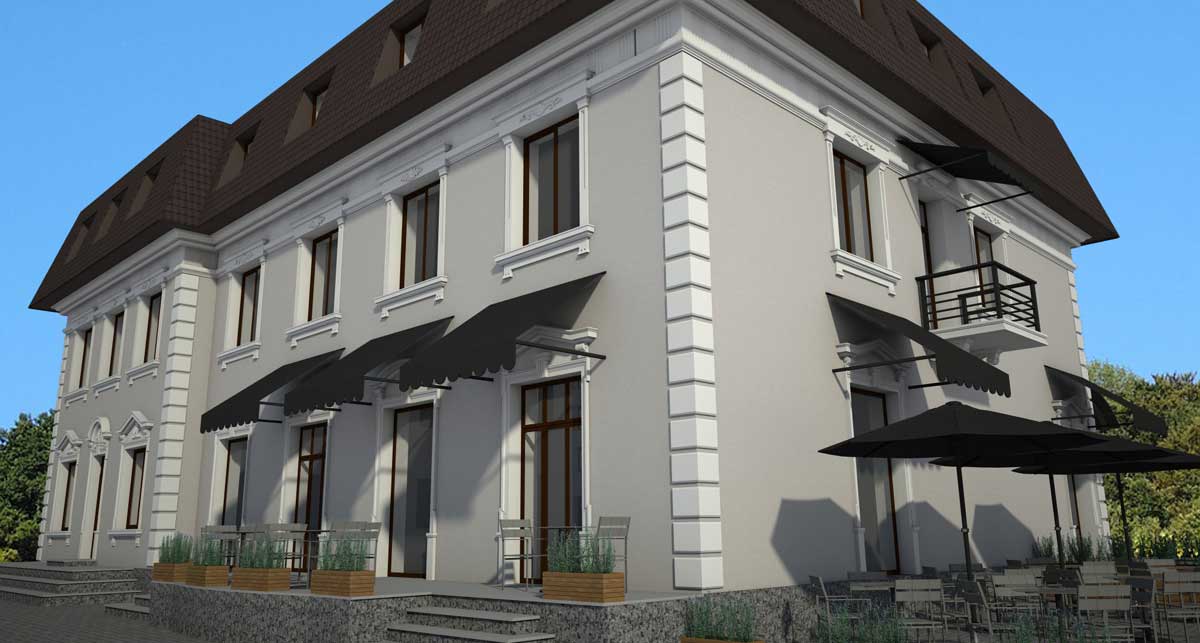
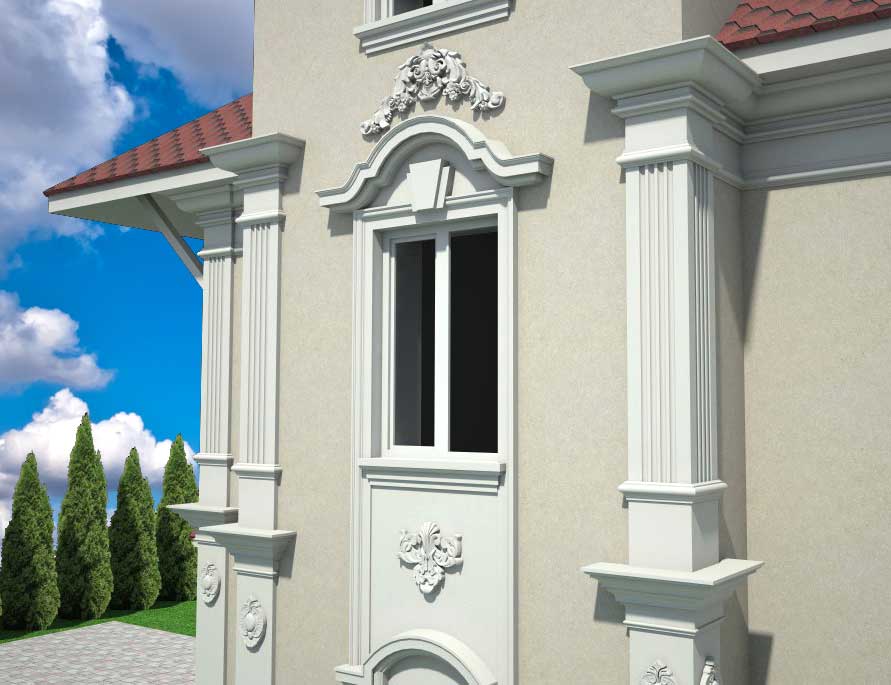
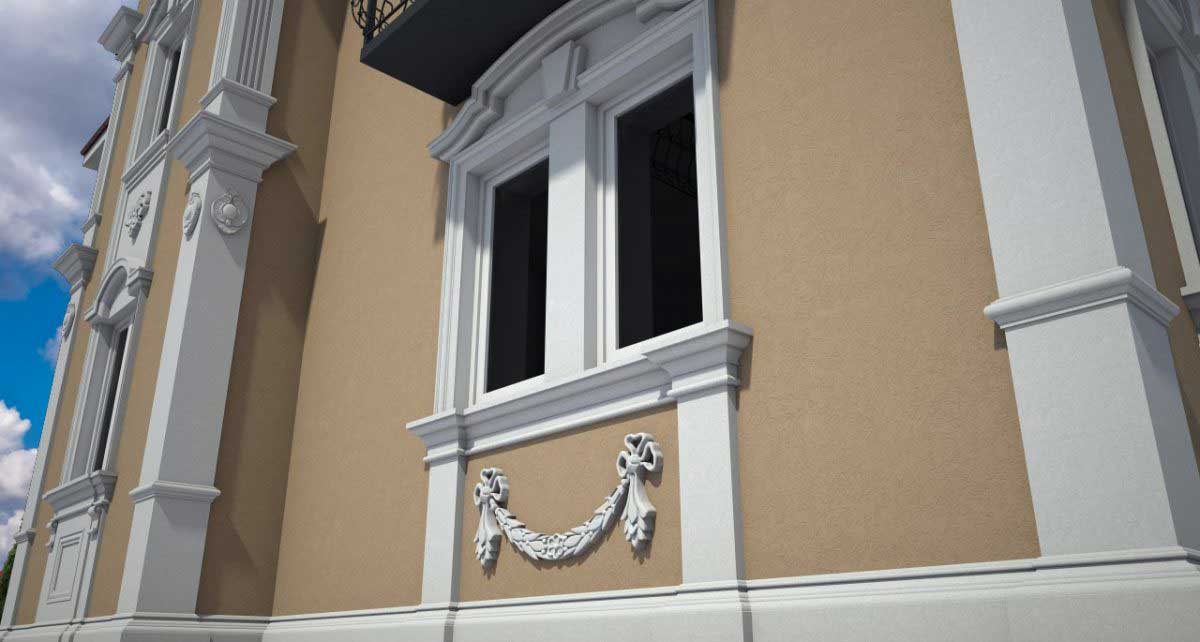
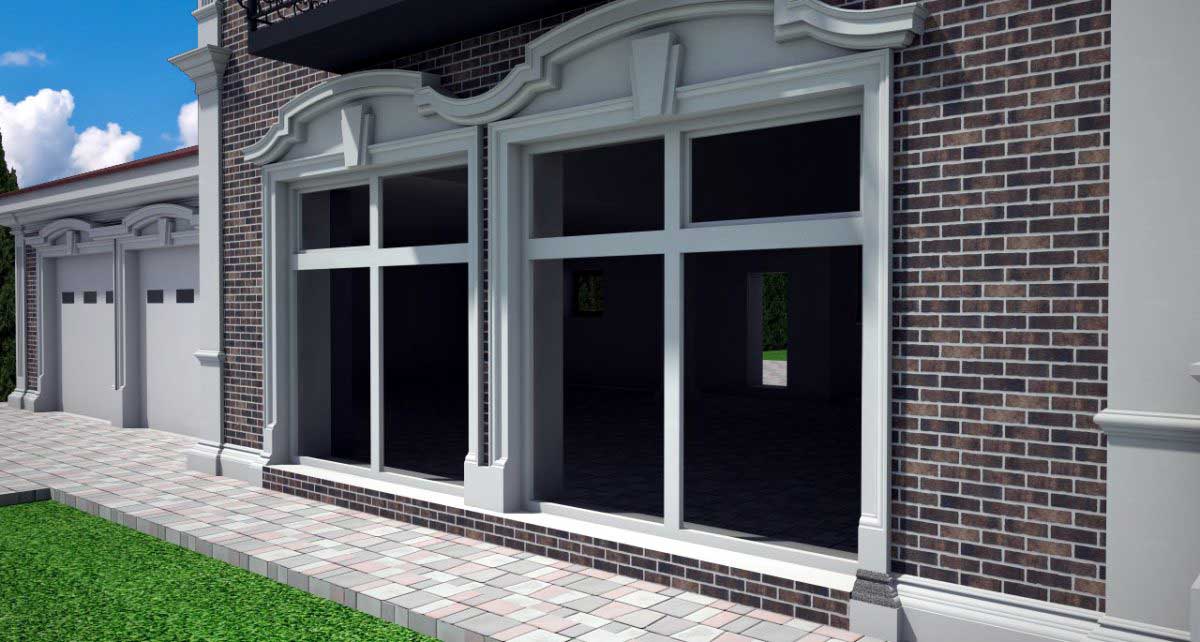
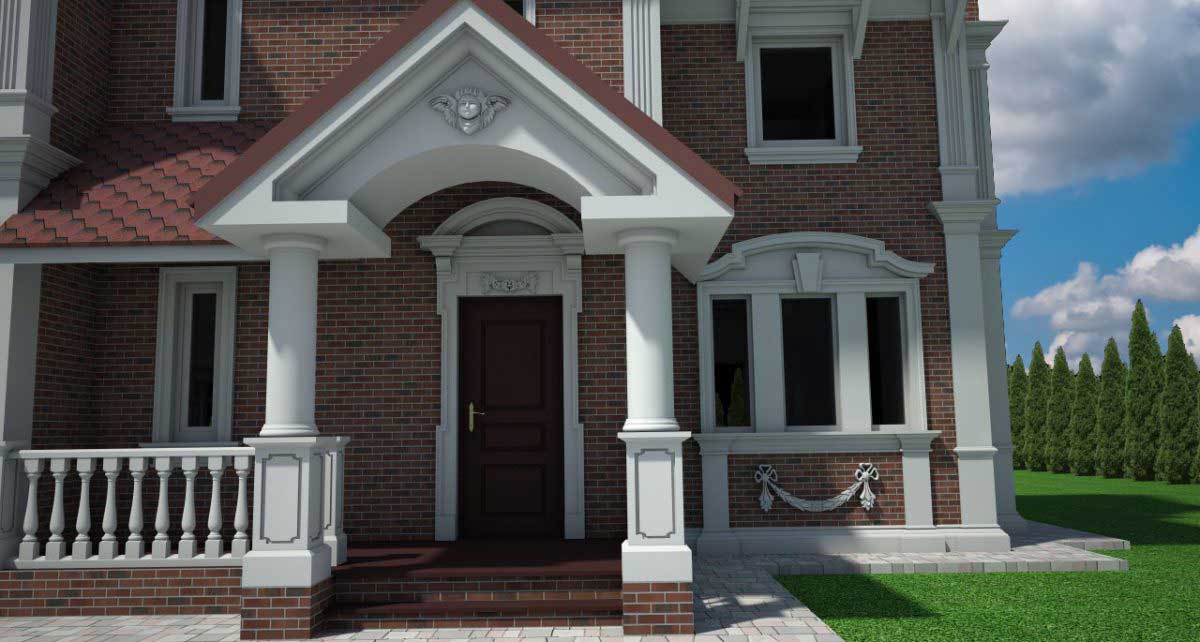
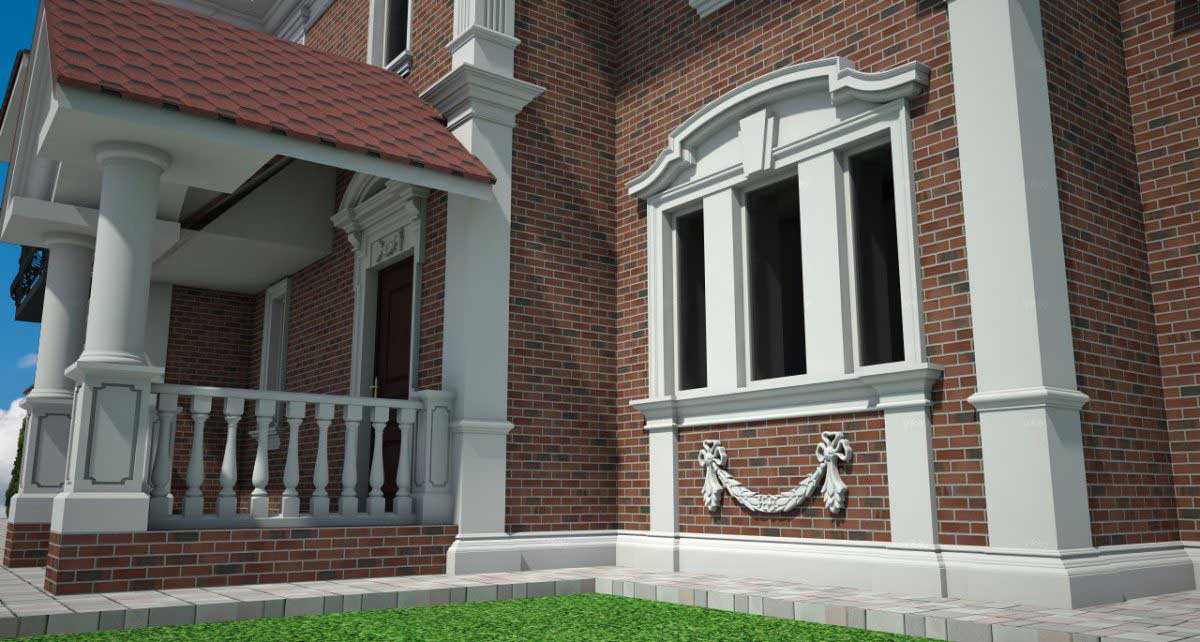
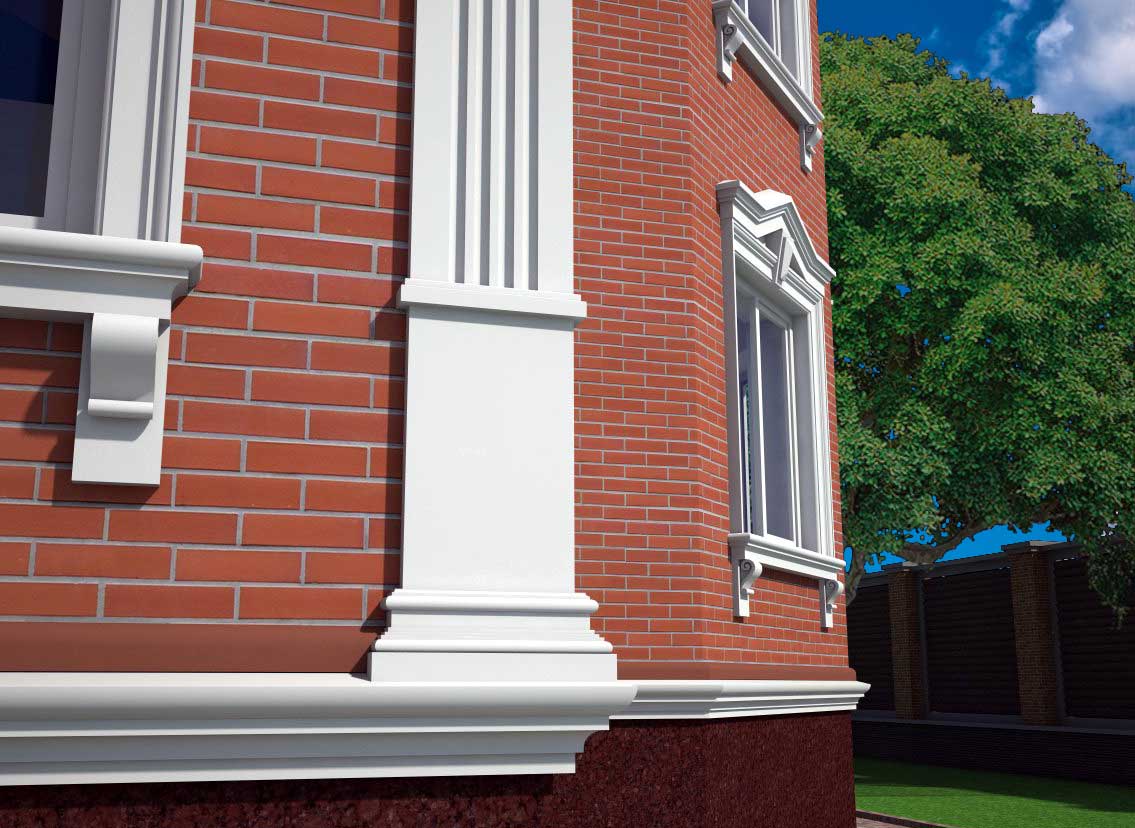
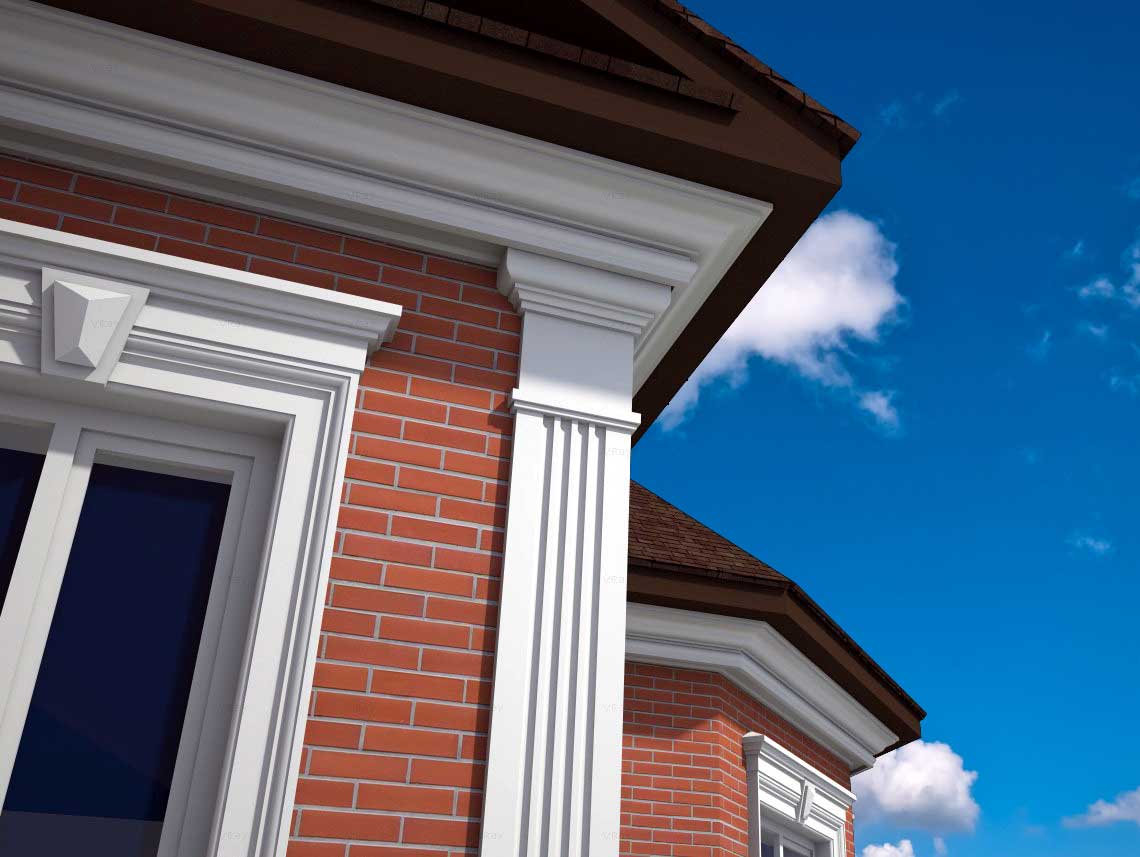
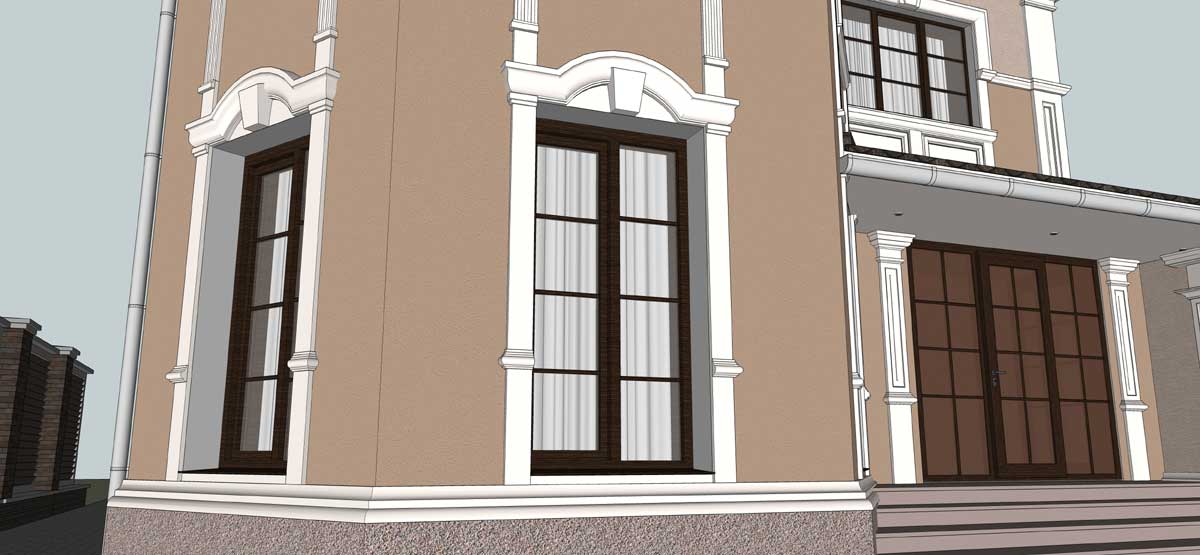
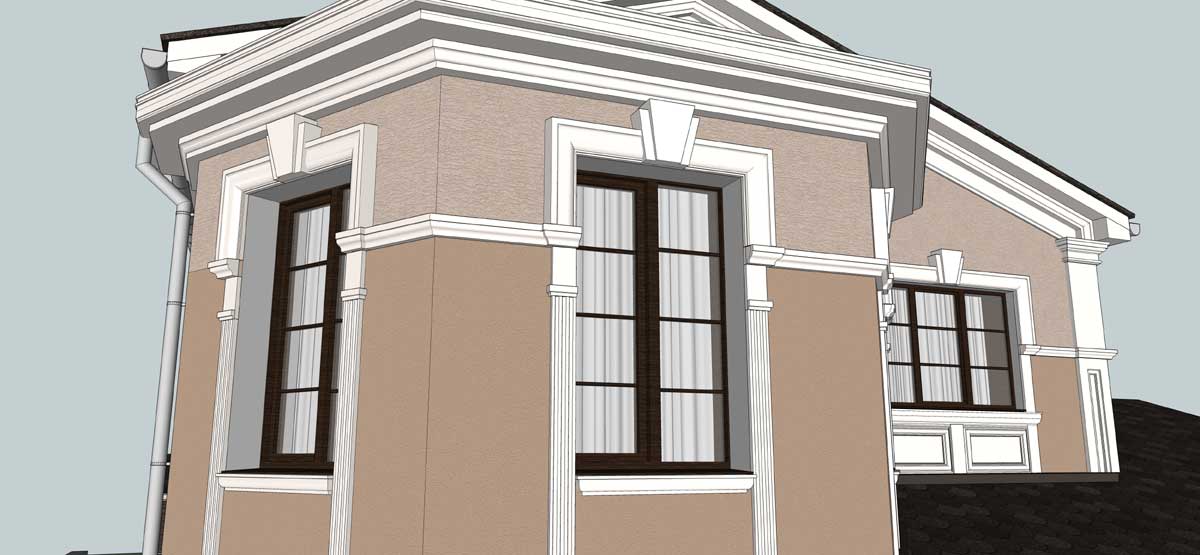
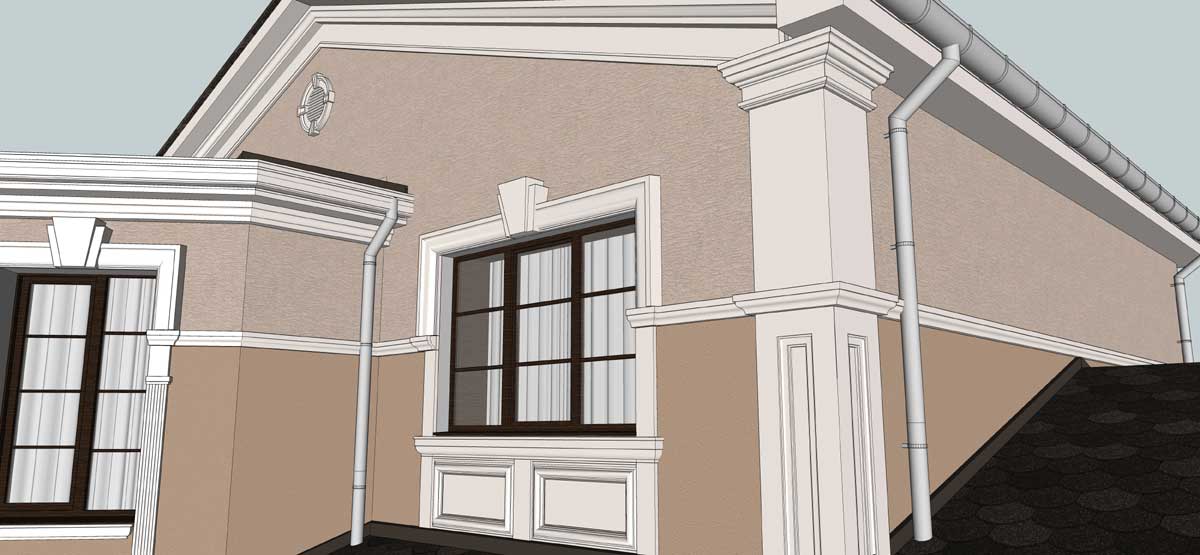
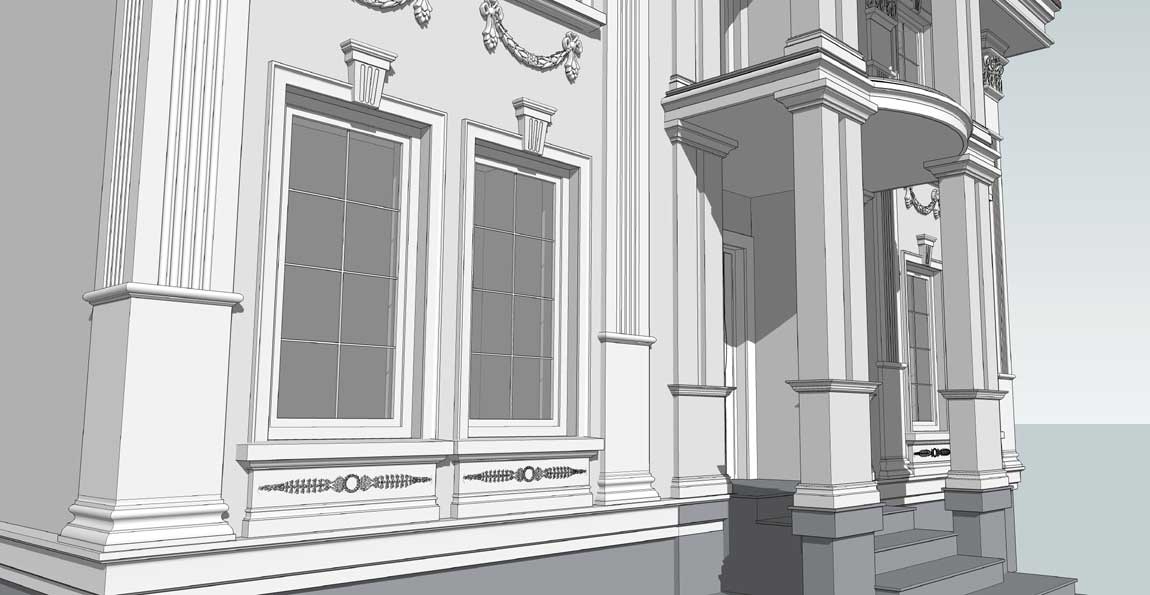
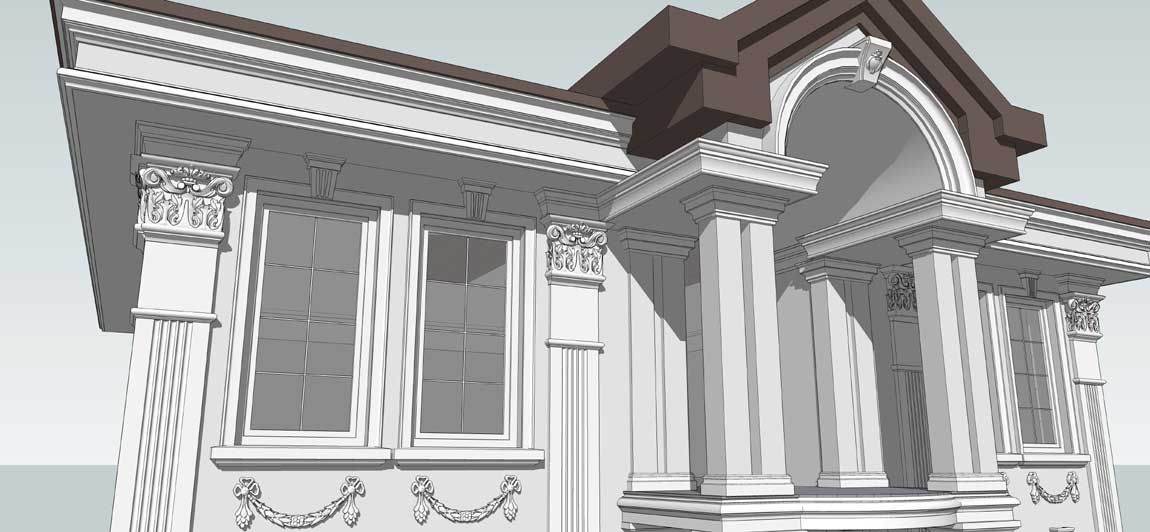
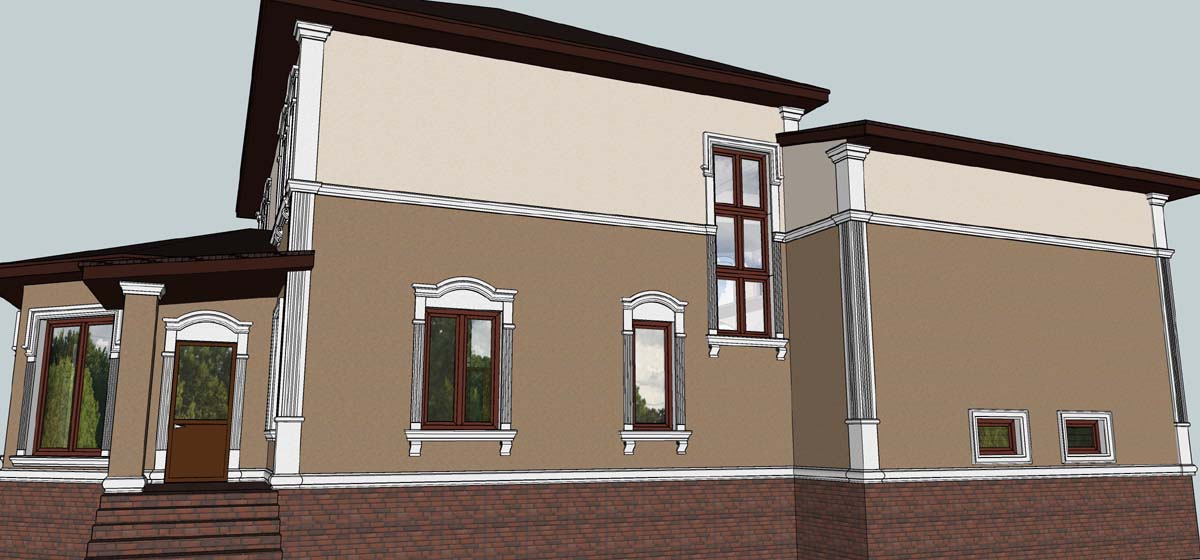
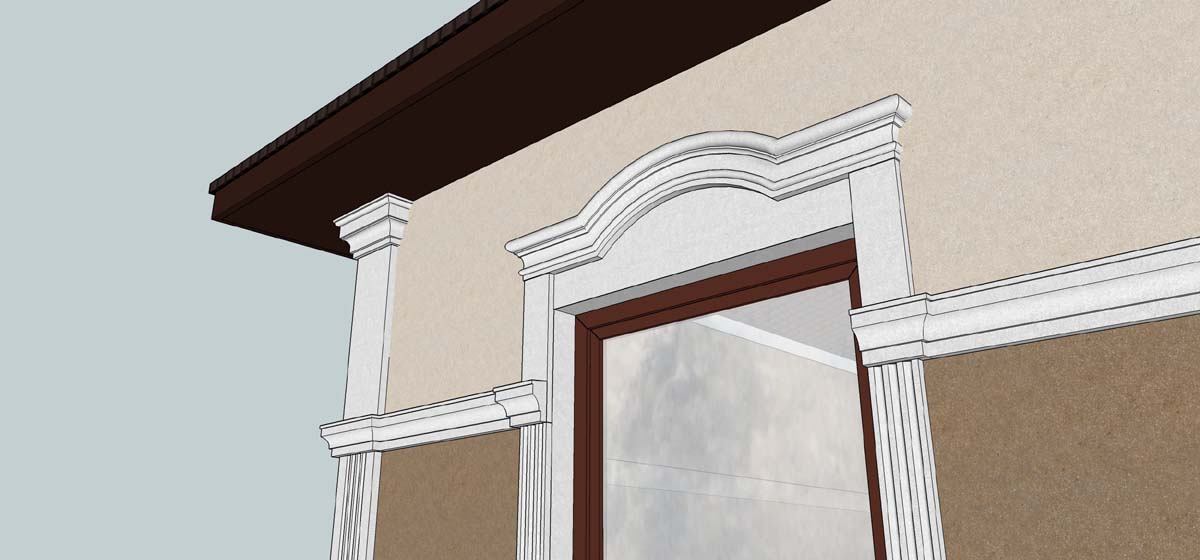
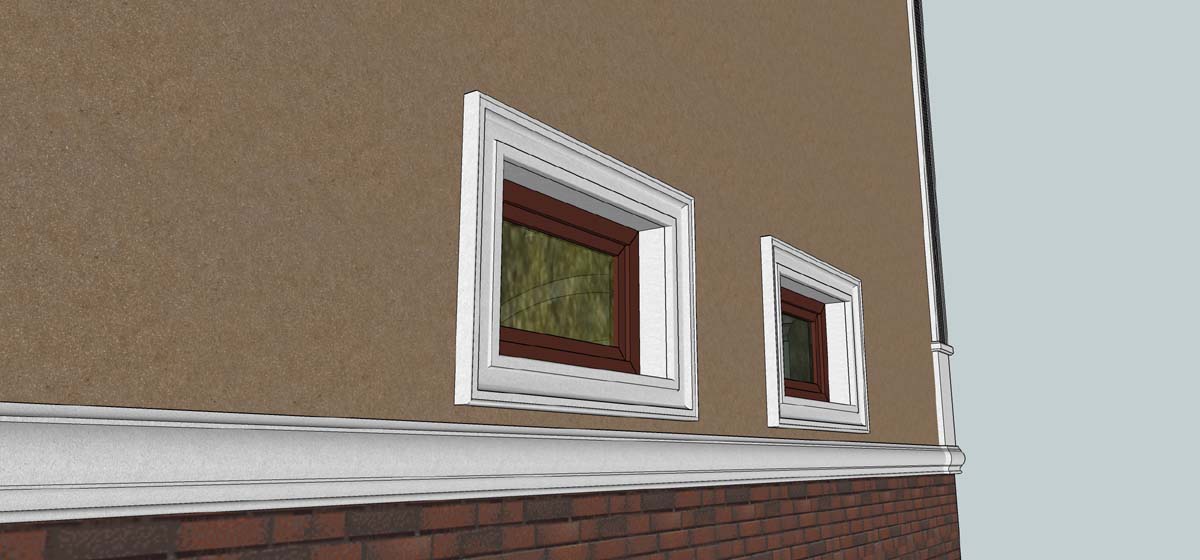
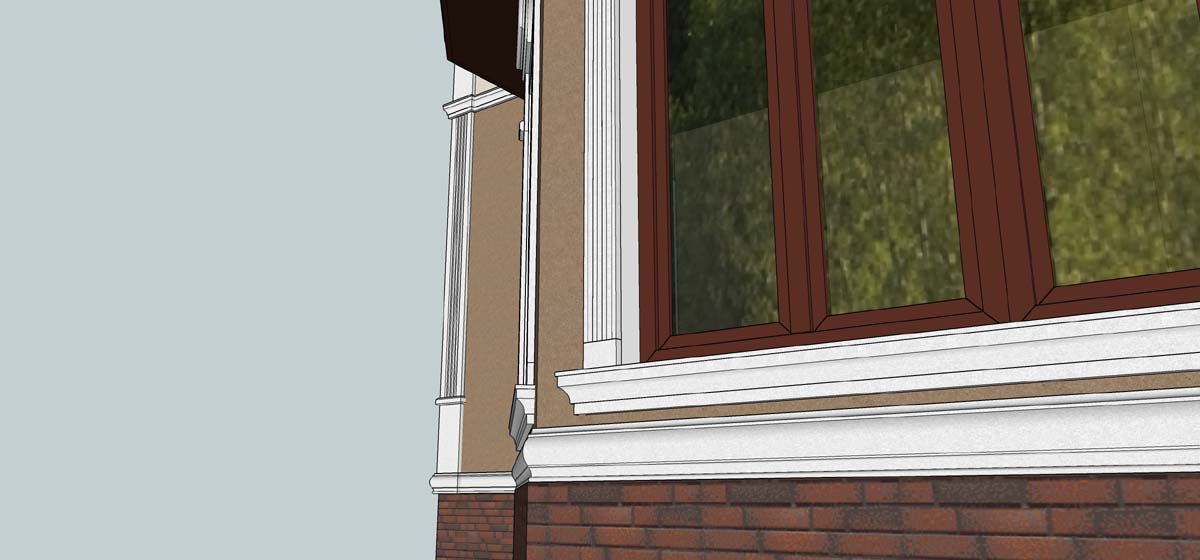
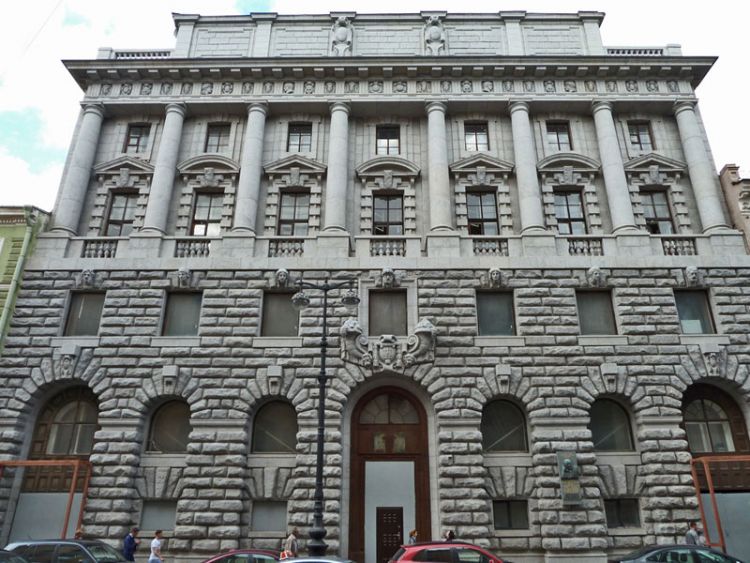
OUR HOUSE FRONT DESIGN FRAGMENTS
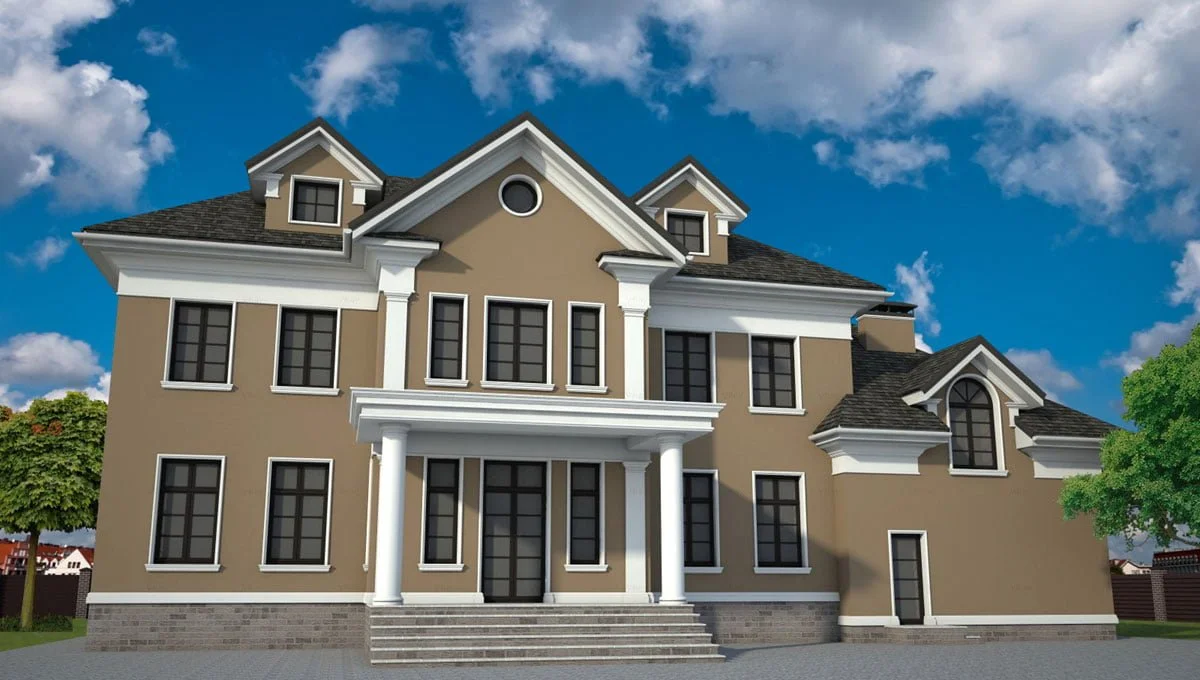
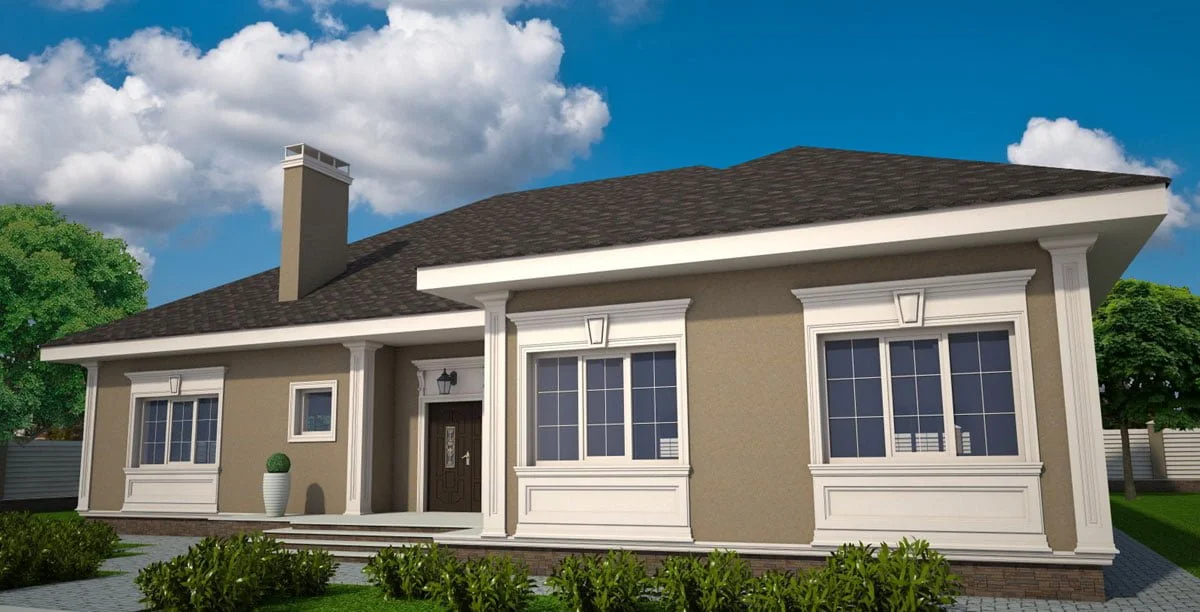
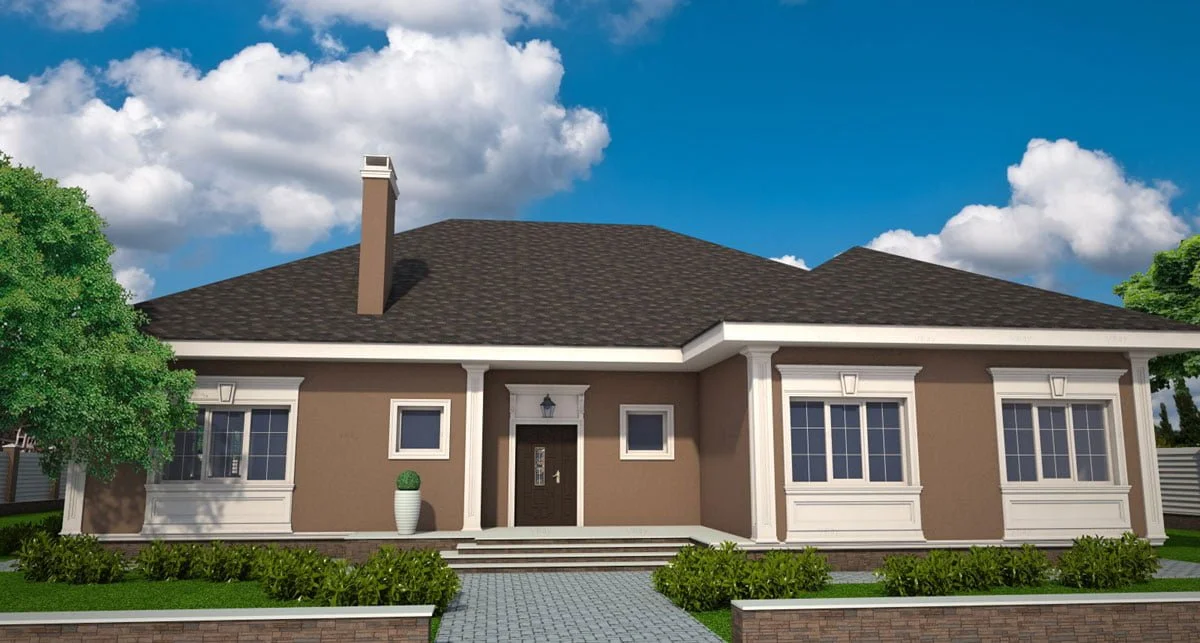
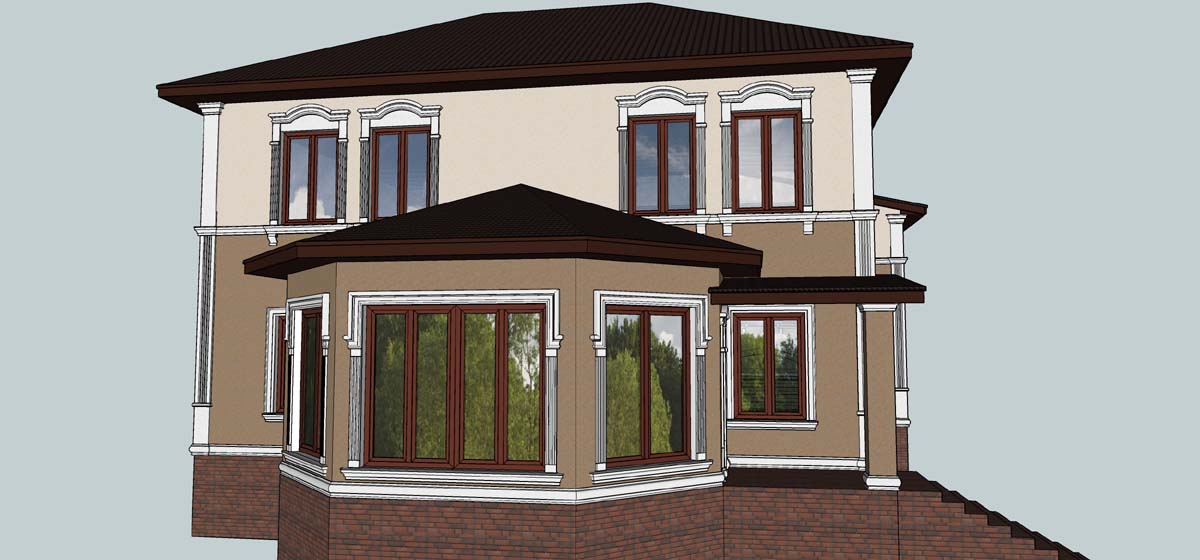
Below you can familiarize yourself with the projects of building facades that we have created for our customers over the past several years. Among them there are representatives of different architectural styles, as well as all of them, to varying degrees, are filled with elements of architectural decor. Perhaps you will like something from what you have seen and want to decorate your house in the same way. With the help of these examples, it will be easier for us to work out the design of the facade of your house.
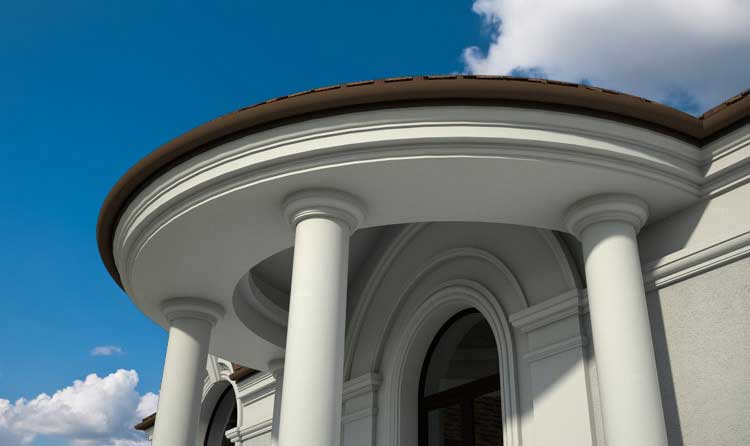
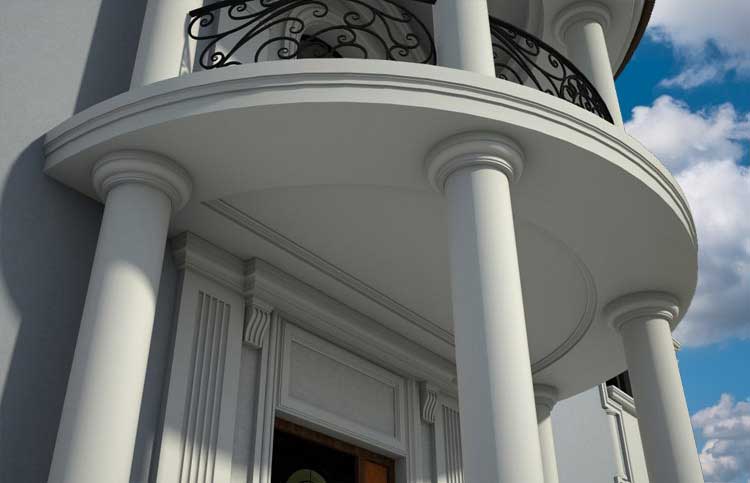
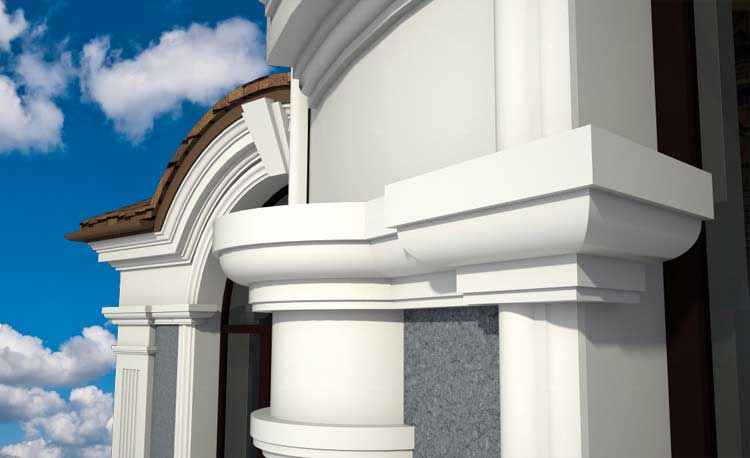
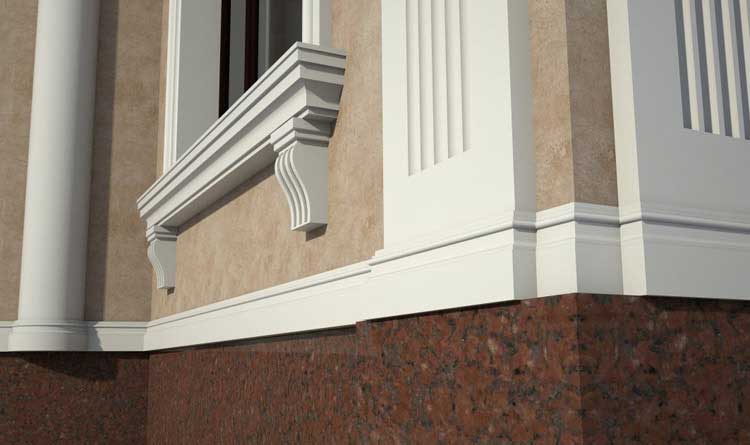



















































































🔻
Our 3D house exterior design process also prioritizes sustainability and eco-friendliness. As we strive to create homes that are both visually appealing and environmentally conscious, we incorporate sustainable materials and energy-efficient technologies whenever possible. Through the use of solar panels, green roofs, and passive heating and cooling techniques, we aim to minimize the environmental footprint of the houses we design while maximizing their long-term performance and durability.
Another significant aspect of our work is the consideration of the surrounding landscape and community in our designs. We believe that a well-designed house should not only complement its natural surroundings but also contribute positively to the aesthetic and social fabric of the neighborhood. By carefully analyzing site-specific factors such as topography, climate, and local architectural styles, we ensure that our designs are harmoniously integrated into their environments and resonate with the character of the area.
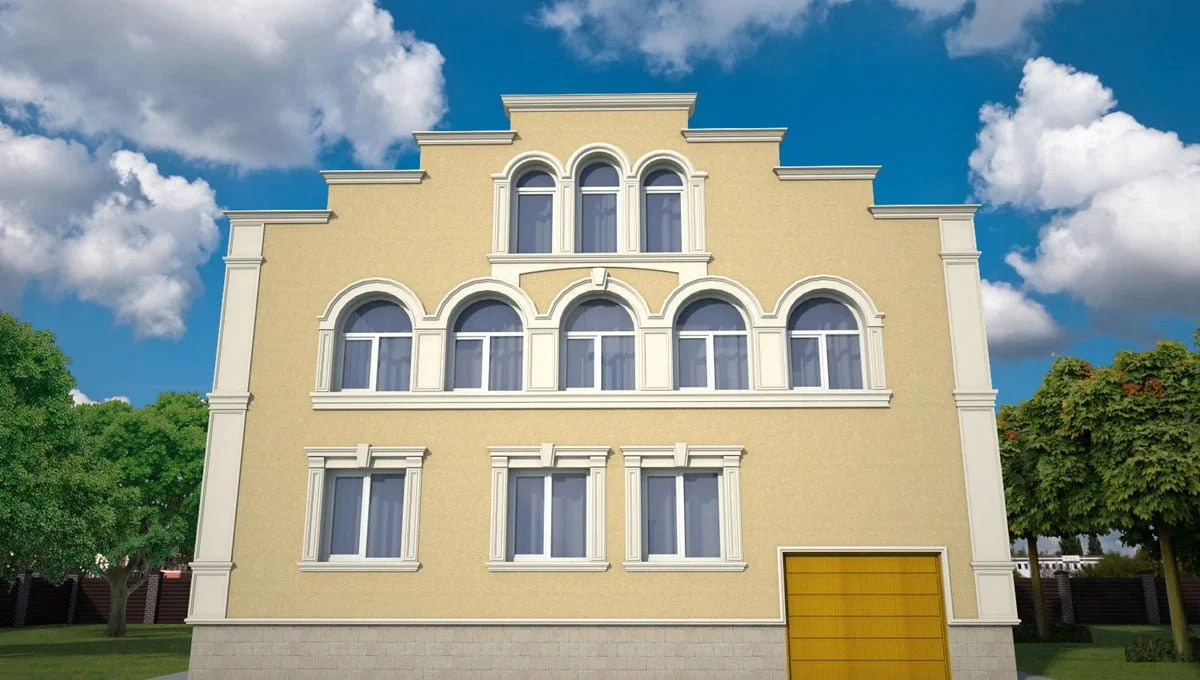
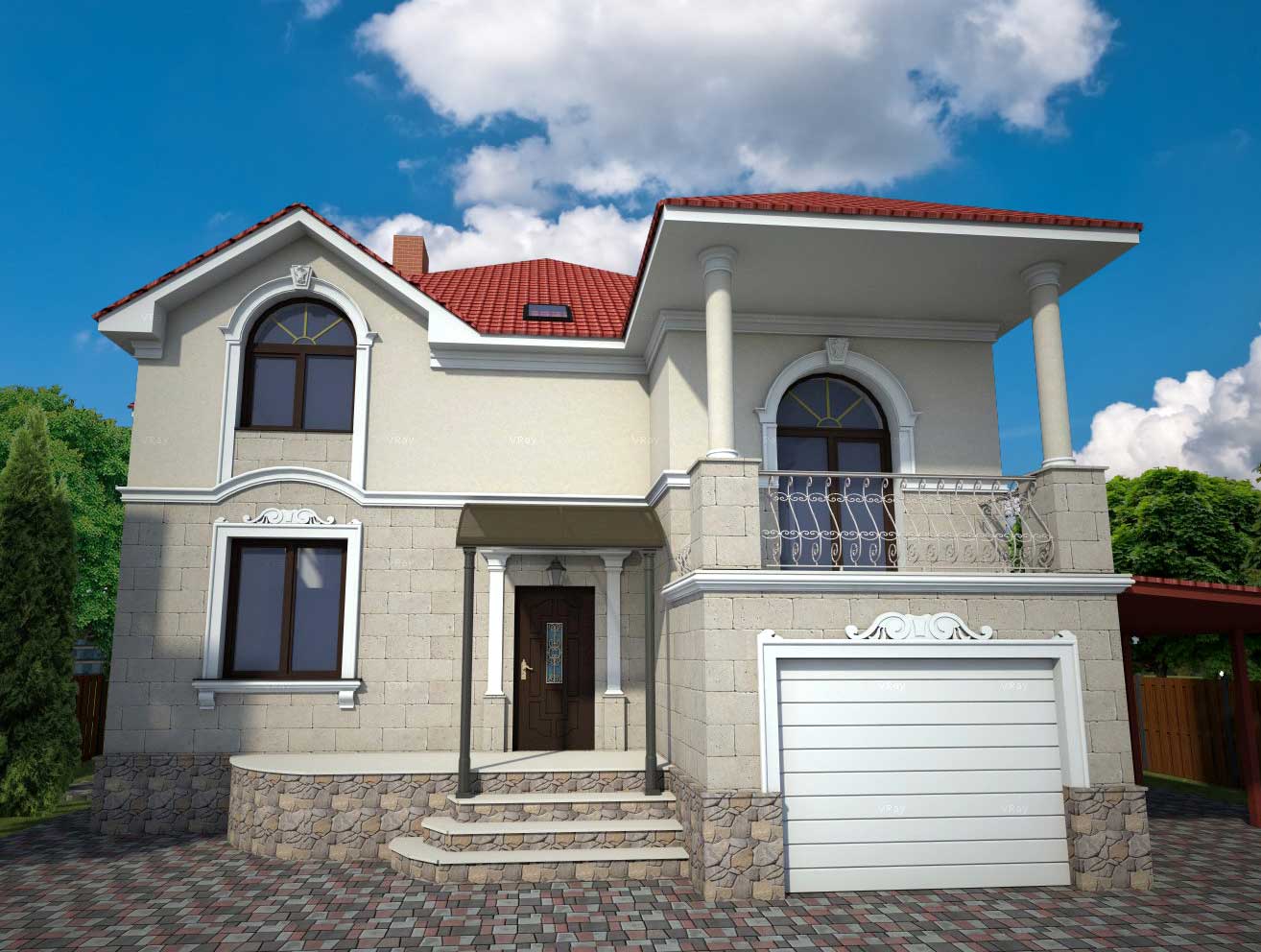
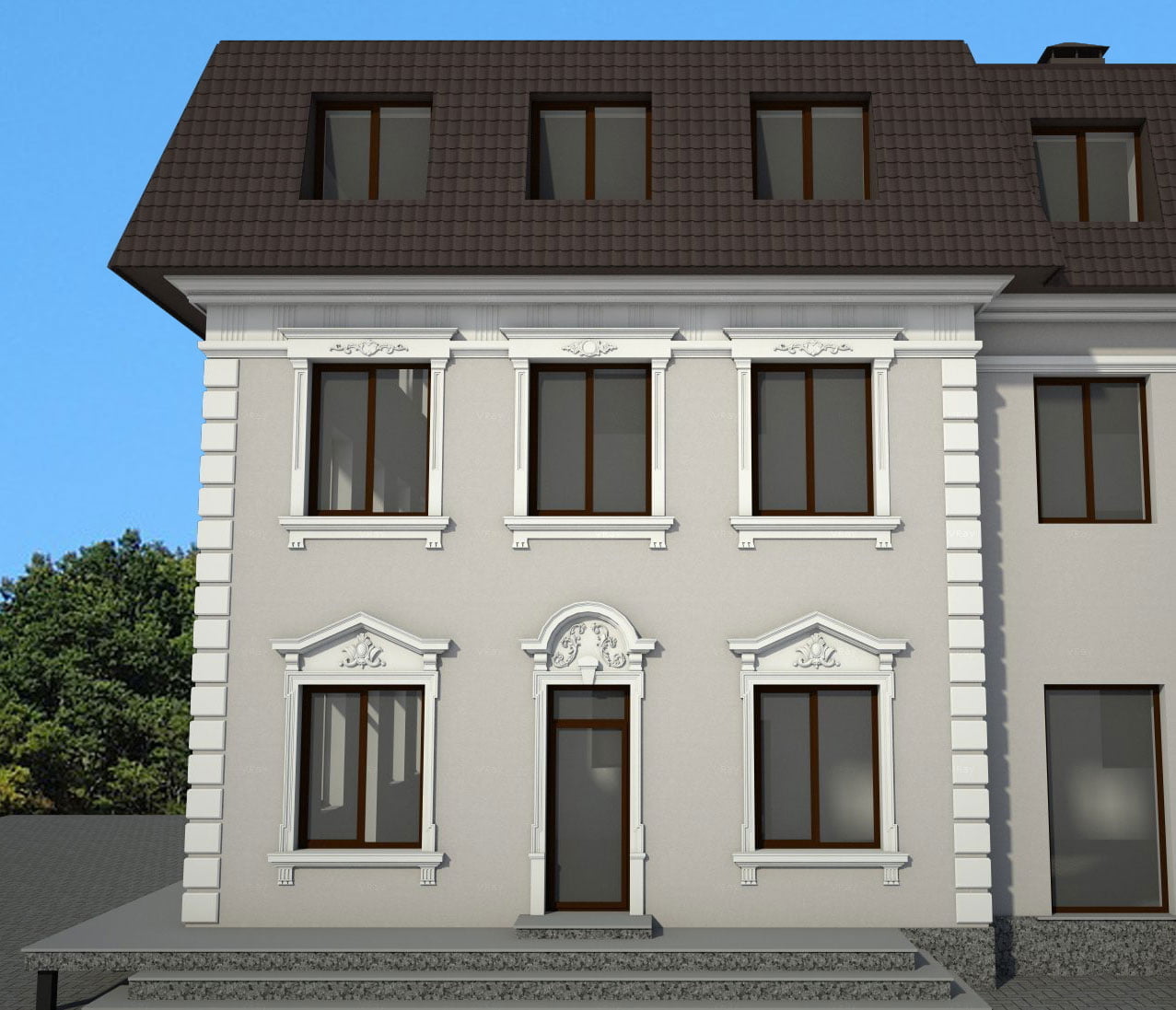
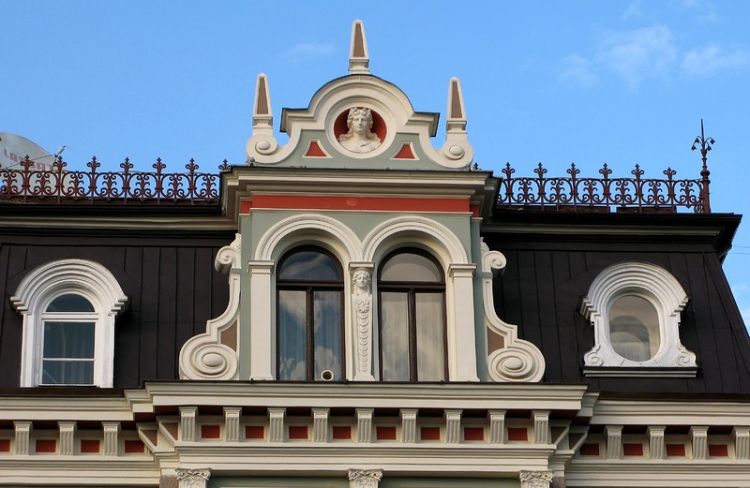
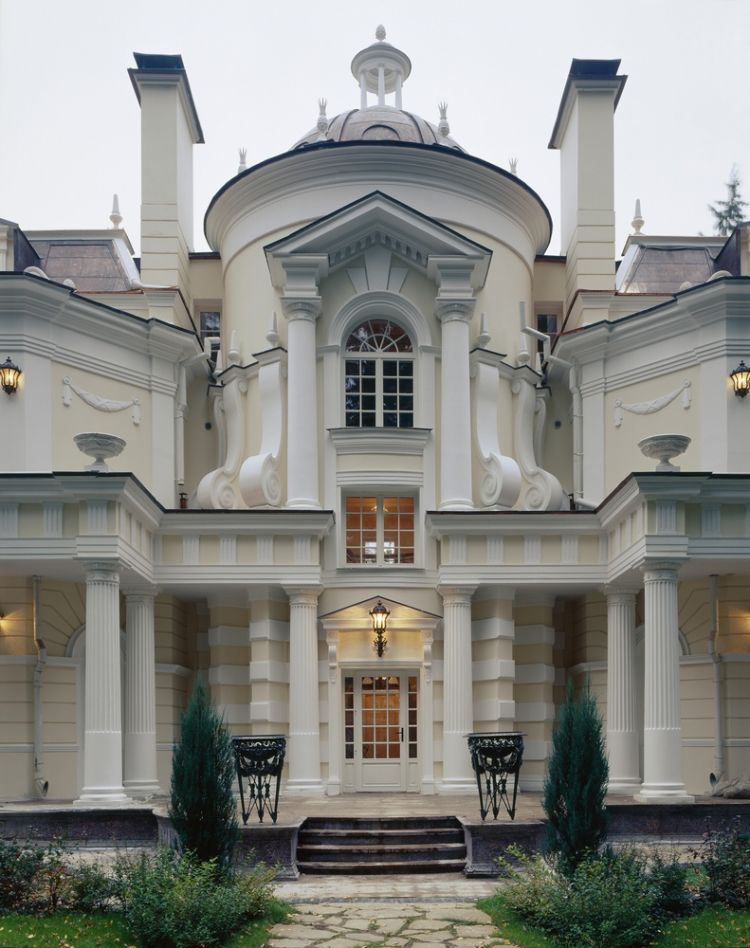
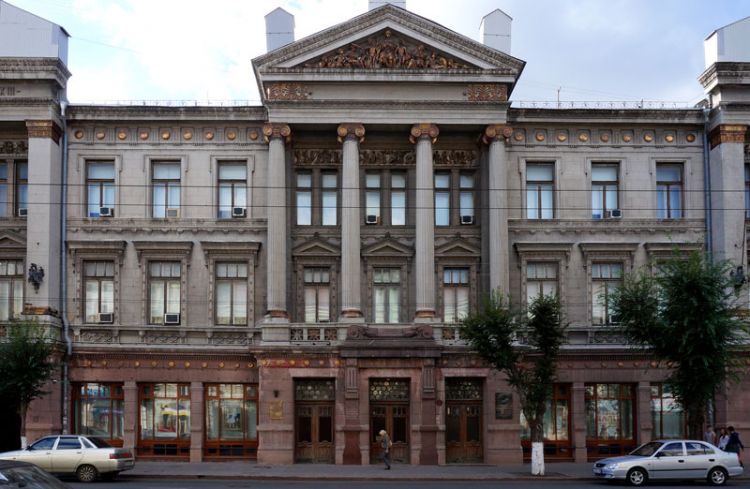
EXAMPLE OF 3D HOUSE FACADE PROJECT













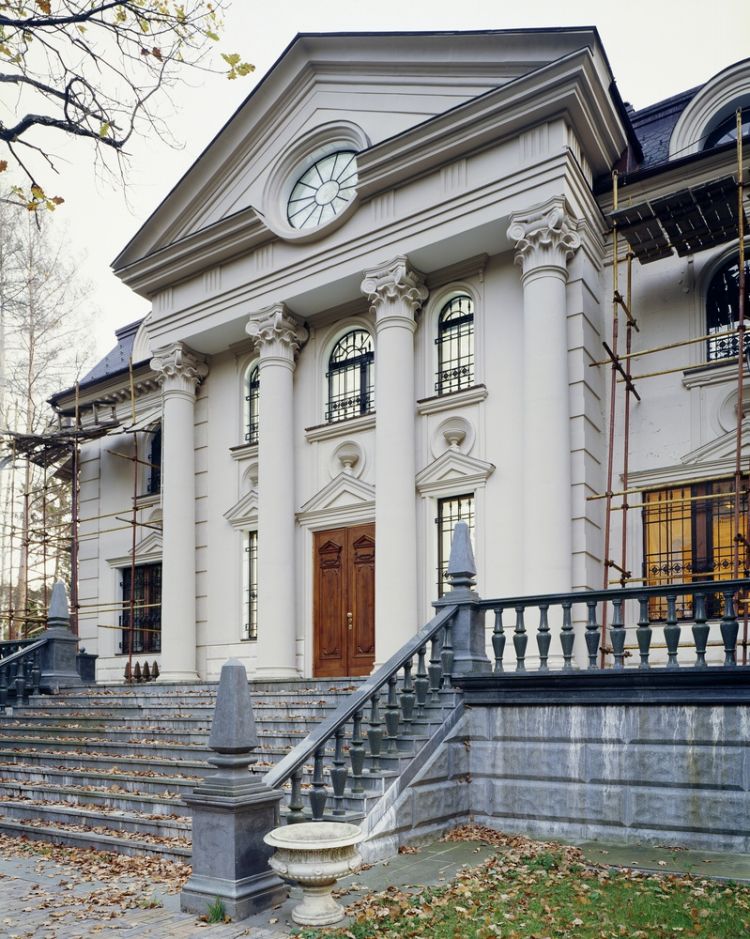
HOUSE STYLES GUIDE
In the world, there are a lot of architectural styles, and for each person there is an architectural style to your liking, repairing the facade of your house, you can always stylize it for a specific architectural style.
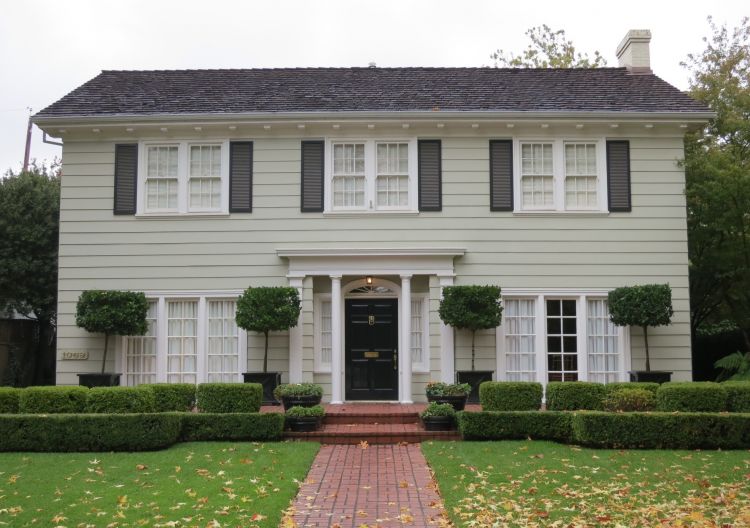
COLONIAL STYLE HOUSE EXTERIOR DESIGN
Colonial style – (from Latin Colonus – column, ancient Roman settler, land tenant, resident of the province). Kolon – attachment to the land of the settlers of the province – was formed in the Roman Empire in the III century. However, this later Latin word began to be called the process of development of new lands by the inhabitants of the Eastern Mediterranean from the end of the 2nd millennium BC. e. The Phoenicians in the IX-VII centuries. BC. e. founded settlements in Cyprus, in North Africa – Carthage, in Sicily, on the coast of Spain – Hades.
Colonial Style Homes Pictures

The Greeks settled the islands of the Aegean Sea, the western coast of Asia Minor, southern Italy, and the northern Black Sea coast. Ancient Greek philosopher Plato (427-347 BC) noted that “the Greeks settle around the seas, like frogs around swamps.” The settlements in Greek were called “apocchio” (Greek apoikii – “resettlement”), and the culture of the metropolis – was autochthonous.
Colonial Style Architecture

Of particular importance for the history of European art were the ancient settlements in Gaul, the Rhineland (from the word colonus comes the name of Cologne), Britain, and the subsequent romanization of the “barbarian” peoples.
Colonial Style Buildings
Other synonyms of the word “colonial” – “vernacular” (English, from Latin vernacular – local, native) and “rustic” (Latin rusticus – rural, rough) – have a slightly disdainful hue: simple, unpretentious, clumsy, artless and therefore sometimes refer generally to folk art, naive art, primitives. In the history of art, the term “colonial architecture” was used to refer to the result of the construction activity of the Franks on the lands of Byzantium after the conquest of Constantinople by the Crusaders in 1204.

The colonists created an original architecture, in general, repeating the West European Romance and Gothic, but in a simplified and coarsened form. The gothic lancet arch became a symbol of the Catholic Church in the East, but not more than a century.
Types Of Colonial Houses

Provincial Art of the English Colonies of America of the XVIII-XIX centuries. , especially architecture, interior decoration, and furniture, is also not an original artistic style, but a mixture of simplified forms of English Gothic, Dutch Baroque, Victorian, and Old English styles. This eclectic art was formed based on the first settlers brought to America by the first colonists, and also in connection with the usual ideas, nostalgia for the comfort of a traditional English house.
American Colonial Style House

Another example of the “colonial style” is the art of the Catholic countries of Latin America of the XVII-XIX centuries. – Argentina, Chile, Peru, Uruguay, Brazil. Introduced in these lands by Spanish and Portuguese conquerors and missionaries, the Baroque style with elements of Mauritanian art typical of Spain, Isabelline, and Plateresque styles was gradually assimilated and, under the influence of local ethnic traditions, assumed fantastic forms. Massiveness, some rudeness of architecture, and sculpture are combined in the Latin American “colonial style” with bright colors and the richness of a dense crushed decor.
Colonial Style Of Architecture

Spanish and Portuguese Baroque was transformed in Latin American countries into “ultra-baroque” – manneristic and decorative style, including European and local folklore elements in combination with archaic thinking, close to Romanesque and even pre-Roman, early Christian art. The “colonial” is the “second Georgian style”, formed in North America in the 1700s-1770s. and “federal style” in the art of the United States of 1780-1850-ies.
Different Colonial Style Homes

The name “colonial style” is conditional, it is rather an epithet than a definition of the historical and artistic style, primarily because of secondary and eclecticism. Hence the ironic use of the word “colonial” as applied to the phenomena of provincial, philistine taste, and amateur art, in which elements of different “historical styles” are mixed in a comic, crushed version (compare naive art; primitive, haymatkunst).
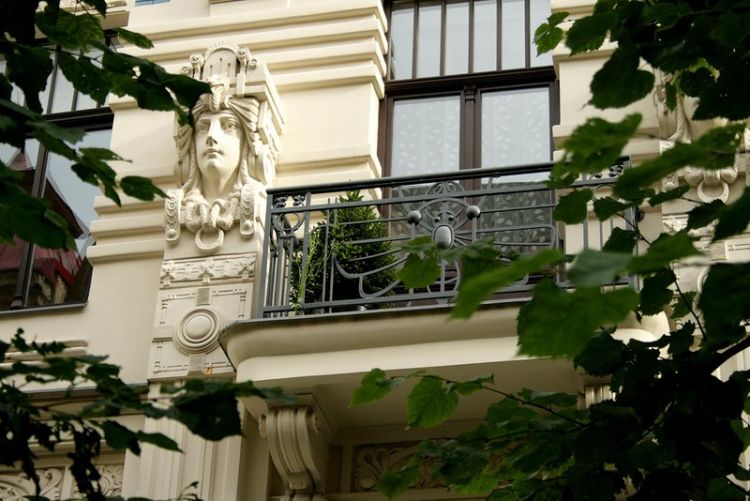
MODERN STYLE HOMES EXTERIOR DESIGN
Modern (from the French moderne – modern), Art Nouveau (French art nouveau, the letter “New Art”), Art Nouveau (German Jugendstil – “young style”) – the artistic direction in art, the most common in the last decade of XIX – the beginning of the XX century (before the First World War). Its distinctive features are the rejection of straight lines and angles in favor of more natural, “natural” lines, interest in new technologies (for example, in architecture), and the flowering of applied art.
Modern Architectural Styles
Modernism sought to combine the artistic and utilitarian functions of the created works, to involve all spheres of human activity in the sphere of beauty. In other countries, it is also called: “Tiffany” (named after L. K. Tiffany) in the USA, “Art Nouveau” and “fin de siècle” (lit. “end of the century”) in France, “Jugendstil” (more precisely, ” Jugendstil “- by the name of the illustrated magazine Die Die Jugend founded in 1896) in Germany,” Secessionsstil “style in Austria,” modern style “, modern style in England,” liberty style “in England Italy, “modernism” in Spain, “Nieuwe Kunst” in the Netherlands, “spruce style” (style Sapin) in Switzerland.
Modern Architectural Designs

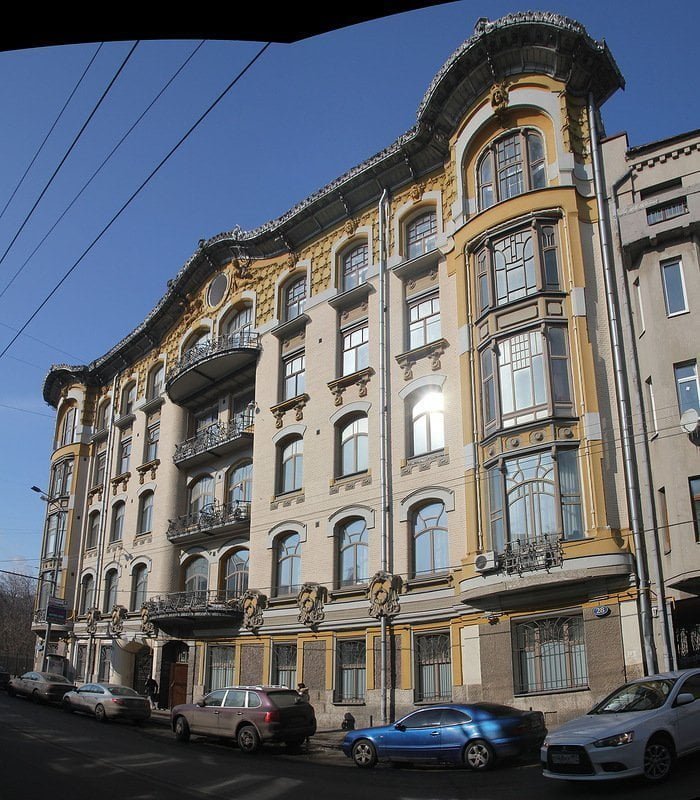
In 1860-1870 in Europe the eclectic style dominated, which consisted in citing and repeating previous artistic styles. The desire to counteract this with his creativity united the anti-epic movement artistic trends and schools in various countries. This led to the fact that in the 1880s a new style was being developed in the works of several masters, which contrasted eclecticism with new artistic techniques.
Modern Home Styles

The founder of modernity is England – the oldest country of capitalism. The new style begins to develop there under the slogan of a return to organicity, simplicity, and functionality of the Middle Ages, the early Renaissance, and folk architecture. The artistic movement associated with the activities of the Pre-Raphaelites, the philosophy and aesthetics of John Ruskin, and the practice of William Morris, is particularly prevalent in applied art and architecture. [1] Morris created interior objects inspired by floral ornaments, and Arthur McMurdo used elegant, wavy patterns in book graphics. His cover for the book “City churches of Rena” (1883) is considered the first implementation of the Art Nouveau style in the field of graphics.
Modern Residential Architecture
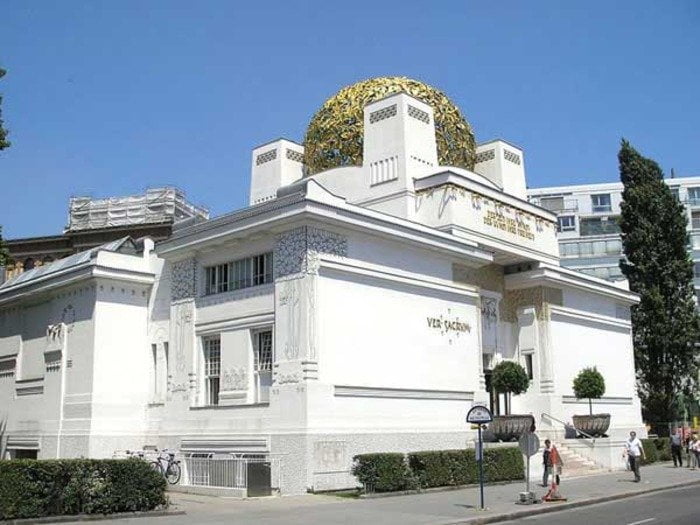
In the European countries, various artistic associations began to be created, working in a new style: the Exhibition Society of Arts and Crafts (1888) in the United Kingdom, the United Artistic Crafts workshops (1897), and the German Workshops of Artistic Crafts (1899) in Germany, “Vienna Workshops” (1903) in Austria, “Nancy School” in France, “World of Art” (1890) in Russia.

The period of the development of modernity has quite clear chronological boundaries: from the late 1880s. until 1914, the beginning of the First World War, ending the natural development of art in most European countries.
Types Of Modern Houses

Conditionally distinguish 3 stages of development of style:
The first (from 1890 to 1900) was the nomination of a task and a decisive renovation of the artistic-figurative language of architecture, the development of new methods of spatial compositions of the structure, and the intensification of the trends in the use of new materials (steel, concrete, etc.), orientation to ornamentation, decorative motifs, etc.

The second (approximately from 1900-1905) – is characterized by a gradual departure from decorative, more consistent development of building materials of a new pattern. The third (lasting approximately until the 1910s) – is marked by the desire for simplicity, rigor, and consistent study of construction equipment.
Modern Contemporary Architecture

The spread of modernity was facilitated by the holding of World Exhibitions, which demonstrated the achievements of modern technology and applied art. The most famous modernism was at the World Exhibition in 1900 in Paris. In the 1910s. the meaning of Art Nouveau began to fade.
Modern Style Buildings

A significant influence on the style of modernity was the art of Japan, which became more accessible in the West with the beginning of the Meiji era. Art nouveau artists also drew inspiration from the art of Ancient Egypt and other ancient civilizations.
Types Of Modern Architecture

Traditionally, modernism has two main areas: constructive (Austria, Scotland) and decorative (Belgium, France, Germany). In addition, in Italy and Russia, the national traditions had a strong influence on it: in these countries, the models of modernity bore the imprint of traditional forms. An example is a Neo-Russian style in Russia’s architecture (not to be confused with the pseudo-Russian style that belonged to the period of eclecticism).
Modern House Architecture Styles

It should be borne in mind that the division of art nouveau into separate periods and styles is conditional. Modern, like none of the other types, absorbed so many different trends and was influenced by so many national cultures and traditions that it is difficult to even for specialists to determine where eclecticism ends and modernity begins and where modernity ends and art deco begins.
Modern Residential Architectural Styles

Modernity included many currents and styles: neo-Romanticism – elements of Romanesque, Gothic, Renaissance, and other styles were used; Neoclassicism; Rationalism, a direction with a predominance of simpler forms; Irrationalism; The brick style, when the architects refused the plaster, and all the decorative details of the building were made of bricks. Depending on its territorial affiliation, it bore different names: Vienna, Berlin, and Paris modern in Western Europe, Moscow, St. Petersburg, Riga, and provincial modern in Russia and Eastern Europe.
Modern Home Architecture Styles

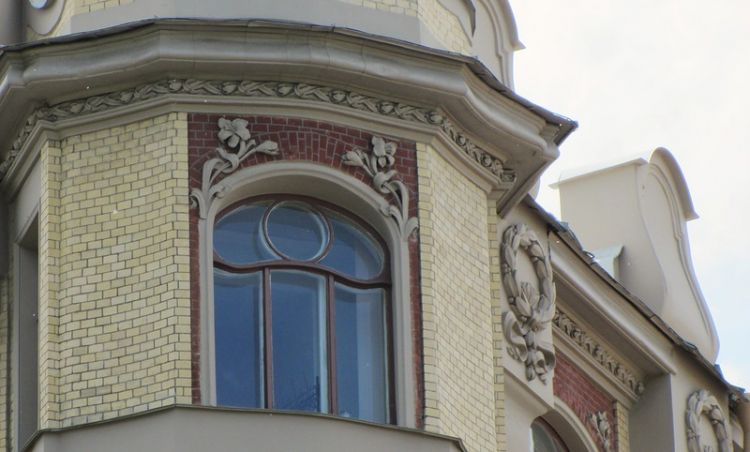
Often artists of modernity took as their basis drawings ornaments from the plant world. The most notable feature of modernity was the rejection of right angles and lines in favor of smoother, curved lines, and imitation of the natural forms of plants. “The calling card” of the style was the embroidery of Herman Obrist (English) Russian. “The blow of the scourge”. The forms of modernity prevailed – the rejection of symmetry, vertical, aspiring dominants, and the flow of forms one into another.
Modern Style Housing

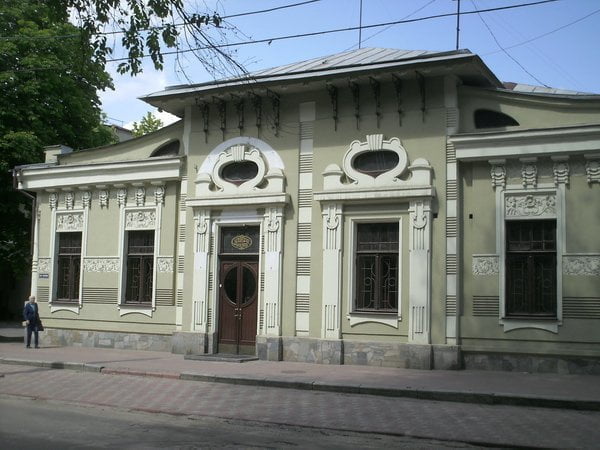
The predominant colors were muted shades – the color of the withered rose, tobacco colors, pearly gray, gray-blue, and dust-lilac tones. The characteristic elements of the interior of Art Nouveau were a combination of planes and curved furniture. In decoration there is a mosaic, enamel, gold background, chasing on copper and brass.
Modern House Styles Pictures

Structural designs are often framed (the supporting element is a steel frame). The windows are rectangular, elongated upwards, often with rich vegetative decor, sometimes arched, “shop windows” – wide, like window-cases. The doors of the Art Nouveau style are rectangular, often arched. Most often flat-shaped, with mosaic ornament, decorated
Moderne House Style
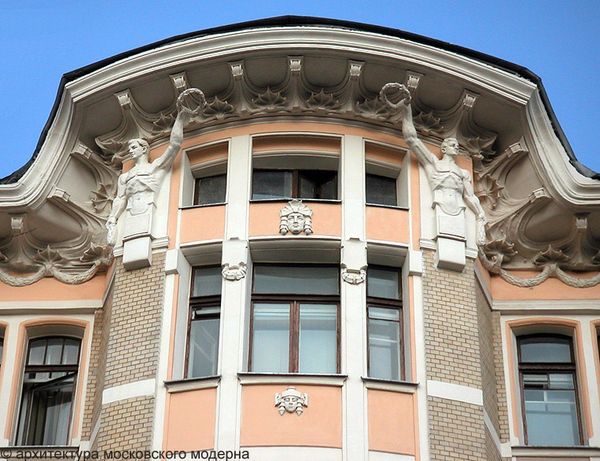

Modernism aspired to become a single synthetic style in which all elements from the human environment were executed in one key. As a result, interest in applied arts has increased: the design of interiors, ceramics, and book graphics.
The development of Art Nouveau art was preceded by a period of formation. The period of the early development of modernity is usually called modernism. This current was formed in different years, in different countries, and by various artists, who, as a rule, did not know each other, but were connected by common ideals and ideas. The directions of modernism were not related to the national traditions of the countries in which they developed.
Different Types Of Modern Houses

Cubism in France had nothing to do with the culture of France. A striking example of this discrepancy is the Eiffel Tower, which, in the opinion of the intelligentsia of that time, did not fit perfectly into the architecture of Paris and caused a storm of indignation. The separation of modernism from national traditions laid the foundation for an “international style” that does not have boundaries. The great influence on modernity was influenced by the East, namely Japan.
Modern Type House Design

The rejection of national traditions was perceived as a desire for cosmopolitanism. The first modernists were artists who were created at the turn of the end of the XIX century, who believed that the spiritual revolution, which, in their opinion, was inevitably born out of the crisis of the old world, demanded the abandonment of socio-political radicalism. A new ideological platform was the spiritual revolution as a qualitatively new consciousness, a new life-understanding.
Types Of Modern Homes

It was based on the intuitionism of A. Bergson and N. Lossky, the phenomenology of E. Husserl, the psychoanalysis of Z. Freud and K. Jung, the existentialism of S. Kierkegaard, M. Heidegger, K. Jaspers, N. Berdyaev and others. The theoretical basis for the future style was formulated by William Morris, but the development of the ideas of early modernism was practiced by many artists of the pre-modern era.
Different Types Of Modern Architecture

The architecture of modernity is distinguished by the rejection of straight lines and angles in favor of more natural, “natural” lines, and the use of new materials (metal, glass). Like several other styles, the architecture of modernity is also distinguished by the desire to create simultaneously aesthetic and functional buildings. Much attention was paid not only to the appearance of buildings but also to the interior, which was carefully studied. All the structural elements – stairs, doors, poles, balconies – were artistically processed.

One of the first architects working in the Art Nouveau style was the Belgian Victor Orta (1861-1947). In his projects, he actively used new materials, first of all, metal and glass. Bearing structures made of iron, he gave unusual shapes, reminiscent of some fantastic plants. Stair rails, lamps hanging from the ceiling, even the door handles – everything was designed in the same style. In France, the idea of modernity was developed by Héctor Guimard, who, among other things, created the entrance pavilions of the Paris Metro.
Even further away from the classical notions of architecture, the Spanish architect Antonio Gaudi left. The buildings built by him are so organically fit into the surrounding landscape that they seem to be the work of nature, not of man.
CLASSIC STYLE HOME FRONT DESIGNS
Classicism (French classicism, from Latin classics – exemplary) – artistic style and aesthetic direction in European art of the XVII-XIX centuries. At the heart of classicism are the ideas of rationalism, which were formed simultaneously with those of Descartes’ philosophy. Artistic work, from the point of view of classicism, must be built based on strict canons, thereby revealing the harmony and consistency of the universe itself.
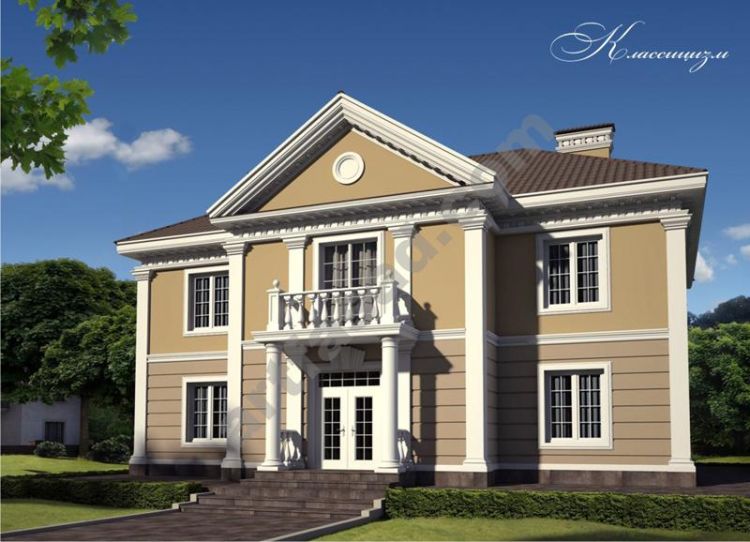

Interest for classicism represents only the eternal, unchanging – in every phenomenon he seeks to recognize only the essential, typological features, discarding random individual attributes. The aesthetics of classicism attaches great importance to the public-educational function of art. Many architectural rules and canons of classicism take from ancient art.
Classic Style House

The main feature of the architecture of classicism was the appeal to the forms of ancient architecture as a standard of harmony, simplicity, rigor, logical clarity, and monumentality. The architecture of classicism as a whole is inherent in the regularity of planning and the clarity of the three-dimensional form. The basis of the architectural language of classicism was the warrant, in proportions and forms close to antiquity. For classicism, symmetrical-axial compositions, restraint of decorative decoration, and regular urban planning systems are characteristic.
Classical Style Architecture

The architectural language of classicism was formulated at the end of the Renaissance by the great Venetian master Palladio and his follower Skamozzi. The principles of the ancient temple architecture of the Venetians were absolutized so much that they used them even in the construction of private mansions. In England, Palladianism took root, and local architects followed Palladio’s precepts with varying degrees of fidelity until the middle of the eighteenth century.
Classic Home Styles

By that time, satiety with the “whipped cream” of the late Baroque and Rococo began to accumulate among the intellectuals of continental Europe. Born by Roman architects Bernini and Borromini, the Baroque was thinned into a rococo, predominantly chamber style with an emphasis on decorating interiors and decorative and applied art. To solve major urban problems these aesthetics were of little use. Even under Louis XV (1715-74) in Paris, urban planning ensembles in the “ancient Roman” taste, such as the Place de la Concorde (architect Jacques-Ange Gabriel) and the church of Saint-Sulpice, and under Louis XVI (1774-92), a similar “noble laconism “is already becoming the main architectural direction.
Classic Architecture Homes

The most significant interiors in the style of classicism were developed by the Scottish Robert Adam, who returned home from Rome in 1758. Upon his return to his homeland, he was made a royal architect in 1762, but in 1768 left this post because he was elected to parliament and engaged in architecture and construction with his brother James. An enormous impression was made on him by archaeological research by Italian scientists. In the interpretation of Adam classicism appeared as a style, by the refinement of interiors hardly inferior to the rococo, which earned him popularity not only among democratically minded circles of society but also among the aristocracy. Like his French counterparts, Adam preached a complete rejection of details devoid of constructive function. This restored the architectural stucco decor (and architectural elements in general) the severity of lines and the correctness of proportions.
Classic House Architecture

Frenchman Jacques-Germain Sufflau during the construction of the Church of Saint-Genevieve in Paris demonstrated the ability of classicism to organize vast urban spaces. The massive grandeur of his projects foreshadowed the megalomania of the Napoleonic Empire and late classicism. In Russia, Vasily Bazhenov moved in one direction with Suffolk. The French Claude-Nicola Ledoux and Etienne-Louis Boullet went even further in the direction of developing a radical visual style with a bias in the abstract geometrization of forms. In revolutionary France, the ascetic civil pathos of their projects was of little use; to fully innovate Leda was appreciated only by the modernists of the 20th century.

The architecture of Napoleonic France
The architects of Napoleonic France drew inspiration from the majestic images of military glory left by imperial Rome, such as the triumphal arch of Septimius Severus and the column of Trajan. On the orders of Napoleon, these images were transferred to Paris in the form of the triumphal arch of Carrousel and the Vendome column. Concerning the monuments of military greatness of the Napoleonic wars, the term “imperial style” is used – Empire. In Russia, Karl Rossi, Andrei Voronikhin, and Andrei Zakharov showed themselves as outstanding artists of the Empire style. In Britain, the empire corresponds to the so-called. “Regent style” (the largest representative – John Nash).
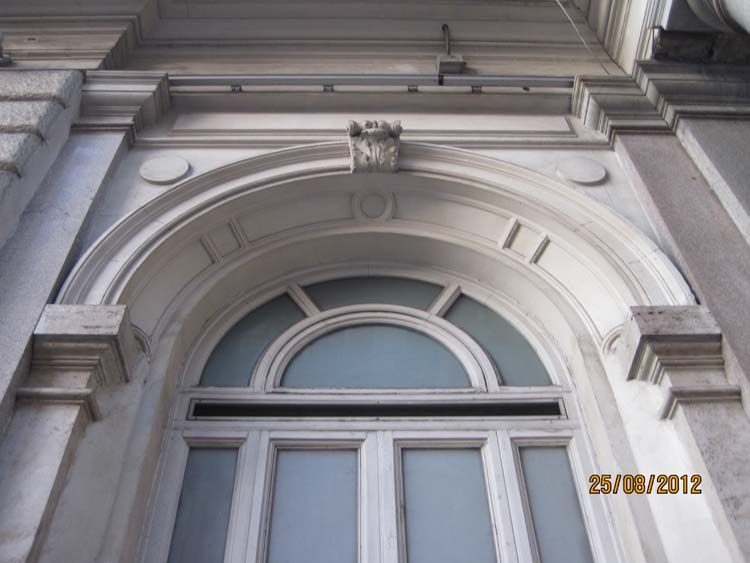

The aesthetics of classicism favored large-scale town-planning projects and led to the ordering of urban development on the scales of entire cities. In Russia, virtually all provincial and many county cities were re-planned by the principles of classic rationalism. As the original museums of classicism opened, cities such as St. Petersburg, Helsinki, Warsaw, Dublin, Edinburgh, and several others have turned. In the whole space from Minusinsk to Philadelphia, a single architectural language reigned back to Palladio. The buildings were built by the albums of standard projects.

In the period that followed the Napoleonic wars, classicism had to get along with the romantically colored eclectic, in particular, with the return of interest to the Middle Ages and fashion to the architectural neo-Gothic.

Brief description of the architectural style of classicism
Characteristic features: A style that appealed to the ancient heritage as a norm and ideal pattern. Reserved décor and expensive high-quality materials (natural wood, stone, silk, etc.) are characteristic. Most often there are decorations with sculptures and stucco molding.
- Predominant colors: saturated colors; green, pink, purple with a gold accent, sky blue.
- Lines: strict repeating vertical and horizontal lines; bas-relief in a round locket; smooth generalized drawing; symmetry.
- Form: clarity and geometric forms; statues on the roof, rotunda; for the Empire style – expressive pompous monumental forms.
- Interior elements: discreet decor; round and ribbed columns, pilasters, statues, antique ornamentation, caisson vault.
- Constructions: massive, stable, monumental, rectangular, arched.
- Windows: rectangular, elongated upwards, with a modest design.
- Doors: rectangular, paneled; with a massive gable portal on round and ribbed columns; with lions, sphinxes, and statues.
FRENCH PROVINCIAL HOMES OUTSIDE DESIGN
Provence (Fr. Provence, Oxen Provença, the letter “province”) is a historical region in the southeast of France, now part of the Provence-Alpes-Côte d’Azur region. Currently in the territory of Provence are the departments of Var, Vaucluse, and Bouches-du-Rhône, as well as parts of the Alps of the Upper Provence and the Maritime Alps. In the east, the region is bounded by the Alps, in the west by the Rhone, and in the south by the Mediterranean Sea.
Provence Villas

The capital of Provence is Aix-en-Provence, one of the oldest French cities. This piece of resort France as a magnet attracts thousands of tourists every year. It is not surprising that those who visit Provence at least once try to recreate even a small part of it in other parts of the globe. By today, among the many architectural styles, the style of Provence is very popular, thought out, and one of the most sought-after.
French Provencal Style
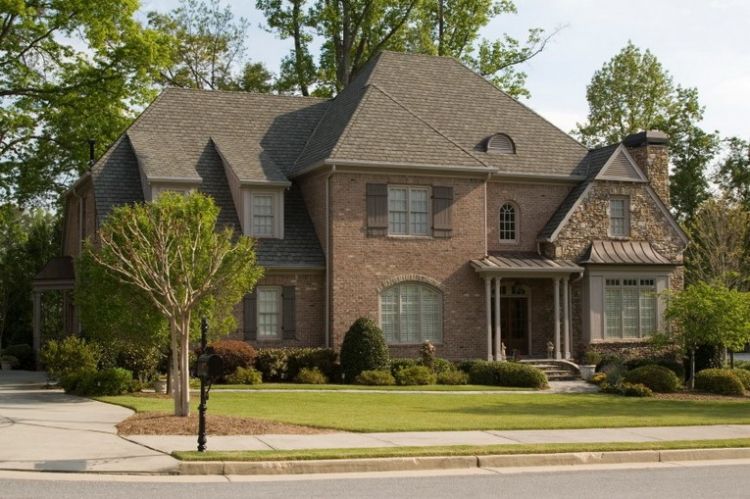

The peculiarity of the house in the style of Provence is considered the refinement and peculiar romantic tenderness of the exterior of the house. A special place belongs to the details. Most often in the style of Provence build country houses. Such a house has almost no socle and such a house naturally does not have a porch that is familiar to us. The garden path just rests on the front door.
French Country Cottages Provence
The walls of the house must be made of brick or stone. Most often the walls are covered with plaster of light tones. In some places, plaster can expose a brick wall, and this does not spoil the impression but gives the house a peculiar zest. The house in the style of Provence is built with two or three floors. Of the features of the exterior finish, it should be noted minimalism in the decoration of the first floor and a certain pretentiousness in the decor of the upper floors.
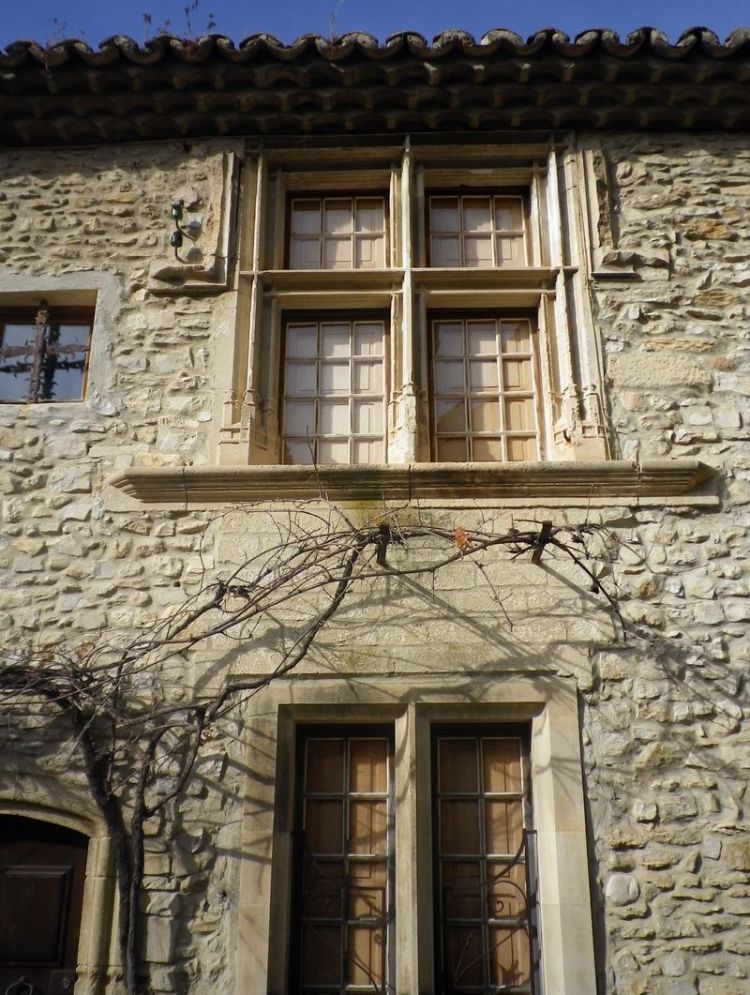

Here you can find balconies with columns or balustrades with carved decorative balusters. As for the windows, on the first floor, they are usually narrow and must have blinds. On the second and third floors, the windows are made larger so that the sun’s rays penetrate as much as possible into the house.
Provence House Style

The roof is a special part of the house in the Provencal style. It is a multi-story high construction under tiles. The decoration of the roof is served by numerous towers with dormer windows. If the house is one-story, then under the roof must necessarily be located attic.
French Provencal Architecture

Since Provence is geographically located on the Mediterranean coast, local culture is also reflected in the second type of roof, often associated with the Provencal style in architecture. These are long gently sloping roofs. These houses have narrow windows, and windows have shutters.
Modern Provence Style

For a house in the style of Provence, an important detail is a door. They should be massive with forged hinges. Each door should have a viewing window.
French Provence Style Homes

Extensions. Traditionally, various extensions are attached to the house. Almost every house that claims to be a house in the Provence style must have a summer kitchen. On the opposite side of the house have a summer outbuilding or a garage.
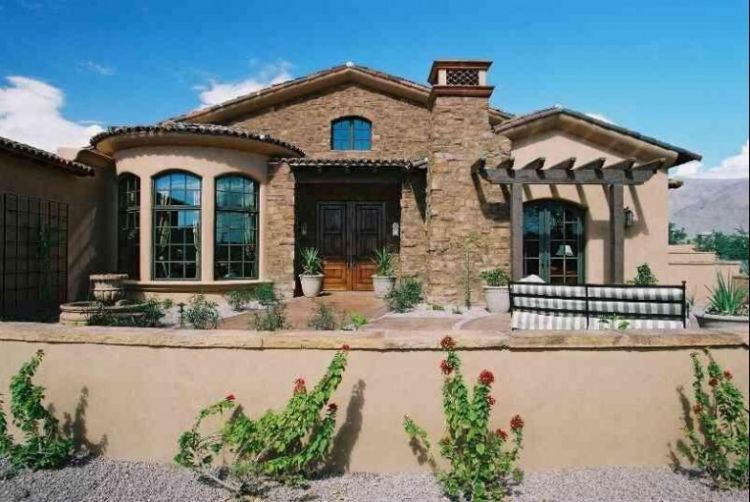
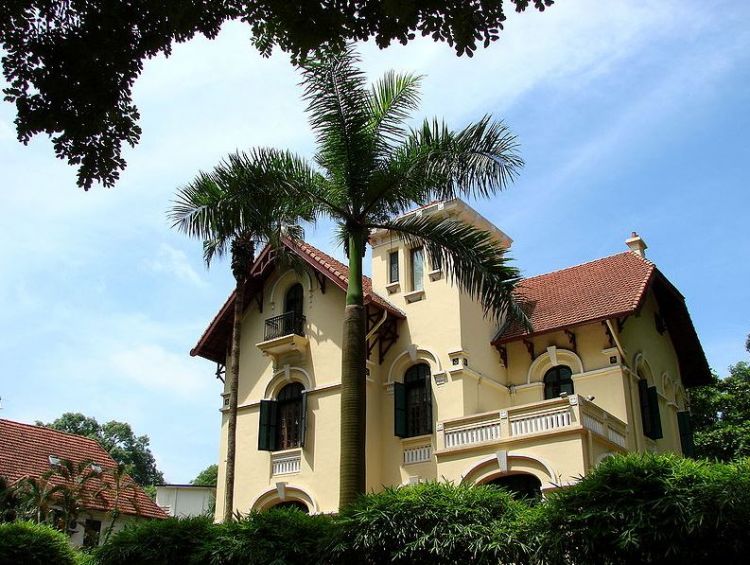
MEDITERRANEAN-STYLE HOUSE OUTSIDE DESIGN
First of all, the architecture of the Mediterranean style stands out with its curved forms of light tones. The obligation of such a background is explained by the desire to keep the interior of the house cool, which in the Mediterranean is highly valued.
The roof of the house is very sloping, it is often possible to meet even a flat roof. It is usually covered with natural tiles, but metal tile is more often used, although the concept of style involves the use of natural materials.
Mediterranean House Design

The facade of the house is faced with natural materials, usually, natural stone – sandstone, wild stone, etc. Using natural materials allows you to keep the life-giving coolness in the house. The façade, faced with both sandstone and wild stone, looks superb.
Mediterranean Architecture

The architecture of the mansion in Italy is unthinkable without a balcony or a spacious, but necessarily covered terrace. The presence of these elements of architecture will allow you to enjoy the evening cool after a hot day. The characteristic of the patio is the patio with tropical fauna.
Mediterranean Style Homes

Modern Mediterranean House

Mediterranean Decor Ideas

Mediterranean Mansion
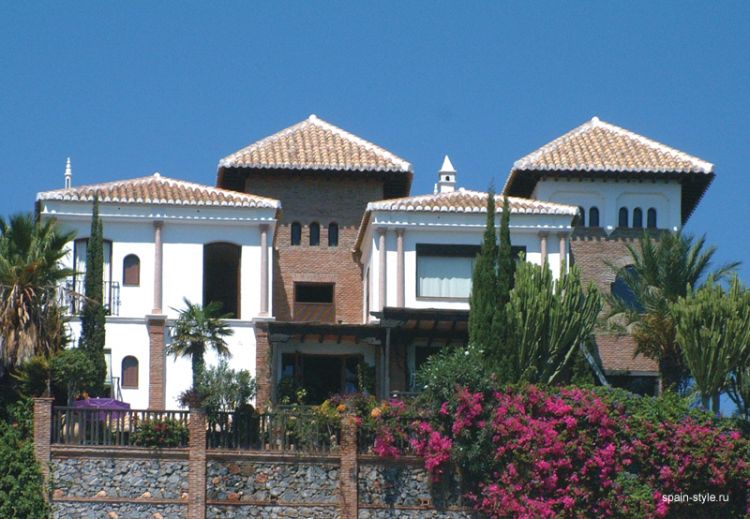

Spanish Mediterranean Homes
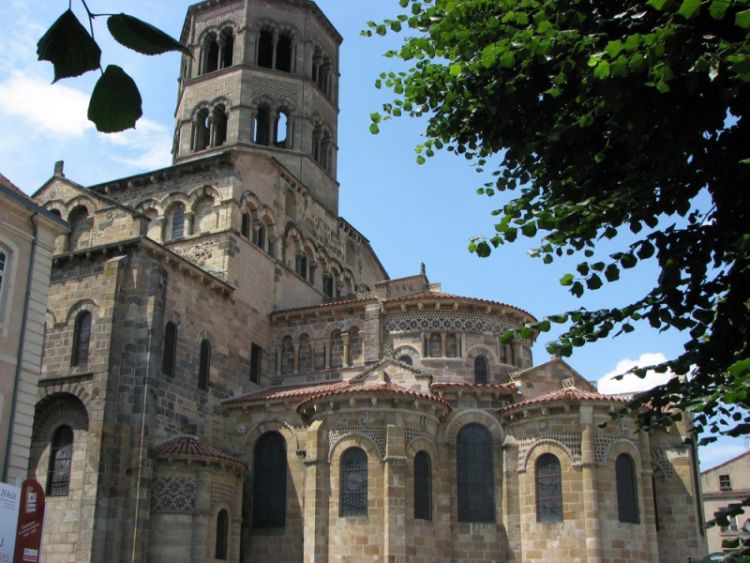

BAROQUE STYLE HOUSE FRONT ELEVATION
The architectural style of baroque. Baroque architecture (L. Bernini, F. Borromini in Italy, B. F. Rastrelli in Russia) is characterized by the spatial scope, fusion, fluidity of complex, usually curvilinear forms, and the richness of stucco decor. Often there are deployed large-scale colonnades, an abundance of sculptures on facades and interiors, volutes, a large number of raskrepovok, luchkovye facades with raskopovkoy in the middle, rustovannye columns, and pilasters. The domes take on complex shapes, often they are stacked like St. Peter’s in Rome. Characteristic details of baroque – telamon (atlant), caryatid, macaron.
Baroque Style Architecture

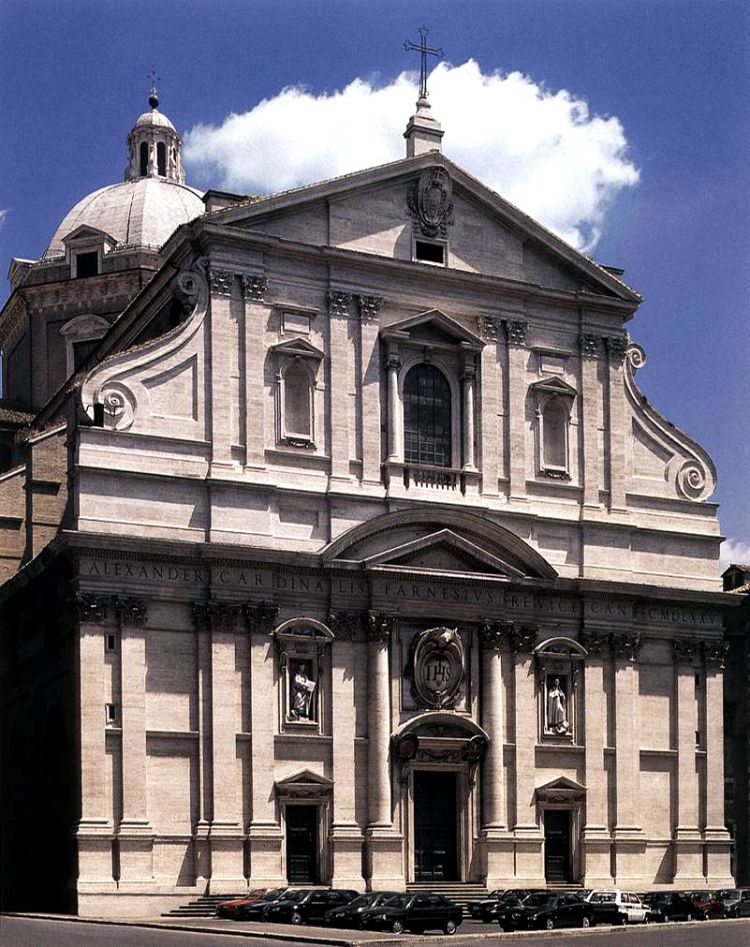
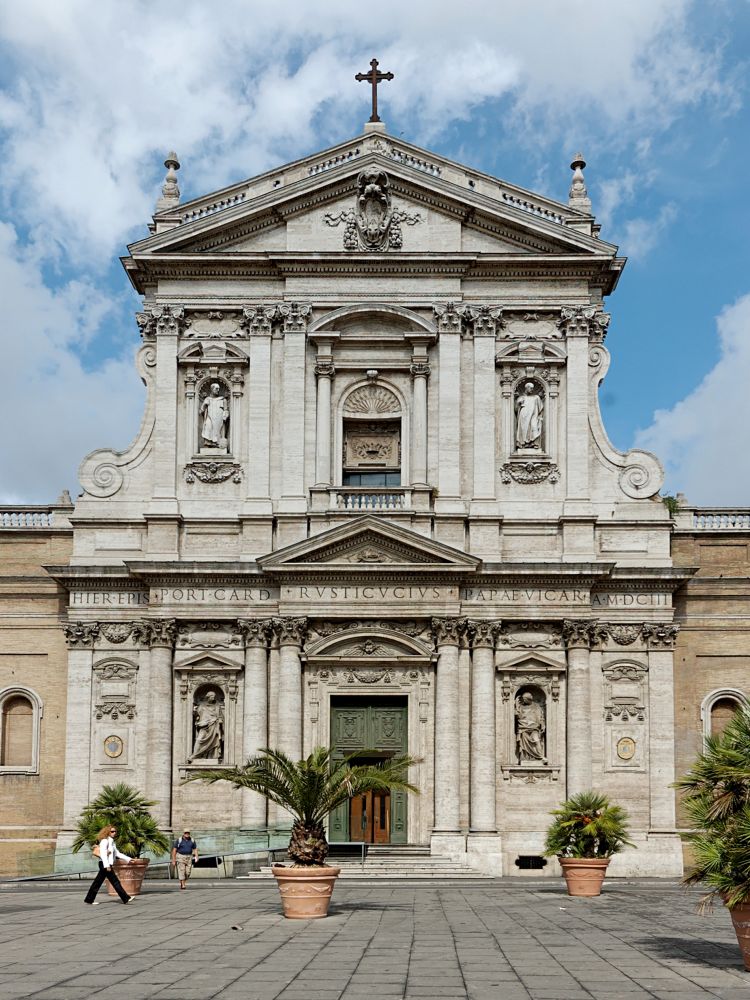
In Italian architecture, the most prominent Baroque representative was Carlo Maderna (1556-1629), who broke with Mannerism (later the Renaissance) and created his style. His main creation is the facade of the Roman church of Santa Susanna (1603) (see the photo on the right). Pay attention to the abundance and complexity of the architectural elements of the facade.
Baroque Facade

The main figure in the development of Baroque sculpture was Lorenzo Bernini, whose first new-style masterpieces date back to about 1620. Bernini is also an architect. He owns the decoration of the square of St. Peter’s Cathedral in Rome (see photo gallery after the article) and interiors, as well as other buildings. A significant contribution was left by D. Fontana, R. Raynaldi, G. Gvarini, B. Longen, L. Vanvitelli, P. da Cortona.
Baroque Architecture Elements
The Queen of Coranaro in the church of Santa Maria Della Vittoria (1645-1652) is considered the quintessence of Baroque, an impressive fusion of painting, sculpture, and architecture (see photo gallery).

French, English, Italian Baroque Architecture
Baroque style is spreading in Spain, Germany, Belgium (then Flanders), the Netherlands, Russia, and France. In France, the Baroque style is more modest than in other countries. It used to be that here the style did not develop at all, and Baroque monuments were considered monuments of classicism. Sometimes use the term “baroque classicism” about the French and English versions of the Baroque.

Now the French Baroque is considered the Palace of Versailles (see photo gallery), along with a regular park, the Luxembourg Palace (see photo on the left), the building of the French Academy in Paris, and other works. They have some features of classicism. A characteristic feature of the Baroque style is the regular style in landscape art, an example of which is Versailles Park.
Baroque Church Architecture

Later, at the beginning of the 18th century. The French have developed their style, a variety of baroque – rococo. It manifested itself not in the external design of the facades of buildings, but only in interiors, as well as in the design of books, in clothing, furniture, and painting. The style was spread throughout Europe and Russia.
Baroque Revival Architecture

Baroque Style Decor
In Russia, baroque appears in the XVII century (“Naryshkin Baroque”, “Golitsyn Baroque”). In the 18th century, in the reign of Peter I, development in St. Petersburg and the suburbs in the work of D. Trezzini – the so-called “Peter’s Baroque” (more reserved) -flourished in the reign of Elizaveta Petrovna. Chevakinsky and B. Rastrelli.

In Germany, the outstanding Baroque monument is the New Palace in Sanssouci (authors – I. G. Bühring, H. L. Munter) and the Summer Palace (see photo) in the same place (G.V. von Knobelsdorf). The largest and most famous baroque ensembles in the world are Versailles (France), Peterhof (Russia), Aranjuez (Spain), Zwinger (Germany), and Schönbrunn (Austria).
Baroque Home Design

Russian Baroque (also Elizabethan, Rastrelli) – style in art (primarily in architecture, sculpture, and painting); Russian “replica” of the European Baroque style, fully developed in Russian art by the end of the first half of the XVIII century.
Modern Baroque Architecture

This style, which gravitated toward the creation of heroic images, to the glorification of the might of the Russian Empire, was most clearly manifested in the middle of the 18th century in the architectural constructions of one of the greatest architects of this direction, F. B. Rastrelli. His projects created magnificent palace ensembles in Petersburg (Winter, 1754-1762, Stroganov Palace, 1752-1754, see the photo on the right) and in Peterhof (1746-1775), in Tsarskoe Selo (Catherine Palace, 1747-1757 (see. a photo)).
Russian Baroque Architecture

The grandiose scale of the buildings, the extraordinary richness, and splendor of the decorative decoration, and the two- and three-color paintings of the facades with the use of gold – all amazed the imagination of the audience, provoking their sincere admiration. The solemn, festive character of Rastrelli’s architecture left an imprint on all Russian art of the mid-18th century.
Baroque Architecture Details

Baroque Pediment
Characteristic features: symmetry in style, and space. A lot of stuccoes. Complex architectural elements. The abundance of decorative bas-reliefs. Gilding of architectural decor.
Predominant colors: muted pastel colors of the facade; red, pink, white, blue with a yellow accent – in the interior.
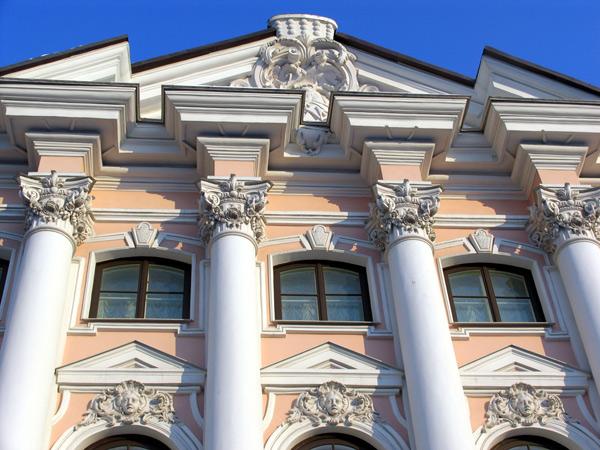

- Lines: a whimsical convex-concave asymmetric pattern; in the form of a semicircle, a rectangle, or an oval; vertical lines of columns; marked horizontal division.
- Form: arched, domed, and rectangular; towers, balconies, bay windows.
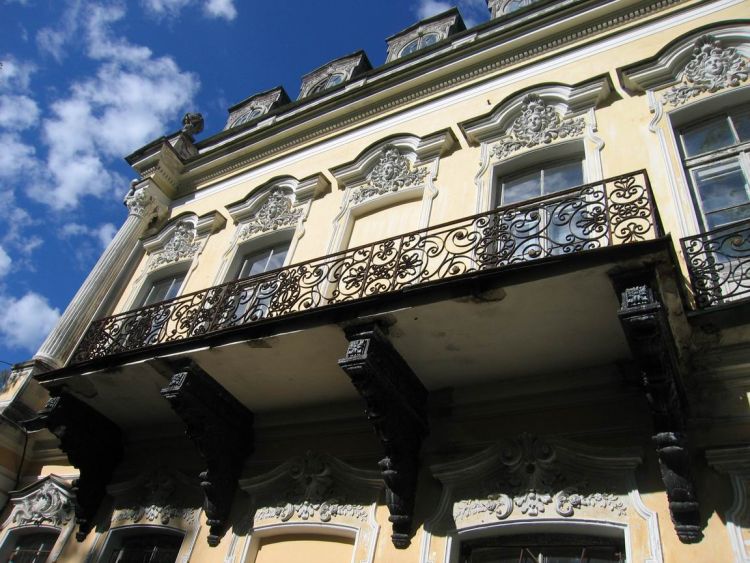
- Elements of an interior: aspiration to greatness and splendor; massive front staircases; columns, pilasters, bas-reliefs, richly decorated stucco trim for windows and doors, stucco and painting, carved ornament; interrelation of design elements.
- Constructions: contrasting, intense, dynamic; Fascinating on the facade and at the same time massive and stable.
- Windows: semi-circular and rectangular; with a vegetative decoration around the perimeter. The plat bands are decorated magnificently.
- Doors: arched openings with columns; vegetable decoration.
ROCOCO STYLE HOUSE FRONT ELEVATION DESIGN
Rococo (rococo, from rocaille – crushed stone, decorative shell, shell, rocaille, less often rococo) – a style in art (mainly in interior design), originated in France in the first half of the XVIII century (during the regency of Philip Orleans) as the development of the Baroque style. Characteristic features of Rococo are refinement, large decorative loading of interiors and compositions, graceful ornamental rhythm, great attention to mythology, and personal comfort. The highest development in architecture was in Bavaria.
Rococo Buildings
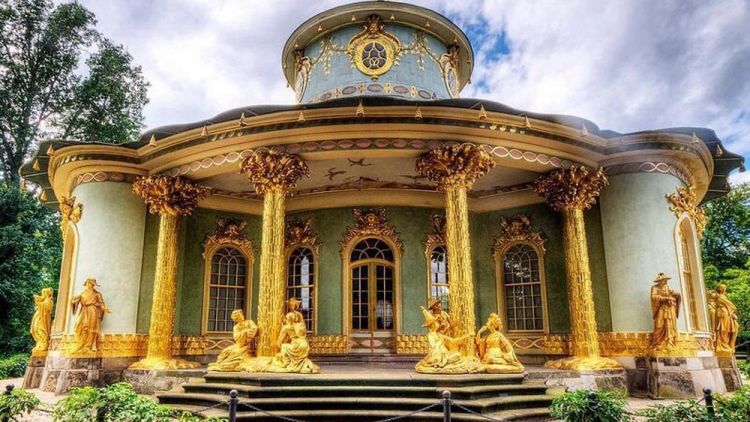

The term “rococo” (or “rocaille”) came into use in the middle of the XIX century. Initially, the “rocaille” is a way of decorating the interiors of grottoes, fountain bowls, etc. with various fossils that mimic natural (natural) formations, and the “rocaille” is the master who creates such decorations.
Rococo Architecture Examples

What we now call “Rococo”, at one time was called “a picturesque taste”, but in the 1750s. the criticism of all the “twisted” and “tortured” became more active, and the name “spoiled taste” began to appear in the literature. Especially successful were the Encyclopaedists who criticized the “spoiled taste” for not having a reasonable beginning.
Rococo Palace
The main elements of the style: rocaille – curl and cartel – the term now forgotten, used for the name of rock casting cartridges. One of the earliest cases of the use of these terms is Montond-son’s grave “The Third Book of Rockcasting and Cartel Forms”, 1736 (see illustrations below). We also find them in the letter (April 7, 1770) of the master Roatier (who made the silver service for Catherine II at the end of the 1760s, later known as the “Orlovsky Service”), the preserved objects are kept in the State Hermitage.

This letter also reflected the change of tastes that occurred at the turn of the 1760-70s: “… since EI V. wants to abandon all kinds of figures and cartels, we will do our best to replace them with antique ornaments and following the best taste, according to the wishes … “(quoted from the document of the RGIA).
Rococo Decorative Style

Despite the popularity of the new “antique forms”, which became fashionable in the late 1750s. (this direction was called “Greek taste”, the items of this style are often mistaken for later Rococo), the so-called Rococo maintained its position right up to the very end of the century. In France, the Rococo period was called the time of Cupid and Venus
French Rococo Architecture

In the 1960s and 1970s, the rococo concept was extended as a result of the baroque grind: “Entering the Rococo phase, the emblem becomes more and more independent, and becomes part of the overall decorative decoration, along with nymphs, naiads, cornucopia, dolphins, and newts […]. ] “Cupids of the deity of love” turn into – putti – rococo
Rococo Architecture Features

Rococo Style Buildings
Architectural (more precisely – decorative) Rococo style appeared in France during the regency of Philip of Orleans (1715-1723) and reached its apogee under Louis XV, moved to other European countries, and dominated it until the 1780s.

Discarding the cold parade, the heavy and boring pompous art of the times of Louis XIV, and the Italian baroque, the architecture of rococo tends to be easy, affable, and playful; she does not care about the organic combination and distribution of the parts of the structure, nor the appropriateness of their forms, but disposes of them with complete arbitrariness, reaching a whim, avoids strict symmetry, endlessly varies the dismemberment and ornamental details and does not stint the latter.
Rococo Architecture Buildings

In the creations of this architecture, straight lines and flat surfaces almost disappear or, at least, are masked by a figured decoration; none of the established warrants is executed in its pure form; the columns are lengthened, then shortened and twisted helically; their capitals are distorted by coquettish changes and additions, cornices are placed above the cornices; high pilasters and huge caryatids prop up insignificant projections with a very prominent cornice; roofs girdle along the edge of balustrades with flakonovymi balusters and with placed at some distance from each other pedestals on which are placed vases or statues; the gables, representing the fracturing convex and sunken lines, are also crowned with vases, pyramids, sculpture figures, trophies, and other similar objects.
Rococo Design Elements
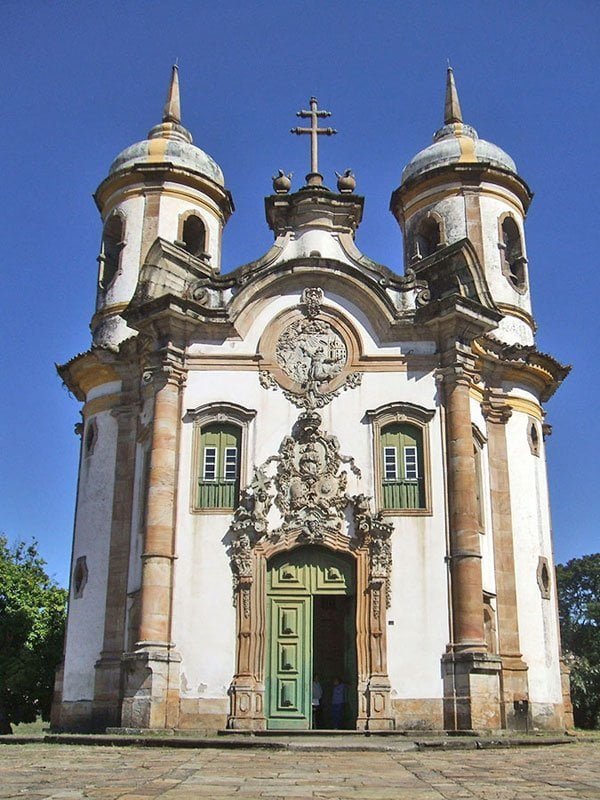

Everywhere, in the frame of windows, doors, wall spaces inside the building, in plafonds, intricate stucco ornamentation consisting of curls remotely resembling leaves of plants, convex shields, improperly surrounded by the same curls, from masks, flower garlands, and festoons, shells, unfinished stones (rocaille), etc.
Rococo Architecture Pictures

Despite this lack of rationality in the use of architectural elements, for such capriciousness, sophistication, and burdensome forms, the Rococo style left many monuments that until now Do not be attracted by their originality, luxury, and cheerful beauty, which are alive to us in the era of blush and whitewash, flies and powdered wigs (hence the German style names: Perückenstil, Zopfstil).
ECLECTIC OUTSIDE WALL DESIGN
The name “eclecticism” came from the Greek εκλεκτός, “the chosen, the choicest”. Eclecticism in architecture is the direction in architecture that dominated Europe and Russia in the 1830s and 1890s. In foreign terminology, it is called romanticism (for the second quarter of the XIX century), Beaux-Arts (bos-ar) (for the second half of the XIX century), and historicism (in the modern world). It is characterized by various “historical” styles, such as neo-Renaissance, neo-Baroque, neo-Rococo, neo-Gothic, neo-Mauritanian style, neo-Byzantine style, pseudo-Russian style, Indo-Saracenic style.
Eclectic Decorating Style

The history of eclecticism
At the beginning of the last century, avant-garde artists in an attempt to create something new all the time “stumbled” into something that had once been created by someone and reflected, for example, in the ancient cultures of China or India, Sumerian manuscripts or sculptures of Mesopotamia.

And it became clear that if you follow the path of borrowing and combining an existing one, you can create something new and interesting. Modern art design mixes Western and Eastern, old and new – art deco with high-tech and ethnic, that is, the interiors of the beginning of the third millennium are stylistically multi-component. It is customary to call Eclecticism (historicism) Famous architectural buildings of Eclecticism and Historians.
Eclectic Home Furnishings

Forms and building styles in eclecticism are tied to their function. The eclectic is “multi-style” in the sense that the buildings of one period are based on different styles of schools, depending on the purpose of the buildings (temples, public buildings, factories, private houses) and customer funds (there is rich decor that fills all surfaces of construction, and economical ” red brick architecture). This fundamental difference of eclecticism from the Empire dictated a single style for buildings of any type.
Eclectic Design Style

Eclectic Style Decorating Ideas
Strictly speaking, eclecticism in itself is not a separate style, since its peculiarity is precisely the blending of different styles on different bases. Quite often in the environment of professional architects, the term eclecticism is negative, as a direction that does not adhere to a specific framework of styles.

On the other hand, it should be noted that sometimes a combination of certain styles, made with a taste and a subtle flair, can create unique works of architecture and interior design. Characteristic features of the eclectic style are close plexus in the construction of the building of technical aspects with artistic, monumentality, and an abundance of decorative elements.
ENGLISH STYLE EXTERIOR WALL DESIGN
The Georgian style in architecture The Georgian style is the common name for several directions in architecture, art, and design that prevailed in England during the reign of the four kings of the Hanover dynasty, from George I to George IV, by whose name the style was named. This period lasted from 1714 to 1830, the Georgian style changed and acquired varieties, while preserving the same basic features: harmony and symmetry of forms, simple mathematical relations, plenty of space, light, pale colors, and elegant decor.
English Home Design

Country houses of early Georgian style reflected the influence of Roman architecture and the palazzo of Northern Italy. Towns and country houses of the early Georgian style reflected the influence of Roman architecture and the palazzo of Northern Italy: the symmetry and regularity of the windows on the facade of the building, accentuating the high and richly decorated cornices and moldings on the first floor of the house.
English Cottage Style Homes

Decorative decoration of the facades was a sign of wealth and position in society: the houses of noblemen and rich bourgeois were decorated with complex stucco molding, woodcarving, and complicated plaster works.
English Country House Style
Ordinary houses were covered with paint, performing a protective and cosmetic function: in the decrees on the construction of residential houses, simplicity and uniformity were recommended. However, architects and entrepreneurs engaged in commercial construction increasingly used the “palace” facade in the central part of the blocked houses, which stood out from the pediment and the pilaster on the sides: such a beautiful, richly decorated facade significantly increased the cost of the building.

The opening of the LateGeorgian style was an artificial stone that could be cast, receiving a variety of beautiful but at the same time, relatively inexpensive facades of apartment houses decorated with stucco flower garlands, decorative panels, and rosettes. architectural elements: castle stones with bas-relief faces, moldings, cornices. The facades of apartment houses were also decorated with stucco flower garlands, decorative panels, and rosettes.
English Architecture Houses

Modern builders and architects in the construction of buildings in the Georgian style prefer stucco molding from foam: unlike artificial stone, it does not create an additional load on the walls, but it is also durable and durable and allows the creation of decorative elements of any complexity. To create the effect of brick walls in conjunction with a white facade decoration, you can now use thermal panels, the front part of which is a neatly laid clinker tile. This creates a classic combination, used in regency styles and Georgian styles.
English Decorating Style

From 1811 to 1830 the country was ruled by George IV, who until 1820 was the regent of the sick father. Hence the name of the period – the regency, which also spread to the art and architecture of this time: not only urban but also suburban construction in the suburbs and on the coast, has become particularly popular due to the growth of middle-class customers.
English Architecture Style

The style of the regency, with special refinement, reflected the classical architectural trends of the XVIII-XIX centuries, as well as the influence of French architecture and design. The windows became more elongated in height, the balconies were decorated with architectural elements with ancient Greek and Roman motifs.
English Cottage House Designs

The front door is the key accent of the building, and its architectural elements – pilasters, gable, and clypeus – are the main decoration of the house in the regency style.
English Cottage Style Architecture

In the regency, special attention was paid to the design of the facades: the emphasis was on geometrically-precise ornaments and carved patterns, decorated with arches, and window openings. The main decoration of the house was still the front door, around which the architectural elements were centered.
Traditional English House Designs

For the simplicity of the door boxes in the modern Greek manner, careful architectural thought was concealed. On the sides of the door were pilasters or stylized moldings. In the fashion was a low elegant porch, resting on twisted consoles.
English Country House Design

If the house opened in the regency, special attention was paid to decorating the facades: the emphasis was on geometrically-precise ornaments and carved patterns, decorated with arches, and window openings. a picturesque view, the architect added a terrace or balcony with a stucco balustrade with graceful balusters, from where one could admire nature.
EMPIRE-STYLE OUTDOOR WALL DESIGN
Empire style (“Empire style”) – style of late (high) classicism in architecture and applied art. Originated in France during the reign of Emperor Napoleon I; developed during the first three decades of the XIX century; was replaced by eclectic currents. The style of Empire is the final stage of classicism, which emerged in the first third of the XIX century. In France, during the epoch of Napoleon Bonaparte, classicism degenerated into a top imperialist style, the essence of which was reflected in its name (from the French empire – “empire”). The style became widespread in many European countries and actively developed during the first three decades of the XIX century.
Second Empire Style House

In imperial France, the empire distinguished the solemnity and splendor of the memorial architecture and palace interiors created by the court architects of Napoleon Charles Persie and Pierre Fontaine
Second Empire Style Homes

In the Russian Empire, this style appeared under Alexander I. The invitation of foreign architects to Russia was a frequent occurrence, as among the titled persons it was fashionable, and at the beginning of the 19th century, there was a passion for French culture in Russia. For the construction of St. Isaac’s Cathedral, Alexander I invited the beginning French architect Henri Louis Auguste Ricard de Montferrand, who later became one of the founders of the “Russian Empire”.
Empire Home Design

Russian Empire was divided into Moscow and St. Petersburg, and this division was determined not so much by the territorial sign, as by the degree of separation from the classicism – Moscow stood closer to him. The most famous representative of the St. Petersburg direction of the Empire was the architect Carlo Rossi, among other representatives of this style, it is customary to call the architects Andreyjan Zakharov, Andrei Voronikhin, Osip Bova, Domenico Gilyardi, Vasily Stasov, the sculptors Ivan Martos, Theodosius Shchedrin. In Russian Empire dominated architecture until 1830-1840.
Second Empire Style Architecture

The revival of the empire in its degenerate forms occurred in Russia during the Soviet period, from the mid-1930s to the mid-1950s. This direction of the Empire is also known as the “Stalin Empire”
French Second Empire Architecture

Empire refers to the so-called “royal styles”, which can be characterized by theatricality in the design of architectural buildings and interior interiors. The peculiarity of the architectural empire consists in the obligatory presence of columns, pilasters, stucco moldings, and other classical elements, as well as motifs that reproduce almost unchanged antique samples of sculpture, like griffins, sphinxes, lions’ feet, and similar sculptural structures.
Empire Building Materials

These elements are arranged in the Empire in an orderly manner, with the observance of balance and symmetry. The artistic design of the style with its massive lapidary and monumental forms, as well as its rich decoration, the content of elements of military symbols, the direct influence of artistic forms primarily of the Roman Empire, as well as Ancient Greece and Hellenism, was intended to emphasize and embody the ideas of the might of power and the state, armies
Second Empire Victorian Homes

Empire style appreciated the elongated silhouette, created with an eye for antique peplows and tunics. Dresses were sewed with a high waist, under a breast intercepted a girdle, and behind put a platen from horsehair. The neck and arms were left open. The clothes of the dresses below were embroidered with gold and silver thread, and green palm leaves.
Empire Style House

The bottom edge was trimmed with chenille, paillettes, and sequins. If the dress was elegant, intended for visits and dances, then he often had short sleeves with puffs. Under tunic dresses, they wore shirts or flesh-colored tights. The female body was visible. Sometimes even dresses made of thin materials were dampened with water to adhere to the body [4]. The decollete was also as open as possible.
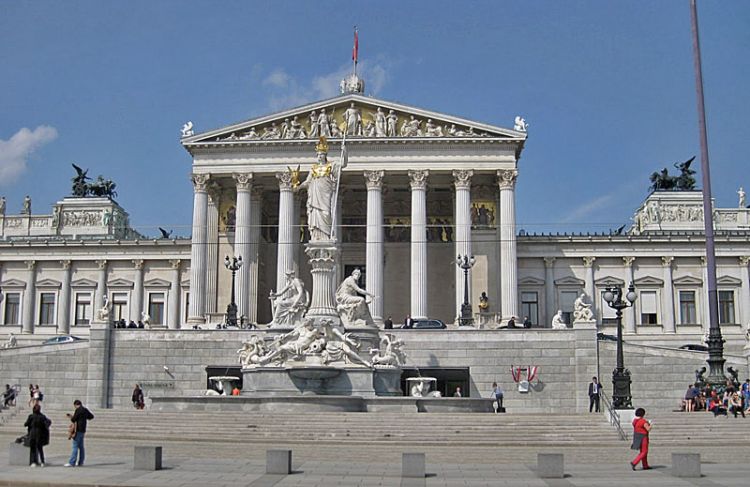
NEOCLASSICAL HOUSE FRONT SIDE DESIGN
Neoclassicism is a term used in Russian art to refer to the artistic phenomena of the last third of the nineteenth and twentieth centuries, which are characterized by an appeal to the traditions of the art of antiquity, Renaissance art, or classicism (in music, also Baroque). In foreign art criticism, neoclassicism refers to classicism in the architecture and fine arts of the second half of the 18th century – the first third of the 19th century, in contrast to the classicism of an earlier period
Neoclassical House

Confusion arose from the fact that in France classicism is called the style of the XVII century, the style of Louis XIV (Louis XIV). Neoclassicism is understood as the style of the second half of the 18th century, the style of Louis XVI (Louis XVI) – what in Russia (as in Germany) is traditionally called classicism (the period 1762-1840).
Neoclassical Buildings
Neoclassicism in Russia and Germany refers to the retrospective style of the beginning of the 20th century, “different from the” good old “Russian classicism and materials (not white plastered columns, but natural stone), and emphasized by the expressive depiction of classical forms and details, and sometimes by cutting details and mixing classical and Renaissance motifs”. Analogs of neoclassicism in foreign practice are the American renaissance and colonial revival in the USA (1876-1914).

At the end of the XIX century, a new architectural style was formed, in Russia called “modern”. But he could not satisfy the urgent need for a large monumental style. Neoclassicism appeared at the beginning of the century as the antithesis of the decorative redundancy of modernity. Reliance on the classic, order system, observance of classical proportions. The desire for coziness, and harmony. Characteristic decorations: leaves, shells, architectural pediments, antique figures. Furniture is light, elegant, and straight lines.
Neoclassical Homes

In parallel with the innovative tendencies in the architecture of the early twentieth century. retrospective trends were gaining momentum. The thirst for novelty quickly gave way to dreams of the past. The “reopening” of the values of classical architecture accelerated the disappointment in architectural innovations and the decline of the “fleeting” style. Neoclassicism and the “neo-Russian style” first influenced the lexicon of modernity, and after 1910 they pushed him to the distant future.
Neoclassical Architecture Characteristics

Neoclassicism set a large-scale task: to revive and confirm the ensemble and style integrity of the capital, to continue its development at the level of the latest achievements, but according to the precepts of antiquity. This contributed to the rise of town-planning ideas, which were mostly historical in color. In this character, the grandiose plan of the residential area “New Petersburg” on the island of Golodai (IA Fomin, FI Lidval) and the competition projects of the monumental ensemble of public buildings on Tuchkov Bujan (I Fomin, OR Munts, M. Kh. Dubinsky, SS Serafimov). “The project of the transformation of St. Petersburg” by F. Ye. Enakiev and L. N. Benois, comparable to the master plan, provided for a comprehensive reconstruction of the city and its infrastructure with the laying of new streets and transport arteries. The implementation of these proposals prevented the First World War.
Neoclassical Architecture Features

At the beginning of the 20th century, the entire Petrograd side, almost all the quarters on the Vasilievsky Island and in the left-bank regions, were almost completely rebuilt. The exemplary street of this time was Kamennoostrovsky Avenue – the “exposition” of the best works of modern and neoclassicism. On the Nevsky Prospekt and in the adjacent blocks the area of Petersburg City was finally formed. The city acquired new features of the capital’s imposing and European gloss. But the revolutionary upheavals tragically broke his fate.
Neoclassical Architecture Elements

Neoclassicism – in fact, the first major architectural style in the history of Petersburg architecture, the main one in its heritage – crossed the boundary in 1917 and continued to develop in completely different conditions until the mid-1920s, when for a short time gave way to constructivism. The lessons of the neoclassicism of the beginning of the century turned out to be extremely fruitful and promising not only for the Soviet traditionalist architecture of the 1930s-1950s; they are again relevant at present.

A BIT OF HISTORY
Man always, at any time, strove for the beauty of his home. Even in the Stone Age, our distant ancestors painted on the walls of the caves of saber-toothed tigers and mammoths. And these were only the first steps in art. Millennia passed, and the civilizations of the Ancient World blossomed on the expanses of the earth. Unforgettable beauty of the palaces and temples of Sumer, Babylon, and Assyria were decorated with gold, ceramic bas-reliefs, carvings on the precious wood, and natural gypsum stone went to the floors and facing the walls – but the skilled craftsmen and builders of these states never thought of the invention of plaster moldings. Historians and archaeologists confidently say that the world history of stucco decoration began only in ancient Egypt 5000 years before our era. It turns out that stucco molding – solemnly white and gilded, of dozens of different styles and thousands of different forms – has been decorating houses and palaces, theaters and temples, museums and estates for seven millennia.
So why not leaf through the pages of the past? Let’s see how the art of stucco art arose – and how it became an integral part of not only architecture but the very history of mankind …
The stucco decoration of Ancient Egypt
Her Majesty History is traditionally inattentive to details – therefore, it did not preserve the exact date of appearance of the molded decor, and archeology, alas, is not all-powerful. But the first samples of stucco molding from Ancient Egypt that date back to us date back to the pre-dynastic era and the times of the Pharaohs of the First Dynasty – from Narmer to Kaa. It was then, for 5000-2800 years before the birth of Christ, that the palace and temple decorations for the first time appeared as molded decorative elements. And the art of plaster molding reached the real heights in Egypt much later, one and a half millennium BC, in the epoch of the heyday of the world ancient Egyptian state during the reign of Queen Hatshepsut, the pharaohs of Thutmose III, and the legendary Tutankhamun.
It was the Egyptian architects and builders who laid the foundation for the art of stucco decoration. And no wonder: the Pharaohs – the all-powerful lords of Upper and Lower Egypt – knew a lot about luxury. Their palaces and temples – “monasteries of millions of years” – were erected by thousands of slaves, but skillful stone-cutters were not found among them infrequently, and more and more stone decorations were required. So it was the first ceramic decoration of baked clay, and then stucco, from plaster.
At first, the use of stucco was mainly utilitarian. For example, the columns simply supported the roof, then the upper part of the columns – the capital – began to decorate with the simplest carved and stucco ornamentation with colored paintings on plaster and stone. Gypsum stucco decorated door portals and door trim, and on the walls appeared convex stucco strips, cartouches, and rosettes – animating plaster. Interestingly, the stucco decor was widely used not only in decorating palaces and temples but also in the magnificent ornaments of the burial chambers of “houses of Eternity” – the pyramids.
Well, what exactly started the history of the ancient Egyptian plaster moldings? Here it is very simple – the ancient Egyptian builders and architects noticed that if you burn a gypsum stone and then the resulting powder – gypsum – mixed with water, fill it with a mold and leave it to dry in the sun, the new material will harden, keeping the new shape with any pattern. Moreover, the gypsum was strong, light, wet, and was also very plastic, and later perfectly suited for processing. Therefore, the Egyptians immediately moved to molded decor with ornamental and vegetable motifs, traditional for the Mesopotamian culture – Sumer.
Long ago the fragile houses of simple Egyptians were dispelled by the dust of millennia, the palaces and temples-the great houses where the gods dwelt-turned into ruins-but the ancient Egyptian civilization survived for a long time fine art of Ancient Egypt. It is believed that art is imbued with a certain mystical gloom – but the Egyptians admired the highest beauty of life on the banks of the Nile. And they expressed their gratitude to the gods in art and architecture. We can admire their creations in museums all over the world and on the Egyptian land itself, in the ruins of tombs and temples … To feel this beauty – once again take a look at the columns adorned with wonderful stucco molding, plaster relief cornices, and fragments of them that have come down to our days.
Fretwork of Ancient Greece and Rome
But the real flowering of the art of decorative stucco brought the era of Antiquity. In the days of Ancient Greece and Rome, the very foundations, aesthetic directions, and technology of making moldings were formed. Even the current name “gypsum” for the unique material of the stucco appeared in Greece, where it was called “gypsum” – literally translated as “boiling stone”.
The Greeks developed many traditions of the cultures of the Ancient World – and clothed them in classical clarity and harmony. In the art of building and finishing the architects of Greece for the first time introduced an order – a clear system of architectural composition, combining structural and artistic, and decorative elements. Ornaments of capitals (crowns) of columns, pilasters, modules, and ornamental cornices – from 1100 BC these stucco elements, often gilded, were widely used to decorate churches, public buildings, and houses of wealthy townspeople. Virtually all forms of architectural decor, invented in Ancient Greece, have become classics for all subsequent times – until our XXI century.
The Romans borrowed the best from the Greeks – but, having departed from the Greek tradition, perfected and significantly enriched the art of stucco. For example, the architects and sculptors of Ellada used geometric stucco ornamentation – but in ancient Rome, with its desire for luxury, rich vegetable motifs were preferred. Vineyards and leaves, laurel branches, flower rosettes, multi-figured scenes from the life of the gods – stucco of the Roman Empire strikes with its diversity and sophistication of the subjects. And, like in Greece, the high social status of the owner of the house is largely evidence
In addition, Rome, and invented a completely new form of stucco – “Stucco.” Alabaster, marble powder and crumbs, glue, and some other impurities were added to the gypsum, and as a result, the stucco was of unprecedented strength, and after careful polishing, it became indistinguishable from the luxurious marble.
It was in Rome, even four centuries before our era, that concrete was first widely used. It would seem – well, what has the topic of our narration? ArtFacadertheless, just the use of concrete contributed to the widest distribution of stucco molding. So, the famous Colosseum is built from molded recurring concrete arches and ceilings – and it was the idea to use repetitive molded elements in architecture that led to the wide use of molded moldings and patterns … As a result, the technology of stucco molding became much simpler and cheaper – and in the architecture of late Rome, stucco was present everywhere.
In stucco patterns, stylized sea waves, dolphins, fish, and shells intertwined. The friezes were decorated with ornate garlands and horns of abundance … Capitals of columns, arches, niches, wall and ceiling rosettes – this beauty, embodied in the art of ancient Roman masters, can not but delight even after two millennia!
Antiquity predetermined the direction of the art of molded relief jewelry, and gave an indispensable impetus, which dominated almost all the further styles of architecture – Gothic and Renaissance, Baroque and Rococo, classicism and modern art …
From the Dark Ages – to “whipped cream” rococo
But meanwhile, the once powerful states of the Ancient World gradually came down from the stage of History. In the fifth century AD, under the onslaught of the barbarians, Rome finally fell – and after that Europe and Byzantium, which replaced the Roman Empire, plunged into the darkness of the Dark Ages …
In the early Middle Ages, most of the cultural and technical achievements of antiquity were forgotten, and the Romanesque style that existed at that time implied not only simple and solid forms of buildings but also a minimal minimum of finishing. The rays of the sun from the narrow window loopholes could not disperse the eternal half-darkness in the palaces of kings and castles of the feudal lords – and the semi-darkness was completely harmonized by the heavy and rough reliefs made of stone. Well, this era did not have the grace of architecture!
Everything changed when the Romanesque style gradually replaced Gothic – but it did not happen soon, only in the XII century. And the cardinal changes were in the church architecture. In place of the gloomy and cumbersome “fortresses of God”, graceful Gothic temples with huge windows turned to heaven. Shamrocks, crucifers, leaves of grape, maple, ash, and oak – all these delicate stucco decorations on columns, ceilings,s and window frames emphasized the elevation and subtle beauty of the architecture of the new era. Legendary Cathedral of Notre Dame, Westminster Abbey, Cologne Cathedral – all architectural monuments of Gothic always delight the eye with magnificent stucco molding. But still, only the Renaissance style (Renaissance) brought true freedom to the world of stucco decor, which replaced the Gothic style in the 14th century …
Curiously, architects, artists, and, in general, art people initially interpreted the Renaissance as a revival of the traditions of Antiquity – as opposed to supposedly barbaric Gothic. The principles of the architecture of the Renaissance are “ancient Roman” order, symmetry, and proportions. In the Renaissance decor, the heaviness of the stone was finally overcome, the new material became gypsum-cement mixtures – and the stucco molding became one of the main elements of the decoration of buildings. Based on ancient examples of stucco molding, they admired and copied with joy. Of course, the former “Roman” pillars of the magnificent Corinthian order gained their former popularity.
Masters of the Renaissance put their souls into the stucco transformation of architecture – and solemn stucco decorations blossomed in the spacious interiors of palaces, city houses, and public buildings. Fine examples of Renaissance stucco can be seen in all the masterpieces of that era – from St. Peter’s in Rome to the Pandolfini Palace in Florence, built by the great Raphael. However, even the Renaissance triumph of the stucco proved to be nothing more than a modest rehearsal in comparison with the true feast of baroque …
The Renaissance ended in 1527, with the famous fall and plunder of Rome, but in the 17th century the baroque style of the dying Renaissance simply eclipsed its predecessor – and this is the era considered the beginning of the victorious march of Western civilization in Europe. The “dull” rationalism was forgotten – the lush and pretentious-vicious baroque curved the strict lines of Renaissance architecture, introducing into it an intricate asymmetry, fluidity of forms, and immense luxury. Stucco molding now abounded everything – ceilings and walls, columns and fireplaces, furniture and door portals, facades, and pediments. Moreover, the baroque stucco was not only gypsum-white – it shone with rich gold and silver, amazed with splendor and variety. Cornices with geometric and floral ornamentation, rosettes and volutes, palmettes and pilasters, bouquets and garlands, medallions and modules, brackets, masks and macarons, cupids, cartouches, plafonds – all these names sound like magic music! And the choice of baroque examples is very wide – from the Luxembourg Palace in Paris and the ensemble Grand Place in Brussels to the creations of the famous architect Rastrelli in the Russian Empire.
Of course, the baroque architecture could be accused of excessive dressing and cold airy bombast, if desired … But in the first half of the 18th century, the baroque interior design turned into a rococo style – seduced by originality and at one time called “picturesque taste”. The playful capriciousness and gracefulness of the rococo forms made it possible to completely forget about strict symmetry, straight lines, and flat surfaces. Whimsical leaves-curls and shells, masks and shields, garlands and festoons – all this intricate stucco decoration triumphed in the decoration of walls and plafonds, doors and windows.
Classicism and Art Nouveau
However, human attachments are impermanent, and fashion is changeable and capricious. In the 18th century, “whipped cream” stucco moldings of late Baroque and Rococo went down in history – they were fed up with architects and aristocrats, customers, and democratically-minded circles of European society. In France, already in the reign of Louis XV (1715-1774), the construction of architectural ensembles in the ancient Roman spirit began. And at the end of the century, under Louis XVI, a new direction – classicism – confidently won
The eclectic has outlived itself, and the modern has resolutely refused clear geometric, symmetry, right angles, and straightforwardness in general. Architectural lines and elements have become more “natural” – natural, free. The appearance of buildings and their interiors combined artistic and utilitarian, aesthetics and functionality. Modernity was to become an unprecedented synthetic style, in which the whole environment of man would be fulfilled in a single key. And, of course, due to this “higher destiny” of modernity, interest in the art of plastic decoration has sharply increased.
The author of truly fantastic buildings is Spaniard Antonio Gaudi, Belgian Victor Horta, American Louis Sullivan, and Russian architect Fyodor Shekhtel – among the “software” modernist architects there are a lot of big names. In their creations, stucco has become fluid and elegant ornamentation, its laconic lines curving like whimsical plants. The ideas and flesh of the stucco decor became everything created by nature – branches and leaves, sea shells and fish scales, a game of waves and flowers of lilies, irises, and cyclamen. For connoisseurs of art, the epoch of Art Nouveau is the time of real treasures included in the gold and world fund and Russian architecture!
It is to the history of Russian architecture and its accompanying history of stucco decor we now turn to – and this story is no less fascinating and rich! Rich in events, the names of great rulers and architects – and truly great architecture.
Stucco decoration in pre-revolutionary Russia
In the Russian state, the first attempts to use stucco molding came at the turn of the XVII and XVIII centuries – the times of an unprecedented collapse of the whole Old Testament way of life and the construction of a new state. Peter the Great with an iron hand performed a miracle, transforming the traditional estate-representative monarchy of the Russian kingdom into an absolute monarchy of the Prussian-Dutch-Swedish model. The Russian Empire became the second largest in the world after the British Empire – and its fundamental documents clearly stated the principle of absolutism: “His Majesty is an autocratic monarch who should not answer to anyone in his affairs.” At the same time, the main centers of the strength of the former Rus – the Boyar Duma and the Patriarchate – lost their power. Earlier it was the traditions of the boyars and the old clergy that determined the very essence of Russian architecture – now everything was done solely by the will of the sovereign. Well, the will of Peter I in the field of architecture was expressed very clearly …
St Petersburg, being rebuilt from scratch, should have surpassed the capitals of Europe on its scale, and its architecture was originally planned in a purely European spirit. And because it the fashionable in Europe baroque stucco decoration decorated the very first buildings and palaces of the new imperial capital.
Curiously, because of the ever-cloudy sky and scattered light, which does not give sharp shadows, St. Petersburg’s architecture used quite bright colors. Residential and public buildings were painted in yellow, bluish-turquoise, red, and green tones. Therefore, contrast-white architectural details – and plaster moldings in the first place – gave the city an unforgettable color.
St. Petersburg became the pearl of Russian urban development – and the capital was quickly followed by noble mansions, estates, and official architecture of Moscow and other cities. But exactly what followed! Therefore, it is interesting to follow the example of St. Petersburg to establish the art of stucco decoration in Russia, as well as the entire architecture of the new state. Moreover, from now on they were bound together indissolubly …
Let’s notice, that really capital, brick, and stone buildings during Peter I and until the reign of Catherine II were built in Petersburg a little. These were wooden buildings, painted under stone or marble, and the quick, light stucco molding of plaster or soft stone was the best way to finish the painting. It’s ridiculous to say that even the Imperial Winter Palace at first resembled a bivouac hiking – in the first versions, it was soon built and just as soon it was destroyed, built up, rebuilt. Did not save and abundant stucco – not only white but also saturated with color and gilding. According to historians, by 1750 Winter “represented a kind of motley, dirty, unworthy place it occupied, and the strangeness of the imperial palace … could not be pleasant to the Empress.”
At the same time, great attention was paid to finishing – the chief architect Rastrelli personally painted the curls of stucco molding, which linked the entire luxurious decoration of the huge building, from the facades to the inner chambers, into a single ensemble. In 1758 alone, more than 1000 best squares worked in the palace, as the gypsum carvers were then called. However, despite the efforts of the architects, Elizabeth did not see the completion of the construction – the palace was received semi-finished in April 1762 by her successor, Peter III. Then, in the summer of the same year, Catherine II the Great entered the throne, at the beginning of their reign of which the palace finally acquired a familiar face.
The new empress first dismissed Rastrelli – his style was not matched
The point in this triumph was put by a banal economy. The Soviet Union suffered enormous material losses in the Patriotic War – and simply could not afford such expenses. The era of Stalin’s Empire style ended in the blink of an eye, with the release in November 1955 of the resolution of the Central Committee of the CPSU and the Council of Ministers on “Elimination of excesses in design and construction.” Under the pressure of Nikita Khrushchev’s stucco molding and facade, the interior was recognized as a relic of the past, ecclesiastical and priestly. Therefore, in the new socialist construction, there was no room for it … It is curious that, with the first decision of the party and the government, the architects began hastily removing all the relapses of the prohibited molding from the finished projects and, in general, any decorative elements. buildings. Everything changed only at the very end of the 20th century when Russian architecture regained its freedom.
Stucco of the new millennium
Stucco molding, whose history in Russia began three centuries ago, and today is the best option for creating an original interior. Stucco radiates a special festive light, awakens nostalgia in the soul and a touch of pleasant sadness, and causes associations with long-gone times of exquisite luxury, grace, and aristocracy.
Now stucco molding due to modern technologies can be not only traditional gypsum, but also polyurethane, and polystyrene – much easier, economical, and convenient to install. Cases of windows and doorways, fireplace portals and chimneys, pilasters, rosettes, skirting boards, columns, and semicolumns – all the diverse stucco elements are easily assembled into any composition. In doing so, stucco can correct many design flaws. Semicolumns best disguise the technological risers and pipes laid in unsuccessful places, and the busses, garlands, and medallions will hide the seams between the panels and the unevenness of the walls.
Transforming the interior and appearance of the house, stucco works as a style-building element. With its help, architects and designers create in the space of the house an aesthetic background of Renaissance and Baroque, classicism and modernity – or even high-tech. In this case, stucco does not necessarily leave a classic white. It can be painted with acrylic paints or treated with patina and wax – this will visually age it, and it will acquire the outer velvety characteristic of the luxurious interiors of the palaces of the distant past. And you can also gild – such stucco decor will create an atmosphere of aristocratic chambers of the 17th-19th century in the house. Stucco is the true queen of decor, it defeats the smoothness of the ceilings and walls and gives them volume and uniqueness. Thanks to stucco, your apartment, office, or country mansion can find a solemnly charming spirit of genuine art.
![[ArtFacade]](https://artfasad.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/01/cropped-dom-100x100-1.jpg)





